| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FabiÅ¡Ãková M et al. | Total synthesis and the anticancer activity of (+)-spisulosine. | 2016 | Carbohydr. Res. | pmid:27693911 |
| Steiner R et al. | Elucidating the chemical structure of native 1-deoxysphingosine. | 2016 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:27165858 |
| Duan J and Merrill AH | 1-Deoxysphingolipids Encountered Exogenously and Made de Novo: Dangerous Mysteries inside an Enigma. | 2015 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:25947379 |
| Esaki K et al. | L-Serine Deficiency Elicits Intracellular Accumulation of Cytotoxic Deoxysphingolipids and Lipid Body Formation. | 2015 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:25903138 |
| Wei N et al. | Altered sphingoid base profiles in type 1 compared to type 2 diabetes. | 2014 | Lipids Health Dis | pmid:25305670 |
| Kowluru A | Deoxysphingolipids: β-cell, beware of these new kids on the block. | 2014 | Diabetes | pmid:24651803 |
| Zuellig RA et al. | Deoxysphingolipids, novel biomarkers for type 2 diabetes, are cytotoxic for insulin-producing cells. | 2014 | Diabetes | pmid:24379346 |
| Calder ED et al. | Preparation of anti-vicinal amino alcohols: asymmetric synthesis of D-erythro-sphinganine, (+)-spisulosine, and D-ribo-phytosphingosine. | 2013 | J. Org. Chem. | pmid:23795558 |
| Abad JL et al. | Straightforward access to spisulosine and 4,5-dehydrospisulosine stereoisomers: probes for profiling ceramide synthase activities in intact cells. | 2013 | J. Org. Chem. | pmid:23679346 |
| Byun HS et al. | Novel sphingosine-containing analogues selectively inhibit sphingosine kinase (SK) isozymes, induce SK1 proteasomal degradation and reduce DNA synthesis in human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. | 2013 | Medchemcomm | pmid:24396570 |
| Xu K et al. | A highly anti-selective asymmetric Henry reaction catalyzed by a chiral copper complex: applications to the syntheses of (+)-spisulosine and a pyrroloisoquinoline derivative. | 2012 | Chemistry | pmid:22907874 |
| Massard C et al. | Phase I dose-escalating study of ES-285 given as a three-hour intravenous infusion every three weeks in patients with advanced malignant solid tumors. | 2012 | Invest New Drugs | pmid:22215532 |
| Vilar E et al. | A phase I dose-escalating study of ES-285, a marine sphingolipid-derived compound, with repeat dose administration in patients with advanced solid tumors. | 2012 | Invest New Drugs | pmid:20820909 |
| Chen BS et al. | Diastereoselective synthesis and bioactivity of long-chain anti-2-amino-3-alkanols. | 2011 | Eur J Med Chem | pmid:21955681 |
| Garofalo K et al. | Oral L-serine supplementation reduces production of neurotoxic deoxysphingolipids in mice and humans with hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type 1. | 2011 | J. Clin. Invest. | pmid:22045570 |
| Scherer SS | The debut of a rational treatment for an inherited neuropathy? | 2011 | J. Clin. Invest. | pmid:22045569 |
| Rotthier A et al. | Characterization of two mutations in the SPTLC1 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase associated with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type I. | 2011 | Hum. Mutat. | pmid:21618344 |
| Merrill AH | Sphingolipid and glycosphingolipid metabolic pathways in the era of sphingolipidomics. | 2011 | Chem. Rev. | pmid:21942574 |
| Schöffski P et al. | Spisulosine (ES-285) given as a weekly three-hour intravenous infusion: results of a phase I dose-escalating study in patients with advanced solid malignancies. | 2011 | Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. | pmid:21465314 |
| Malik G et al. | Aziridines from intramolecular alkene aziridination of sulfamates: reactivity toward carbon nucleophiles. application to the synthesis of spisulosine and its fluoro analogue. | 2011 | J. Org. Chem. | pmid:21812488 |
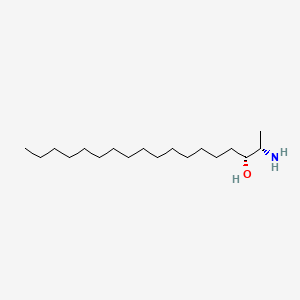
Spisulosine
Spisulosine is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. Spisulosine is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Renal impairment and Lesion of brain. The involved functions are known as Gene Expression, Cell Cycle, Drug Kinetics, Signal Transduction and Cell Cycle Arrest. Spisulosine often locates in Body tissue, Microfilaments, Skin, Stress Fibers and Tissue specimen.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Spisulosine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Spisulosine?
Spisulosine is suspected in Infection, Renal impairment, Lesion of brain and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Spisulosine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Spisulosine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Spisulosine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Spisulosine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Spisulosine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with Spisulosine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.