| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edler E et al. | Membrane localization and dynamics of geranylgeranylated Rab5 hypervariable region. | 2017 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:28455099 |
| Palacios-Ortega J et al. | Regulation of Sticholysin II-Induced Pore Formation by Lipid Bilayer Composition, Phase State, and Interfacial Properties. | 2016 | Langmuir | pmid:27003246 |
| Lee J et al. | CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. | 2016 | J Chem Theory Comput | pmid:26631602 |
| Sodt AJ et al. | Hexagonal Substructure and Hydrogen Bonding in Liquid-Ordered Phases Containing Palmitoyl Sphingomyelin. | 2015 | Biophys. J. | pmid:26331252 |
| Sakamoto S et al. | Effect of glycyrrhetinic acid on lipid raft model at the air/water interface. | 2015 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:25445675 |
| Venable RM et al. | CHARMM all-atom additive force field for sphingomyelin: elucidation of hydrogen bonding and of positive curvature. | 2014 | Biophys. J. | pmid:24988348 |
| Yang Y et al. | Lipidomic analyses of female mice lacking hepatic lipase and endothelial lipase indicate selective modulation of plasma lipid species. | 2014 | Lipids | pmid:24777581 |
| Depner CM et al. | A metabolomic analysis of omega-3 fatty acid-mediated attenuation of western diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in LDLR-/- mice. | 2013 | PLoS ONE | pmid:24358308 |
| Sergelius C et al. | Cholesterol's interactions with serine phospholipids - a comparison of N-palmitoyl ceramide phosphoserine with dipalmitoyl phosphatidylserine. | 2013 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:23159809 |
| Quinn PJ | Structure of sphingomyelin bilayers and complexes with cholesterol forming membrane rafts. | 2013 | Langmuir | pmid:23863113 |
| Kwiatek JM et al. | Characterization of a new series of fluorescent probes for imaging membrane order. | 2013 | PLoS ONE | pmid:23390489 |
| Ionova IV et al. | Phase diagram of ternary cholesterol/palmitoylsphingomyelin/palmitoyloleoyl-phosphatidylcholine mixtures: spin-label EPR study of lipid-raft formation. | 2012 | Biophys. J. | pmid:22768941 |
| Maula T et al. | Importance of the sphingoid base length for the membrane properties of ceramides. | 2012 | Biophys. J. | pmid:23199915 |
| Polley A et al. | Atomistic simulations of a multicomponent asymmetric lipid bilayer. | 2012 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:23088327 |
| Wang T et al. | Nanomechanical recognition of sphingomyelin-rich membrane domains by atomic force microscopy. | 2012 | Biochemistry | pmid:22148674 |
| Leung SS et al. | Insights into sphingolipid miscibility: separate observation of sphingomyelin and ceramide N-acyl chain melting. | 2012 | Biophys. J. | pmid:23260048 |
| Becucci L et al. | Gel-phase microdomains and lipid rafts in monolayers affect the redox properties of ubiquinone-10. | 2011 | Biophys. J. | pmid:21723823 |
| Nyholm TK et al. | Construction of a DOPC/PSM/cholesterol phase diagram based on the fluorescence properties of trans-parinaric acid. | 2011 | Langmuir | pmid:21627141 |
| Saito H and Shinoda W | Cholesterol effect on water permeability through DPPC and PSM lipid bilayers: a molecular dynamics study. | 2011 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:22081997 |
| Becucci L et al. | Influence of gel-phase microdomains and lipid rafts in lipid monolayers on the electron transfer of a lipophilic redox probe: dioctadecylviologen. | 2011 | Phys Chem Chem Phys | pmid:21210041 |
| Tumaneng PW et al. | Self-consistent mean-field model for palmitoyloleoylphosphatidylcholine-palmitoyl sphingomyelin-cholesterol lipid bilayers. | 2011 | Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys | pmid:21517541 |
| Janosi L and Gorfe A | Importance of the sphingosine base double-bond geometry for the structural and thermodynamic properties of sphingomyelin bilayers. | 2010 | Biophys. J. | pmid:21044593 |
| Chu S et al. | Solid-state NMR paramagnetic relaxation enhancement immersion depth studies in phospholipid bilayers. | 2010 | J. Magn. Reson. | pmid:20851650 |
| Westerlund B et al. | Ceramide acyl chain length markedly influences miscibility with palmitoyl sphingomyelin in bilayer membranes. | 2010 | Eur. Biophys. J. | pmid:19908035 |
| Busto JV et al. | Cholesterol displaces palmitoylceramide from its tight packing with palmitoylsphingomyelin in the absence of a liquid-disordered phase. | 2010 | Biophys. J. | pmid:20712995 |
| Vácha R et al. | Molecular model of a cell plasma membrane with an asymmetric multicomponent composition: water permeation and ion effects. | 2009 | Biophys. J. | pmid:19486672 |
