| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin K Deficiency | D014813 | 5 associated lipids |
| Thromboembolism | D013923 | 6 associated lipids |
| Exanthema | D005076 | 11 associated lipids |
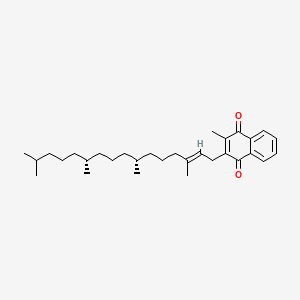
phylloquinone
Phylloquinone is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Phylloquinone is associated with abnormalities such as Vitamin K Deficiency, Malnutrition, Consumption-archaic term for TB, Osteoporosis and Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal. The involved functions are known as Ingestion, Blood Circulation, Genetic Polymorphism, Intestinal Absorption and Process. Phylloquinone often locates in Blood, Body tissue, Hepatic, Membrane and Entire bony skeleton. The associated genes with phylloquinone are Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase Complex, Subunit 1, GGCX gene, CYP4F2 gene, Alleles and APOE gene. The related lipids are Micelles, 208-G, Fatty Acids, Total cholesterol and Sphingolipids. The related experimental models are Knock-out.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of phylloquinone, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with phylloquinone?
phylloquinone is suspected in Vitamin K Deficiency, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Diabetes, vitamin depletion, Malnutrition, Osteoporosis and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with phylloquinone
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with phylloquinone
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with phylloquinone?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with phylloquinone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with phylloquinone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with phylloquinone?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with phylloquinone?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'A dedicated thioesterase of the Hotdog-fold family is required for the biosynthesis of the naphthoquinone ring of vitamin K1.' (Widhalm JR et al., 2009) and Knock-out are used in the study 'Deficiency in phylloquinone (vitamin K1) methylation affects prenyl quinone distribution, photosystem I abundance, and anthocyanin accumulation in the Arabidopsis AtmenG mutant.' (Lohmann A et al., 2006).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with phylloquinone
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GUTTAS CG et al. | Studies on the anticoagulant phenylindanedione. I. The effect of emulsified vitamin K1 on phenylindanedione-induced hypoprothrombinemia. | 1953 | Blood | pmid:13032197 |
| CHALMERS JN et al. | Antagonistic effect of oral vitamin K1 on the action of ethyl biscoumacetate and phenylindanedione. | 1954 | Br Med J | pmid:13199354 |
| DAWSON P | Effect of intravenous vitamin K1 on the action of phenindione. | 1955 | Br Med J | pmid:13269887 |
| ENGLISH A et al. | Vitamin K1 in the control of phenylindanedione-induced anticoagulant therapy. | 1955 | Can Med Assoc J | pmid:13231011 |
| BEAMISH RE and STORRIE VM | Severe haemolytic reaction following the intravenous administration of emulsified vitamin K (mephyton). | 1956 | Can Med Assoc J | pmid:13284670 |
| BEYER RE | The effect of ultraviolet light on mitochondria. II. Restoration of oxidative phosphorylation with vitamin K1 after near-ultraviolet treatment. | 1959 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:13641285 |
| ANDERSON WW and DALLAM RD | The effect of vitamin K1 on oxidative phosphorylation of rat liver mitochondria irradiated with ultraviolet light. | 1959 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:13630920 |
| MUSHETT CW et al. | Efficacy of water-soluble derivatives of vitamin K1 in counteracting drug-induced hypoprothrombinemia. | 1959 | Blood | pmid:13607577 |
| LOWENTHAL J and TAYLOR JD | A method for measuring the activity of compounds with an activity like vitamin K against indirect anticoagulants in rats. | 1959 | Br J Pharmacol Chemother | pmid:13651573 |
| WOSILAIT WD | The reduction of vitamin K1 by an enzyme from dog liver. | 1960 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:13846011 |