| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphoma, Large-Cell, Anaplastic | D017728 | 3 associated lipids |
| Acne Vulgaris | D000152 | 35 associated lipids |
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
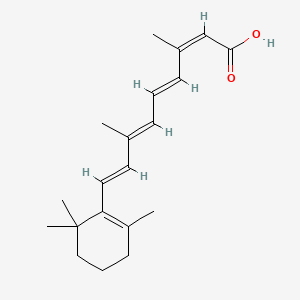
13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. 13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin is associated with abnormalities such as Dermatitis, Phototoxic. The involved functions are known as Regulation, Pigment, chromophore, Light absorption and Pupil constriction. 13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin often locates in Neurosecretory Systems. The associated genes with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin are melanopsin.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin is suspected in Dermatitis, Phototoxic and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sharquie KE et al. | The therapeutic role of isotretinoin in the management of Behçet's disease: a single-blinded, controlled therapeutic study. | 2013 | J Drugs Dermatol | pmid:23652909 |
| Elpern DJ | Isotretinoin and one patient's teary eyes: "please listen or I'll cry". | 2013 | Int. J. Dermatol. | pmid:23679883 |
| Stobaugh DJ et al. | Alleged isotretinoin-associated inflammatory bowel disease: disproportionate reporting by attorneys to the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. | 2013 | J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. | pmid:23683730 |
| Ali FR and Al-Niaimi F | Acne vulgaris. | 2013 | Br J Hosp Med (Lond) | pmid:23656986 |
| Dawson AL and Dellavalle RP | Acne vulgaris. | 2013 | BMJ | pmid:23657180 |
| Moreno L et al. | About the benefits of immunotherapy for high-risk neuroblastoma. | 2013 | J. Clin. Oncol. | pmid:23295791 |
| Stobaugh DJ et al. | Concomitant antibiotic usage does not augment the risk of inflammatory bowel disease with isotretinoin treatment for acne: a review of the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. | 2013 | Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. | pmid:23052415 |
| Alhusayen RO et al. | Isotretinoin use and the risk of inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based cohort study. | 2013 | J. Invest. Dermatol. | pmid:23096714 |
| Rademaker M | Isotretinoin: dose, duration and relapse. What does 30 years of usage tell us? | 2013 | Australas. J. Dermatol. | pmid:23013115 |
| Raza K et al. | Nanocolloidal carriers of isotretinoin: antimicrobial activity against Propionibacterium acnes and dermatokinetic modeling. | 2013 | Mol. Pharm. | pmid:23544848 |
| Balakirski G et al. | [Morbihan disease as a special form of rosacea: review of pathogenesis and new therapeutic options]. | 2013 | Hautarzt | pmid:24201653 |
| Baratli J and Megahed M | [Lupoid perioral dermatitis as a special form of perioral dermatitis: review of pathogenesis and new therapeutic options]. | 2013 | Hautarzt | pmid:24201654 |
| McIntee TJ and Bruckner AL | Challenges in optimizing isotretinoin use for acne vulgaris. | 2013 | JAMA Dermatol | pmid:24172999 |
| Blasiak RC et al. | High-dose isotretinoin treatment and the rate of retrial, relapse, and adverse effects in patients with acne vulgaris. | 2013 | JAMA Dermatol | pmid:24173086 |
| Petruzzi M et al. | Topical retinoids in oral lichen planus treatment: an overview. | 2013 | Dermatology (Basel) | pmid:23548887 |
| Melnik BC and Schmitz G | Are therapeutic effects of antiacne agents mediated by activation of FoxO1 and inhibition of mTORC1? | 2013 | Exp. Dermatol. | pmid:23800068 |
| BaÅŸak PY et al. | The effects of systemic isotretinoin and antibiotic therapy on the microbial floras in patients with acne vulgaris. | 2013 | J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol | pmid:22239608 |
| Cakir GA et al. | Isotretinoin treatment in nodulocystic acne with and without polycystic ovary syndrome: efficacy and determinants of relapse. | 2013 | Int. J. Dermatol. | pmid:22998438 |
| Tankurt E et al. | Esophageal ulcers: a possible adverse effect of isotretinoin. | 2013 | Turk J Gastroenterol | pmid:24623299 |
| Gan EY et al. | Isotretinoin is safe and efficacious in Asians with acne vulgaris. | 2013 | J Dermatolog Treat | pmid:22390469 |