| Silva LC et al. | Lipid raft composition modulates sphingomyelinase activity and ceramide-induced membrane physical alterations. | 2009 | Biophys. J. | pmid:19383465 |
| Busto JV et al. | Coexistence of immiscible mixtures of palmitoylsphingomyelin and palmitoylceramide in monolayers and bilayers. | 2009 | Biophys. J. | pmid:19917225 |
| Björkqvist YJ et al. | N-palmitoyl-sulfatide participates in lateral domain formation in complex lipid bilayers. | 2008 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:18206111 |
| Halling KK et al. | Cholesterol interactions with fluid-phase phospholipids: effect on the lateral organization of the bilayer. | 2008 | Biophys. J. | pmid:18641061 |
| Bartels T et al. | Raftlike mixtures of sphingomyelin and cholesterol investigated by solid-state 2H NMR spectroscopy. | 2008 | J. Am. Chem. Soc. | pmid:18839945 |
| Aittoniemi J et al. | Insight into the putative specific interactions between cholesterol, sphingomyelin, and palmitoyl-oleoyl phosphatidylcholine. | 2007 | Biophys. J. | pmid:17114220 |
| Mehnert T et al. | Structure and lipid interaction of N-palmitoylsphingomyelin in bilayer membranes as revealed by 2H-NMR spectroscopy. | 2006 | Biophys. J. | pmid:16284259 |
| Collado MI et al. | Domain formation in sphingomyelin/cholesterol mixed membranes studied by spin-label electron spin resonance spectroscopy. | 2005 | Biochemistry | pmid:15779918 |
| de Almeida RF et al. | Lipid rafts have different sizes depending on membrane composition: a time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer study. | 2005 | J. Mol. Biol. | pmid:15701521 |
| Veatch SL and Keller SL | Miscibility phase diagrams of giant vesicles containing sphingomyelin. | 2005 | Phys. Rev. Lett. | pmid:15904115 |
| Halling KK and Slotte JP | Membrane properties of plant sterols in phospholipid bilayers as determined by differential scanning calorimetry, resonance energy transfer and detergent-induced solubilization. | 2004 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:15328048 |
| Mombelli E et al. | Hydrogen-bonding propensities of sphingomyelin in solution and in a bilayer assembly: a molecular dynamics study. | 2003 | Biophys. J. | pmid:12609857 |
| de Almeida RF et al. | Sphingomyelin/phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol phase diagram: boundaries and composition of lipid rafts. | 2003 | Biophys. J. | pmid:14507704 |
| Maiorano JN and Davidson WS | The orientation of helix 4 in apolipoprotein A-I-containing reconstituted high density lipoproteins. | 2000 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:10751383 |
| Bushnev AS and Liotta DC | Practical synthesis of N-palmitoylsphingomyelin and N-palmitoyldihydrosphingomyelin. | 2000 | Meth. Enzymol. | pmid:10563348 |
| Schmelz EM et al. | Suppression of aberrant colonic crypt foci by synthetic sphingomyelins with saturated or unsaturated sphingoid base backbones. | 1997 | Nutr Cancer | pmid:9200154 |
| Maulik PR and Shipley GG | N-palmitoyl sphingomyelin bilayers: structure and interactions with cholesterol and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. | 1996 | Biochemistry | pmid:8672507 |
| Slotte JP | Lateral domain formation in mixed monolayers containing cholesterol and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine or N-palmitoylsphingomyelin. | 1995 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:7756352 |
| Dong Z and Butcher JA | An efficient route to N-palmitoyl-D-erythro-sphingomyelin and its 13C-labeled derivatives. | 1993 | Chem. Phys. Lipids | pmid:8118917 |
| Speyer JB et al. | Magnetic orientation of sphingomyelin-lecithin bilayers. | 1987 | Biophys. J. | pmid:3580492 |
| pmid: |
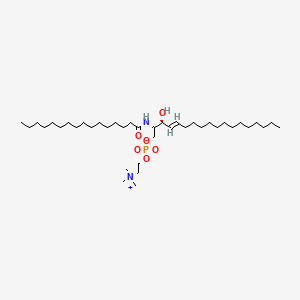
C16 Sphingomyelin
C16 Sphingomyelin is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. The involved functions are known as Drug Interactions, Molecular Dynamics, Force, Energy Transfer and Signal Transduction. C16 sphingomyelin often locates in Membrane, Tissue membrane, Cell membrane, biological membrane and lipid raft. The related lipids are 1,2-oleoylphosphatidylcholine, Sphingolipids, lipid structure, Sterols and campesterol.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of C16 Sphingomyelin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with C16 Sphingomyelin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with C16 Sphingomyelin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with C16 Sphingomyelin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with C16 Sphingomyelin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with C16 Sphingomyelin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with C16 Sphingomyelin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with C16 Sphingomyelin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.