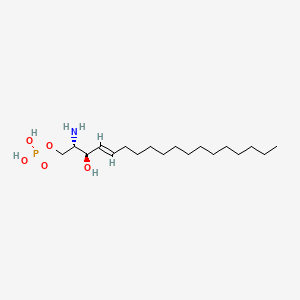
Sphingosine 1-phosphate
Sphingosine 1-phosphate is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. Sphingosine 1-phosphate is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Painful Bladder Syndrome, Atherosclerosis, Hyperglycemia and Rheumatoid Arthritis. The involved functions are known as Phosphorylation, Regulation, enzyme activity, Energy Absorption and Vascular Permeability. Sphingosine 1-phosphate often locates in Endothelium, Tissue membrane, Vascular System, Protoplasm and Microfilaments. The associated genes with Sphingosine 1-phosphate are MBTPS1 gene, FBXL15 gene, TEK gene, NTRK1 gene and Gene Family. The related lipids are Promega, Lipopolysaccharides, lysophosphatidic acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines and Lysophospholipids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Transgenic Model, Disease model and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Sphingosine 1-phosphate, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Sphingosine 1-phosphate?
Sphingosine 1-phosphate is suspected in Lymphopenia, Ischemia, Infection, Atherosclerosis, Multiple Sclerosis, Asthma and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Sphingosine 1-phosphate
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Sphingosine 1-phosphate
Lipid pathways are not clear in current pathway databases. We organized associated pathways with Sphingosine 1-phosphate through full-text articles, including metabolic pathways or pathways of biological mechanisms.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Pathway name | Related literatures |
|---|
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Sphingosine 1-phosphate?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Sphingosine 1-phosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Sphingosine 1-phosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Sphingosine 1-phosphate?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Sphingosine 1-phosphate?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'Sphingosine 1-phosphate-dependent trafficking of peritoneal B cells requires functional NFkappaB-inducing kinase in stromal cells.' (Kunisawa J et al., 2008), Knock-out are used in the study 'Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) mediates angiogenic effect of S1P in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells.' (Markiewicz M et al., 2011), Knock-out are used in the study 'Chasing sphingosine-1-phosphate, a lipid mediator for cardiomyocyte survival.' (Yang Q, 2007), Knock-out are used in the study 'Local application of FTY720 to the lung abrogates experimental asthma by altering dendritic cell function.' (Idzko M et al., 2006) and Knock-out are used in the study 'Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 modulates endothelial cell motility through the small G-protein Rho.' (Gratzinger D et al., 2003).
Mouse Model
Mouse Model are used in the study 'Regulation of the micromechanical properties of pulmonary endothelium by S1P and thrombin: role of cortactin.' (Arce FT et al., 2008), Mouse Model are used in the study 'Sequential delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor and sphingosine 1-phosphate for angiogenesis.' (Tengood JE et al., 2010), Mouse Model are used in the study 'S1P(5) is required for sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced autophagy in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells.' (Chang CL et al., 2009), Mouse Model are used in the study 'Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces an antiinflammatory phenotype in macrophages.' (Hughes JE et al., 2008) and Mouse Model are used in the study 'The alliance of sphingosine-1-phosphate and its receptors in immunity.' (Rivera J et al., 2008).
Transgenic Model
Transgenic Model are used in the study 'Role for matrix metalloproteinase-2 in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced activation of the sphingomyelin/ceramide pathway and smooth muscle cell proliferation.' (Augé N et al., 2004), Transgenic Model are used in the study 'Sphingosine-1-phosphate antibodies as potential agents in the treatment of cancer and age-related macular degeneration.' (Sabbadini RA, 2011) and Transgenic Model are used in the study 'Still benched on its way to the bedside: sphingosine kinase 1 as an emerging target in cancer chemotherapy.' (Gault CR and Obeid LM, 2011).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Sphingosine 1-phosphate
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yatomi Y et al. | Quantitative measurement of sphingosine 1-phosphate in biological samples by acylation with radioactive acetic anhydride. | 1995 | Anal. Biochem. | pmid:7503424 |
| Törnquist K et al. | Sphingosine derivatives inhibit depolarization-evoked calcium entry in rat GH4C1 cells. | 1995 | Endocrinology | pmid:7588222 |
| Yatomi Y et al. | Sphingosine-1-phosphate: a platelet-activating sphingolipid released from agonist-stimulated human platelets. | 1995 | Blood | pmid:7795224 |
| Liu R et al. | Effects of sphingosine derivatives on MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts: psychosine elicits release of calcium from intracellualr stores. | 1995 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:7677781 |
| Jalink K et al. | Lysophosphatidic acid-induced Ca2+ mobilization in human A431 cells: structure-activity analysis. | 1995 | Biochem. J. | pmid:7733903 |
| Goodemote KA et al. | Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein in the mitogenic signaling pathways of sphingosine 1-phosphate. | 1995 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:7730331 |
| Pyne S et al. | Sphingomyelin-derived lipids differentially regulate the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK-2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signal cascades in airway smooth muscle. | 1996 | Eur. J. Biochem. | pmid:8647130 |
| Van Koppen CJ et al. | A distinct G(i) protein-coupled receptor for sphingosylphosphorylcholine in human leukemia HL-60 cells and human neutrophils. | 1996 | Mol. Pharmacol. | pmid:8649355 |
| Okajima F et al. | Involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding proteins in sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced activation of phospholipase C-Ca2+ system in HL60 leukemia cells. | 1996 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:8603702 |
| Berger A et al. | Structural requirements of sphingosylphosphocholine and sphingosine-1-phosphate for stimulation of activator protein-1 activity. | 1996 | Mol. Pharmacol. | pmid:8794881 |