| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bahtiar A et al. | Identification of a novel L-serine analog that suppresses osteoclastogenesis in vitro and bone turnover in vivo. | 2009 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:19837662 |
| Sims K et al. | Kdo2-lipid A, a TLR4-specific agonist, induces de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis in RAW264.7 macrophages, which is essential for induction of autophagy. | 2010 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:20876532 |
| Song WQ et al. | Characterization of two cotton cDNAs encoding trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase reveals a putative novel NADPH-binding motif. | 2009 | J. Exp. Bot. | pmid:19286916 |
| Momin AA et al. | A method for visualization of "omic" datasets for sphingolipid metabolism to predict potentially interesting differences. | 2011 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:21415121 |
| Chigorno V et al. | Activity of 3-ketosphinganine synthase during differentiation and aging of neuronal cells in culture. | 1997 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:9215544 |
| Gupta SD et al. | Tsc10p and FVT1: topologically distinct short-chain reductases required for long-chain base synthesis in yeast and mammals. | 2009 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:19141869 |
| Park H et al. | Transcript profiling and lipidomic analysis of ceramide subspecies in mouse embryonic stem cells and embryoid bodies. | 2010 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:19786568 |
| Pruett ST et al. | Biodiversity of sphingoid bases ("sphingosines") and related amino alcohols. | 2008 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:18499644 |
| Radin NS | Biosynthesis of the sphingoid bases: a provocation. | 1984 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:6442338 |
| Messmer TO et al. | Sphingolipid biosynthesis by rat liver cells: effects of serine, fatty acids and lipoproteins. | 1989 | J. Nutr. | pmid:2495341 |
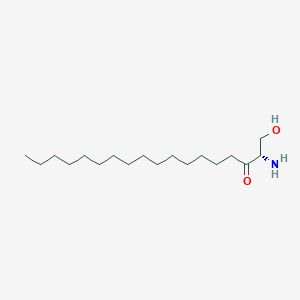
3-Ketosphinganine
3-Ketosphinganine is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. The involved functions are known as Anabolism and establishment and maintenance of localization. 3-ketosphinganine often locates in Membrane and membrane raft.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 3-Ketosphinganine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with 3-Ketosphinganine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.