| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Birth Weight | D001724 | 23 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Cholestasis | D002779 | 23 associated lipids |
| Colitis, Ulcerative | D003093 | 24 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
| Fetal Resorption | D005327 | 15 associated lipids |
| Gastroesophageal Reflux | D005764 | 10 associated lipids |
| Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage | D006471 | 27 associated lipids |
| Shock, Hemorrhagic | D012771 | 4 associated lipids |
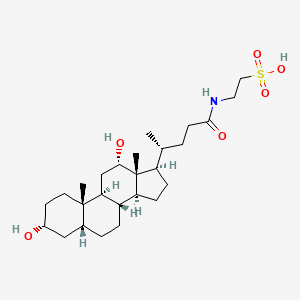
Taurodeoxycholic acid
Taurodeoxycholic acid is a lipid of Sterol Lipids (ST) class. Taurodeoxycholic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia and Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. The involved functions are known as Cell Proliferation, Transcriptional Activation, Phosphorylation, Anabolism and Biochemical Pathway. Taurodeoxycholic acid often locates in Body tissue, Epithelium, Blood, Mucous Membrane and Hepatic. The associated genes with Taurodeoxycholic acid are NOX5 gene, GPBAR1 gene, NR1H4 gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are cholanic acid, taurolithocholic acid 3-sulfate, Sterols, 7-dehydrocholesterol and tauromuricholic acid.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Taurodeoxycholic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Taurodeoxycholic acid is suspected in Ischemia and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Taurodeoxycholic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jang H et al. | Effects of protein concentration and detergent on endotoxin reduction by ultrafiltration. | 2009 | BMB Rep | pmid:19643046 |
| Torchia EC et al. | Differential modulation of cellular death and survival pathways by conjugated bile acids. | 2001 | BMC Biochem. | pmid:11707155 |
| Krasowski MD et al. | The evolution of farnesoid X, vitamin D, and pregnane X receptors: insights from the green-spotted pufferfish (Tetraodon nigriviridis) and other non-mammalian species. | 2011 | BMC Biochem. | pmid:21291553 |
| Dib M et al. | Role of mast cells in the development of pancreatitis-induced multiple organ dysfunction. | 2002 | Br J Surg | pmid:11856129 |
| Grill JP et al. | Bile salt toxicity to some bifidobacteria strains: role of conjugated bile salt hydrolase and pH. | 2000 | Can. J. Microbiol. | pmid:11068673 |
| Ohgaki H et al. | Effects of 4-week treatment with gastric carcinogens and enhancing agents on proliferation of gastric mucosa cells in rats. | 1989 | Cancer Lett. | pmid:2752382 |
| Morotomi M et al. | Production of diacylglycerol, an activator of protein kinase C, by human intestinal microflora. | 1990 | Cancer Res. | pmid:2340507 |
| Hong J et al. | Bile acid reflux contributes to development of esophageal adenocarcinoma via activation of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase Cgamma2 and NADPH oxidase NOX5-S. | 2010 | Cancer Res. | pmid:20086178 |
| Dunphy DR et al. | X-ray characterization of self-assembled long-chain phosphatidylcholine/bile salt/silica mesostructured films with nanoscale homogeneity. | 2011 | Chem. Commun. (Camb.) | pmid:21135947 |
| Murata Y et al. | Adsorption of bile acid by chitosan-orotic acid salt and its application as an oral preparation. | 2004 | Chem. Pharm. Bull. | pmid:15467231 |