| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furster C and Wikvall K | Identification of CYP3A4 as the major enzyme responsible for 25-hydroxylation of 5beta-cholestane-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-triol in human liver microsomes. | 1999 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:9931427 |
| Suzuki Y | [Other peroxisomal diseases]. | 1998 | Ryoikibetsu Shokogun Shirizu | pmid:9645078 |
| Fricker G et al. | Enterohepatic circulation of scymnol sulfate in an elasmobranch, the little skate (Raja erinacea). | 1997 | Am. J. Physiol. | pmid:9374698 |
| Pikuleva IA et al. | Expression, purification, and enzymatic properties of recombinant human cytochrome P450c27 (CYP27). | 1997 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:9210654 |
| Une M et al. | Comparative studies on omega-hydroxylation of 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha, 7 alpha, 12 alpha-triol in the mitochondrial and microsomal fraction of the liver from several vertebrates. | 1997 | Steroids | pmid:9185292 |
| Ikegawa S et al. | Stereoisomeric inversion of (25R)- and (25S)-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-trihydroxy-5 beta-cholestanoic acids in rat liver peroxisome. | 1995 | Biol. Pharm. Bull. | pmid:7581245 |
| Betsholtz IH and Wikvall K | Cytochrome P450 CYP27-catalyzed oxidation of C27-steroid into C27-acid. | 1995 | J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. | pmid:7577714 |
| Dueland S et al. | 26-hydroxylation of 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-triol by isolated nonparenchymal cells and hepatocytes from rat liver. | 1982 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:7161561 |
| Noshiro M et al. | The involvement of cytochrome b5 in 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha, 7 alpha, 12 alpha-triol 25-hydroxylation and taurodeoxycholate 7 alpha-hydroxylation of rat liver. | 1982 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:7115387 |
| Björkhem I et al. | Assay of intermediates in bile acid biosynthesis using isotope dilution--mass spectrometry: hepatic levels in the normal state and in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. | 1981 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:7017048 |
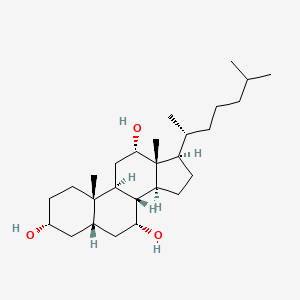
Trihydroxycoprostane
Trihydroxycoprostane is a lipid of Sterol Lipids (ST) class. The involved functions are known as Uptake, Enterohepatic Circulation, Metabolic Inhibition and Ionization. Trihydroxycoprostane often locates in Hepatic, Entire gastrointestinal tract and Abdominal Cavity. The related lipids are 3,7,12-trihydroxycoprostane, (3beta,5beta,7alpha,12alpha)-isomer, Cholestanes and scymnol.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Trihydroxycoprostane, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Trihydroxycoprostane?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Trihydroxycoprostane
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Trihydroxycoprostane?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Trihydroxycoprostane?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Trihydroxycoprostane?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Trihydroxycoprostane?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with Trihydroxycoprostane?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.