| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Acne Vulgaris | D000152 | 35 associated lipids |
Retinoic Acid
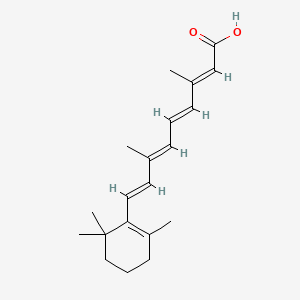
Retinoic acid is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Retinoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Asthma, Dermatologic disorders, Acne, Psoriasis and Vitamin A Deficiency. The involved functions are known as Oxidation, Anabolism, Saturated, 9-cis-retinoic acid biosynthesis and Gene Expression. Retinoic acid often locates in Mouse Testis, Tissue membrane, Body tissue, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Retinoic Acid are Homologous Gene, SLC33A1 gene, P4HTM gene, RARS gene and NCOR2 gene. The related lipids are Promega, Lipopolysaccharides, Fatty Acids, Steroids and Sterols. The related experimental models are Mouse Model.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Retinoic Acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Retinoic Acid?
Retinoic Acid is suspected in Retinoic acid syndrome, Dermatologic disorders, Congenital Abnormality, Renal glomerular disease, Acne, Alzheimer's Disease and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Retinoic Acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Retinoic Acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Retinoic Acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Retinoic Acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Retinoic Acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Retinoic Acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Retinoic Acid?
Mouse Model
Mouse Model are used in the study 'Targeted disruption of the mouse cis-retinol dehydrogenase gene: visual and nonvisual functions.' (Shang E et al., 2002) and Mouse Model are used in the study '9-Cis retinoic acid reduces 1alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol-induced renal calcification by altering vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation of matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein in A/J male mice.' (Fu X et al., 2008).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Retinoic Acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kikuchi H et al. | Resveratrol strongly enhances the retinoic acid-induced superoxide generating activity via up-regulation of gp91-phox gene expression in U937Â cells. | 2018 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:29183727 |
| Kartal D et al. | Effects of isotretinoin on the olfactory function in patients with acne. | 2017 Mar-Apr | An Bras Dermatol | pmid:28538877 |
| Okitsu T et al. | Alternative Formation of Red-Shifted Channelrhodopsins: Noncovalent Incorporation with Retinal-Based Enamine-Type Schiff Bases and Mutated Channelopsin. | 2017 | Chem. Pharm. Bull. | pmid:28381675 |
| Zou H et al. | Upregulation of CD54 and downregulation of HLA‑ABC contribute to the novel enhancement of the susceptibility of HL-60 cells to NK cell-mediated cytolysis induced by ATRA plus VPA. | 2017 | Oncol. Rep. | pmid:27840957 |
| Yao S et al. | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate promotes all-trans retinoic acid-induced maturation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells via PTEN. | 2017 | Int. J. Oncol. | pmid:28766684 |
| Nakazawa T et al. | Effect of vitamin E on 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol-induced necroptosis-like cell death and apoptosis. | 2017 | J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. | pmid:26953980 |
| Li C et al. | Effects of Pre- and Post-Administration of Vitamin A on the Growth of Refractory Cancers in Xenograft Mice. | 2017 | Biol. Pharm. Bull. | pmid:28100867 |
| Roomi MW et al. | Cytokines, inducers and inhibitors modulate MMP-2 and MMP‑9 secretion by human Fanconi anemia immortalized fibroblasts. | 2017 | Oncol. Rep. | pmid:28098879 |
| Kumar P et al. | Inhibition of HDAC enhances STAT acetylation, blocks NF-κB, and suppresses the renal inflammation and fibrosis in haplotype male mice. | 2017 | Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. | pmid:28566502 |
| Mijiddorj T et al. | Retinoic acid and retinaldehyde dehydrogenase are not involved in the specific induction of the follicle-stimulating hormone β subunit by trichostatin A, a selective inhibitor of histone deacetylase. | 2017 | Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. | pmid:26654743 |