| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang W et al. | Marinospirillum alkaliphilum sp. nov., a new alkaliphilic helical bacterium from Haoji soda lake in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China. | 2002 | Extremophiles | pmid:11878559 |
| Denner EB et al. | Vibrio calviensis sp. nov., a halophilic, facultatively oligotrophic 0.2 microm-fiIterabIe marine bacterium. | 2002 | Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. | pmid:11931167 |
| Sul D and Kaneshiro ES | Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. carinii synthesizes de novo four homologs of ubiquinone. | 2001 Mar-Apr | J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. | pmid:12095106 |
| Jonassen T et al. | Development and fertility in Caenorhabditis elegans clk-1 mutants depend upon transport of dietary coenzyme Q8 to mitochondria. | 2002 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:12324451 |
| Asencio C et al. | Silencing of ubiquinone biosynthesis genes extends life span in Caenorhabditis elegans. | 2003 | FASEB J. | pmid:12709403 |
| Saiki R et al. | Pleiotropic phenotypes of fission yeast defective in ubiquinone-10 production. A study from the abc1Sp (coq8Sp) mutant. | 2003 | Biofactors | pmid:14695938 |
| Matsuura K et al. | Dioxygen reduction by bo-type quinol oxidase from Escherichia coli studied by submillisecond-resolved freeze-quench EPR spectroscopy. | 2004 | Biochemistry | pmid:14979725 |
| Hsieh EJ et al. | A tRNA(TRP) gene mediates the suppression of cbs2-223 previously attributed to ABC1/COQ8. | 2004 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:15063807 |
| Okunuki S et al. | Changes in phosphorus removing performance and bacterial community structure in an enhanced biological phosphorus removal reactor. | 2004 | Water Res. | pmid:15142805 |
| Yoon JH et al. | Kangiella koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Kangiella aquimarina sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat of the Yellow Sea in Korea. | 2004 | Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. | pmid:15388751 |
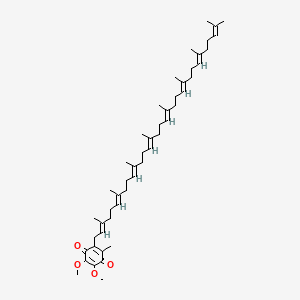
Coenzyme Q8
Coenzyme q8 is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The involved functions are known as Binding (Molecular Function) and Synthesis.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Coenzyme Q8, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Coenzyme Q8?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Coenzyme Q8
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Coenzyme Q8?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with Coenzyme Q8?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Coenzyme Q8?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Coenzyme Q8?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with Coenzyme Q8?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.