| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Colitis, Ulcerative | D003093 | 24 associated lipids |
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Cholestasis | D002779 | 23 associated lipids |
| Birth Weight | D001724 | 23 associated lipids |
| Shock, Hemorrhagic | D012771 | 4 associated lipids |
| Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage | D006471 | 27 associated lipids |
| Tay-Sachs Disease | D013661 | 2 associated lipids |
| Fetal Resorption | D005327 | 15 associated lipids |
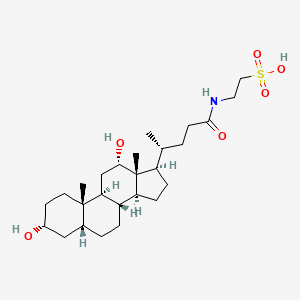
Taurodeoxycholic acid
Taurodeoxycholic acid is a lipid of Sterol Lipids (ST) class. Taurodeoxycholic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia and Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. The involved functions are known as Cell Proliferation, Transcriptional Activation, Phosphorylation, Anabolism and Biochemical Pathway. Taurodeoxycholic acid often locates in Body tissue, Epithelium, Blood, Mucous Membrane and Hepatic. The associated genes with Taurodeoxycholic acid are NOX5 gene, GPBAR1 gene, NR1H4 gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are cholanic acid, taurolithocholic acid 3-sulfate, Sterols, 7-dehydrocholesterol and tauromuricholic acid.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Taurodeoxycholic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Taurodeoxycholic acid is suspected in Ischemia and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Taurodeoxycholic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Taurodeoxycholic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campbell NB et al. | Physiological concentrations of bile salts inhibit recovery of ischemic-injured porcine ileum. | 2004 | Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. | pmid:15087278 |
| Mühlbauer M et al. | Differential effects of deoxycholic acid and taurodeoxycholic acid on NF-kappa B signal transduction and IL-8 gene expression in colonic epithelial cells. | 2004 | Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. | pmid:14726307 |
| Cao W et al. | Expression of bile acid receptor TGR5 in gastric adenocarcinoma. | 2013 | Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. | pmid:23238937 |
| Zhou Y et al. | Effect of indomethacin on bile acid-phospholipid interactions: implication for small intestinal injury induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. | 2010 | Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. | pmid:20203063 |
| Cai SY et al. | The farnesoid X receptor FXRalpha/NR1H4 acquired ligand specificity for bile salts late in vertebrate evolution. | 2007 | Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. | pmid:17567710 |
| Venkatasubramanian J et al. | Differences in Ca(2+) signaling underlie age-specific effects of secretagogues on colonic Cl(-) transport. | 2001 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | pmid:11171585 |
| Kanchanapoo J et al. | Role of protein kinase C-delta in the age-dependent secretagogue action of bile acids in mammalian colon. | 2007 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | pmid:17898130 |
| Lang J et al. | Synergistic effect of hydrochloric acid and bile acids on the pars esophageal mucosa of the porcine stomach. | 1998 | Am. J. Vet. Res. | pmid:9736398 |
| Reiner JL et al. | Determination of perfluorinated compounds in human plasma and serum Standard Reference Materials using independent analytical methods. | 2011 | Anal Bioanal Chem | pmid:21912833 |
| Ruhaak LR et al. | Glycan labeling strategies and their use in identification and quantification. | 2010 | Anal Bioanal Chem | pmid:20225063 |
| Tiss A et al. | Effects of gum arabic on lipase interfacial binding and activity. | 2001 | Anal. Biochem. | pmid:11412003 |
| Schägger H and von Jagow G | Blue native electrophoresis for isolation of membrane protein complexes in enzymatically active form. | 1991 | Anal. Biochem. | pmid:1812789 |
| Rani K et al. | Measurement of bile acid in serum and bile with arylamine-glass-bound 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and diaphorase. | 2004 | Anal. Biochem. | pmid:15301946 |
| Shaw R et al. | Bile acids LIII. Application of reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography to the analysis of conjugated bile acids in bile samples. | 1978 | Anal. Biochem. | pmid:655409 |
| Liang G et al. | Highly sensitive chiral analysis of amino acids by in-line single drop microextraction and capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. | 2010 | Anal. Chim. Acta | pmid:20850587 |
| Fimognari C et al. | Apoptosis and modulation of cell cycle control by bile acids in human leukemia T cells. | 2009 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:19723064 |
| Strauch ED et al. | NF-kappaB regulates intestinal epithelial cell and bile salt-induced migration after injury. | 2003 | Ann. Surg. | pmid:12677145 |
| Turner DJ et al. | Bile salts induce resistance to apoptosis through NF-kappaB-mediated XIAP expression. | 2007 | Ann. Surg. | pmid:17435549 |
| Mrówczynska L et al. | Inhibition of MRP1-mediated efflux in human erythrocytes by mono-anionic bile salts. | 2005 Sep-Oct | Anticancer Res. | pmid:16101123 |
| Chen S et al. | Study on improvement of extracellular production of recombinant Thermobifida fusca cutinase by Escherichia coli. | 2011 | Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. | pmid:21594592 |
