| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphoma, Large-Cell, Anaplastic | D017728 | 3 associated lipids |
| Acne Vulgaris | D000152 | 35 associated lipids |
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
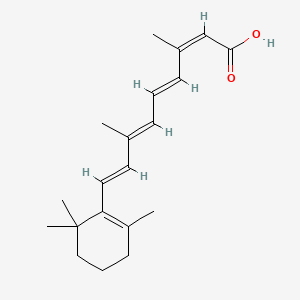
13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. 13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin is associated with abnormalities such as Dermatitis, Phototoxic. The involved functions are known as Regulation, Pigment, chromophore, Light absorption and Pupil constriction. 13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin often locates in Neurosecretory Systems. The associated genes with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin are melanopsin.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin is suspected in Dermatitis, Phototoxic and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang JG et al. | The effects of vitamin A derivatives on in vitro antibody production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from normal blood donors and patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). | 1997 | Clin. Exp. Immunol. | pmid:9010257 |
| Shih TW et al. | Nonenzymatic isomerization of 9-cis-retinoic acid catalyzed by sulfhydryl compounds. | 1997 | Drug Metab. Dispos. | pmid:9010626 |
| Thiberville L et al. | Molecular follow-up of a preinvasive bronchial lesion treated by 13-cis-retinoic acid. | 1997 | Hum. Pathol. | pmid:9013842 |
| Papadimitrakopoulou VA et al. | Low-dose isotretinoin versus beta-carotene to prevent oral carcinogenesis: long-term follow-up. | 1997 | J. Natl. Cancer Inst. | pmid:9017007 |
| Isaacs CE et al. | Inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication by retinoic acid. | 1997 | Antiviral Res. | pmid:9021053 |
| Coberly S et al. | Retinoic acid embryopathy: case report and review of literature. | 1996 Sep-Oct | Pediatr Pathol Lab Med | pmid:9025880 |
| Ena P et al. | Erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp in skin grafts: report of three cases. | 1997 | Dermatology (Basel) | pmid:9031801 |
| Hoffmann W et al. | 13-cis retinoic acid and interferon-alpha +/- irradiation in the treatment of squamous-cell carcinomas. | 1997 | Int. J. Cancer | pmid:9033659 |
| Toma S et al. | Combination of alpha-interferon 2a (alpha-IFN 2a) and 13-cis-retinoic acid (13cRA) in recurrent, pre-treated squamous-cell carcinoma of head and neck (SCCHN). | 1997 | Int. J. Cancer | pmid:9033664 |
| Waladkhani AR and Clemens MR | Differences in the pharmacokinetics of 13-cis retinoic acid in cancer patients. | 1997 | Int. J. Cancer | pmid:9033665 |
| Tzimas G et al. | Retinoid metabolism and transplacental pharmacokinetics in the cynomolgus monkey following a nonteratogenic dosing regimen with all-trans-retinoic acid. | 1996 | Teratology | pmid:9035347 |
| Römisch M et al. | [13-cis retinoic acid and interferon-alfa-2a as palliative therapy in pretreated, recurrent squamous epithelial carcinoma of the cervix uteri and vulva]. | 1996 | Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd | pmid:9036064 |
| Sander CA et al. | Chemotherapy for disseminated actinic keratoses with 5-fluorouracil and isotretinoin. | 1997 | J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. | pmid:9039175 |
| Koren G and Pastuszak A | How to ensure fetal safety when mothers use isotretinoin (Accutane). | 1997 | Can Fam Physician | pmid:9040906 |
| Wilkin JK | Potential subversion of pregnancy prevention program in the managed care setting. | 1997 | Arch Dermatol | pmid:9041846 |
| Allison MA et al. | Acne fulminans treated with isotretinoin and "pulse" corticosteroids. | 1997 Jan-Feb | Pediatr Dermatol | pmid:9050763 |
| Toma S et al. | Effects of all-trans-retinoic acid and 13-cis-retinoic acid on breast-cancer cell lines: growth inhibition and apoptosis induction. | 1997 | Int. J. Cancer | pmid:9052765 |
| Mestre JR et al. | Retinoids suppress phorbol ester-mediated induction of cyclooxygenase-2. | 1997 | Cancer Res. | pmid:9067275 |
| Kok TC et al. | 13-cis-retinoic acid and alpha-interferon in advanced squamous cell cancer of the oesophagus. | 1997 | Eur. J. Cancer | pmid:9071918 |
| Chochrad D et al. | Isotretinoin-induced vasculitis imitating polyarteritis nodosa, with perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody in titers correlated with clinical symptoms. | 1997 | Rev Rhum Engl Ed | pmid:9085448 |