| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
| Acne Vulgaris | D000152 | 35 associated lipids |
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Lymphoma, Large-Cell, Anaplastic | D017728 | 3 associated lipids |
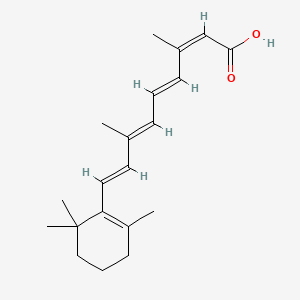
13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. 13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin is associated with abnormalities such as Dermatitis, Phototoxic. The involved functions are known as Regulation, Pigment, chromophore, Light absorption and Pupil constriction. 13-cis-retinoic acid,isotretinoin often locates in Neurosecretory Systems. The associated genes with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin are melanopsin.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin is suspected in Dermatitis, Phototoxic and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with 13-cis-retinoic acid,Isotretinoin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ucak H et al. | Effect of oral isotretinoin treatment on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. | 2014 Jul-Aug | J Cutan Med Surg | pmid:25008440 |
| Grando LR et al. | Pseudo-acne fulminans associated with oral isotretinoin. | 2014 Jul-Aug | An Bras Dermatol | pmid:25054758 |
| Rouzès A and Jonville-Béra AP | [Exposure to isotretinoin during pregnancy in France: 25 years of follow-up]. | 2014 Jan-Feb | Therapie | pmid:24698189 |
| Mutizwa MM and Berk DR | Dichotomous long-term response to isotretinoin in two patients with fordyce spots. | 2014 Jan-Feb | Pediatr Dermatol | pmid:22486258 |
| Mobacken H et al. | [30 years with isotretinoin. "Miracle medicine" against acne with many side effects]. | 2014 Jan 15-28 | Lakartidningen | pmid:24552013 |
| Yoon JH et al. | Concomitant use of an infrared fractional laser with low-dose isotretinoin for the treatment of acne and acne scars. | 2014 | J Dermatolog Treat | pmid:23336106 |
| Cetinözman F et al. | Insulin sensitivity, androgens and isotretinoin therapy in women with severe acne. | 2014 | J Dermatolog Treat | pmid:23163983 |
| Pariente A | [Isotretinoin does not increase the risk of intestinal inflammatory disease]. | 2014 | Rev Prat | pmid:25090755 |
| Peleg H et al. | Radiologic features of acne fulminans. | 2014 | Isr. Med. Assoc. J. | pmid:25059007 |
| Pillai RN et al. | Interferon alpha plus 13-cis-retinoic acid modulation of BCL-2 plus paclitaxel for recurrent small-cell lung cancer (SCLC): an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study (E6501). | 2014 | Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. | pmid:24858462 |
| Duffy EK et al. | Spurious elevation of aspartate aminotransferase in a patient on isotretinoin. | 2014 | J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. | pmid:25219729 |
| Dai C et al. | Isotretinoin and risk of inflammatory bowel disease. | 2014 | Am. J. Gastroenterol. | pmid:25196874 |
| Racine A et al. | Response to Dai et al. | 2014 | Am. J. Gastroenterol. | pmid:25196875 |
| Wootton CI et al. | Should isotretinoin be stopped prior to surgery? A critically appraised topic. | 2014 | Br. J. Dermatol. | pmid:24547720 |
| Maschan M et al. | Control of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura by sirolimus in a child with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia and somatic N-RAS mutation. | 2014 | Pediatr Blood Cancer | pmid:24590757 |
| Sardana K and Garg VK | Antibiotic resistance in acne: is it time to look beyond antibiotics and Propionobacterium acnes? | 2014 | Int. J. Dermatol. | pmid:24738843 |
| Lebwohl B et al. | Isotretinoin use and celiac disease: a population-based cross-sectional study. | 2014 | Am J Clin Dermatol | pmid:25022269 |
| Shah N et al. | PBX1 is a favorable prognostic biomarker as it modulates 13-cis retinoic acid-mediated differentiation in neuroblastoma. | 2014 | Clin. Cancer Res. | pmid:24947929 |
| D'souza P et al. | Porokeratosis ptychotropica: a rare variant of porokeratosis. | 2014 | Dermatol. Online J. | pmid:24945649 |
| Barnes LE et al. | Common reasons why acne patients call the office. | 2014 | Dermatol. Online J. | pmid:24852769 |