| Brown AJ and Kolattukudy PE | Evidence that pancreatic lipase is responsible for the hydrolysis of cutin, a biopolyester present in mammalian diet, and the role of bile salt and colipase in this hydrolysis. | 1978 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:708069 |
| Holmes EH and Macher BA | Specificity of fucose transfer to GlcNAc residues of extended chain neolacto-series glycolipids catalyzed by human alpha 1-->3fucosyltransferases: effect of the lipidic environment on the myeloid enzyme form. | 1993 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:8442661 |
| Leclerc MC et al. | Identification, characterization, and immunolocalization of a nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase in pig liver. | 2000 | Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | pmid:10845716 |
| Shim WS et al. | Decreased secretory transport of a quarternary ammonium, TBuMA, across LLC-PK1 cells by the anionic kidney extract. | 2008 | Arch. Pharm. Res. | pmid:18481027 |
| Chae HW et al. | Effect of ion-pair formation with bile salts on the in vitro cellular transport of berberine. | 2008 | Arch. Pharm. Res. | pmid:18277615 |
| Piepoli AL et al. | Tauroursodeoxycholic acid reduces damaging effects of taurodeoxycholic acid on fundus gastric mucosa. | 2002 | Arch. Physiol. Biochem. | pmid:12221520 |
| Bernstein C et al. | Carcinogenicity of deoxycholate, a secondary bile acid. | 2011 | Arch. Toxicol. | pmid:21267546 |
| De Bernardi di Valserra M et al. | Chronic toxicity of taurohyodeoxycholic acid in rats. | 1993 | Arzneimittelforschung | pmid:8216447 |
| Feletti F et al. | Chronic toxicity of taurohyodeoxycholic acid in dogs. | 1993 | Arzneimittelforschung | pmid:8216448 |
| Feletti F et al. | Reproductive toxicity of taurohyodeoxycholic acid. | 1993 | Arzneimittelforschung | pmid:8216449 |
| Tripodi AS et al. | In vitro and in vivo mutagenicity studies on taurohyodeoxycholic acid. | 1993 | Arzneimittelforschung | pmid:8216450 |
| Li YT et al. | Occurrence of ceramide-glycanase in the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris. | 1987 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:3689409 |
| Noshiro M et al. | The involvement of cytochrome b5 in 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha, 7 alpha, 12 alpha-triol 25-hydroxylation and taurodeoxycholate 7 alpha-hydroxylation of rat liver. | 1982 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:7115387 |
| Raufman JP et al. | Muscarinic receptor agonists stimulate matrix metalloproteinase 1-dependent invasion of human colon cancer cells. | 2011 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:22027145 |
| Murakami K et al. | Partial purification and characterization of taurodeoxycholate 7 alpha-monooxygenase. | 1980 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:7396953 |
| Verkade HJ et al. | Interactions between organic anions, micelles and vesicles in model bile systems. | 1996 | Biochem. J. | pmid:9003381 |
| McIntyre JC et al. | The role of aromatic side chain residues in micelle binding by pancreatic colipase. Fluorescence studies of the porcine and equine proteins. | 1987 | Biochem. J. | pmid:3663193 |
| Yedgar S and Gatt S | Enzymic hydrolysis of sphingomyelin in the presence of bile salts. | 1980 | Biochem. J. | pmid:6248032 |
| Castro J et al. | A small component of the endoplasmic reticulum is required for store-operated Ca2+ channel activation in liver cells: evidence from studies using TRPV1 and taurodeoxycholic acid. | 2009 | Biochem. J. | pmid:19007332 |
| Gatt S et al. | Effect of bile salts on the hydrolysis of gangliosides, glycoproteins and neuraminyl-lactose by the neuraminidase of Clostridium perfringens. | 1981 | Biochem. J. | pmid:6272704 |
| Piessen G et al. | Regulation of the human mucin MUC4 by taurodeoxycholic and taurochenodeoxycholic bile acids in oesophageal cancer cells is mediated by hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha. | 2007 | Biochem. J. | pmid:17037983 |
| Campbell CH et al. | Incorporation of mannose 6-phosphate receptors into liposomes. Receptor topography and binding of alpha-mannosidase. | 1983 | Biochem. J. | pmid:6311183 |
| Fluharty AL et al. | Bile salt activation of cerebroside sulphate sulphohydrolase. | 1980 | Biochem. J. | pmid:6109529 |
| Cheng K et al. | Matrix metalloproteinase-7-catalyzed release of HB-EGF mediates deoxycholyltaurine-induced proliferation of a human colon cancer cell line. | 2007 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | pmid:17222808 |
| Leveau P et al. | Severity of pancreatitis-associated gut barrier dysfunction is reduced following treatment with the PAF inhibitor lexipafant. | 2005 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | pmid:15826603 |
| Narayanan VS and Storch J | Fatty acid transfer in taurodeoxycholate mixed micelles. | 1996 | Biochemistry | pmid:8652524 |
| Aeed PA et al. | Effect of membrane perturbants on the activity and phase distribution of inositol phosphorylceramide synthase; development of a novel assay. | 2004 | Biochemistry | pmid:15222759 |
| Donovan JM and Jackson AA | Transbilayer movement of fully ionized taurine-conjugated bile salts depends upon bile salt concentration, hydrophobicity, and membrane cholesterol content. | 1997 | Biochemistry | pmid:9298964 |
| Wieloch T et al. | High-resolution proton magnetic resonance study of porcine colipase and its interactions with taurodeoxycholate. | 1979 | Biochemistry | pmid:570855 |
| Albalak A et al. | Effects of submicellar bile salt concentrations on biological membrane permeability to low molecular weight non-ionic solutes. | 1996 | Biochemistry | pmid:8672496 |