| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Dicrocoeliasis | D004011 | 1 associated lipids |
| Thyroglossal Cyst | D013955 | 1 associated lipids |
| Postmortem Changes | D011180 | 1 associated lipids |
| Glomus Tumor | D005918 | 1 associated lipids |
| Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia | D009377 | 1 associated lipids |
| Neuroma, Acoustic | D009464 | 1 associated lipids |
| Callosities | D002145 | 1 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Insipidus, Neurogenic | D020790 | 1 associated lipids |
| Sprue, Tropical | D013182 | 1 associated lipids |
| Snoring | D012913 | 1 associated lipids |
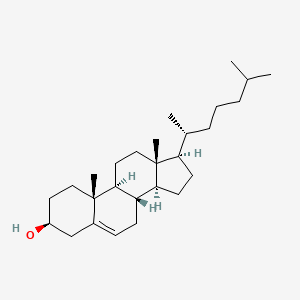
cholesterol
cholesterol is a lipid of Sterol Lipids (ST) class. Cholesterol is associated with abnormalities such as Trypanosomiasis, Chagas Disease, Cleft Palate, Chondrodysplasia punctata 2, X-linked dominant and Child syndrome. The involved functions are known as Blood Circulation, Sterol Biosynthesis Pathway, Receptor Mediated Endocytosis, Methylation and Signal. Cholesterol often locates in Animal tissue, Blood, Membrane, Plasma membrane and peroxisome. The associated genes with cholesterol are MBD2 gene, SIM, SLC33A1 gene, Genome and NSDHL gene. The related lipids are Sterols, zymosterol, fecosterol, Total cholesterol and 7-dehydrocholesterol. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out, Genetically Engineered Mouse and Disease model.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of cholesterol, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with cholesterol?
cholesterol is suspected in Atherosclerosis, Hypercholesterolemia, cholesterol gallstones, Obesity, SVEINSSON CHORIORETINAL ATROPHY, Congenital Abnormality and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with cholesterol
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with cholesterol
Lipid pathways are not clear in current pathway databases. We organized associated pathways with cholesterol through full-text articles, including metabolic pathways or pathways of biological mechanisms.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Pathway name | Related literatures |
|---|
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with cholesterol?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with cholesterol?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with cholesterol?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with cholesterol?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with cholesterol?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'Acid sphingomyelinase-deficient macrophages have defective cholesterol trafficking and efflux.' (Leventhal AR et al., 2001), Knock-out are used in the study 'On the regulatory role of side-chain hydroxylated oxysterols in the brain. Lessons from CYP27A1 transgenic and Cyp27a1(-/-) mice.' (Ali Z et al., 2013), Knock-out are used in the study 'Regulation of classic and alternative bile acid synthesis in hypercholesterolemic rabbits: effects of cholesterol feeding and bile acid depletion.' (Xu G et al., 1998), Knock-out are used in the study 'Functional redundancy of steroid C26-monooxygenase activity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis revealed by biochemical and genetic analyses.' (Johnston JB et al., 2010) and Knock-out are used in the study 'Marked reduction in bile acid synthesis in cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase-deficient mice does not lead to diminished tissue cholesterol turnover or to hypercholesterolemia.' (Schwarz M et al., 1998).
Mouse Model
Mouse Model are used in the study 'Fenofibrate reduces intestinal cholesterol absorption via PPARalpha-dependent modulation of NPC1L1 expression in mouse.' (Valasek MA et al., 2007), Mouse Model are used in the study 'Functional redundancy of steroid C26-monooxygenase activity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis revealed by biochemical and genetic analyses.' (Johnston JB et al., 2010), Mouse Model are used in the study 'Cholic acid aids absorption, biliary secretion, and phase transitions of cholesterol in murine cholelithogenesis.' (Wang DQ et al., 1999), Mouse Model are used in the study 'Feedback inhibition of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway in patients with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome as demonstrated by urinary mevalonate excretion.' (Pappu AS et al., 2002) and Mouse Model are used in the study 'Disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis: prototypic metabolic malformation syndromes.' (Herman GE, 2003).
Disease model
Disease model are used in the study 'Amphotericin B lipid complex or amphotericin B multiple-dose administration to rabbits with elevated plasma cholesterol levels: pharmacokinetics in plasma and blood, plasma lipoprotein levels, distribution in tissues, and renal toxicities.' (Ramaswamy M et al., 2001) and Disease model are used in the study 'Increased cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase expression and size of the bile acid pool in the lactating rat.' (Wooton-Kee CR et al., 2008).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with cholesterol
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rashduni DL et al. | Glycation of high-density lipoprotein does not increase its susceptibility to oxidation or diminish its cholesterol efflux capacity. | 1999 | Metab. Clin. Exp. | pmid:10024072 |
| Fields M and Lewis CG | Cholesterol-lowering nature of unsaturated fat in rats may be due to its inability to increase hepatic iron. | 1999 | Metab. Clin. Exp. | pmid:10024082 |
| Inouye M et al. | Glycated hemoglobin and lipid peroxidation in erythrocytes of diabetic patients. | 1999 | Metab. Clin. Exp. | pmid:10024083 |
| Verrips A et al. | Effect of simvastatin in addition to chenodeoxycholic acid in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. | 1999 | Metab. Clin. Exp. | pmid:10024088 |
| Jenkins DJ et al. | Colonic bacterial activity and serum lipid risk factors for cardiovascular disease. | 1999 | Metab. Clin. Exp. | pmid:10024093 |
| Walker AR | Cholesterol: how low is low enough? Effect of a given concentration depends on several factors. | 1999 | BMJ | pmid:10024281 |
| Brouillet E et al. | The amyloid precursor protein interacts with Go heterotrimeric protein within a cell compartment specialized in signal transduction. | 1999 | J. Neurosci. | pmid:10024358 |
| Oi Y et al. | Allyl-containing sulfides in garlic increase uncoupling protein content in brown adipose tissue, and noradrenaline and adrenaline secretion in rats. | 1999 | J. Nutr. | pmid:10024610 |
| Castenmiller JJ et al. | The food matrix of spinach is a limiting factor in determining the bioavailability of beta-carotene and to a lesser extent of lutein in humans. | 1999 | J. Nutr. | pmid:10024612 |
| Hart DM et al. | Long-term effects of continuous combined HRT on bone turnover and lipid metabolism in postmenopausal women. | 1998 | Osteoporos Int | pmid:10024902 |