| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bauerly K et al. | Altering pyrroloquinoline quinone nutritional status modulates mitochondrial, lipid, and energy metabolism in rats. | 2011 | PLoS ONE | pmid:21814553 |
| Uchida Y | The role of fatty acid elongation in epidermal structure and function. | 2011 | Dermatoendocrinol | pmid:21695014 |
| Grimm MO et al. | Intracellular APP Domain Regulates Serine-Palmitoyl-CoA Transferase Expression and Is Affected in Alzheimer's Disease. | 2011 | Int J Alzheimers Dis | pmid:21660213 |
| Koeller CM and Heise N | The Sphingolipid Biosynthetic Pathway Is a Potential Target for Chemotherapy against Chagas Disease. | 2011 | Enzyme Res | pmid:21603271 |
| Chao DY et al. | Sphingolipids in the root play an important role in regulating the leaf ionome in Arabidopsis thaliana. | 2011 | Plant Cell | pmid:21421810 |
| Momin AA et al. | A method for visualization of "omic" datasets for sphingolipid metabolism to predict potentially interesting differences. | 2011 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:21415121 |
| BÅ‚achnio-Zabielska A et al. | Aerobic training in rats increases skeletal muscle sphingomyelinase and serine palmitoyltransferase activity, while decreasing ceramidase activity. | 2011 | Lipids | pmid:21181285 |
| Sweeley CC | Reflections on my career in analytical chemistry and biochemistry. | 2010 | Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B, Phys. Biol. Sci. | pmid:20948176 |
| Schmitz-Peiffer C | Targeting ceramide synthesis to reverse insulin resistance. | 2010 | Diabetes | pmid:20876726 |
| Sims K et al. | Kdo2-lipid A, a TLR4-specific agonist, induces de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis in RAW264.7 macrophages, which is essential for induction of autophagy. | 2010 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:20876532 |
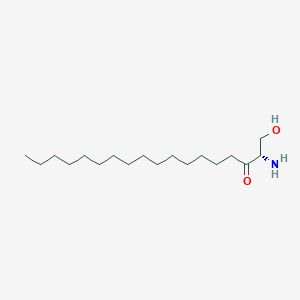
3-Ketosphinganine
3-Ketosphinganine is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. The involved functions are known as Anabolism and establishment and maintenance of localization. 3-ketosphinganine often locates in Membrane and membrane raft.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 3-Ketosphinganine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.