| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dai R et al. | Inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis transaminase BioA by aryl hydrazines and hydrazides. | 2014 | Chembiochem | pmid:24482078 |
| Cobessi D et al. | Biochemical and structural characterization of the Arabidopsis bifunctional enzyme dethiobiotin synthetase-diaminopelargonic acid aminotransferase: evidence for substrate channeling in biotin synthesis. | 2012 | Plant Cell | pmid:22547782 |
| Shi C and Aldrich CC | Design and synthesis of potential mechanism-based inhibitors of the aminotransferase BioA involved in biotin biosynthesis. | 2012 | J. Org. Chem. | pmid:22724679 |
| Nijkamp JF et al. | De novo sequencing, assembly and analysis of the genome of the laboratory strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK113-7D, a model for modern industrial biotechnology. | 2012 | Microb. Cell Fact. | pmid:22448915 |
| Waller JC et al. | Mitochondrial and plastidial COG0354 proteins have folate-dependent functions in iron-sulphur cluster metabolism. | 2012 | J. Exp. Bot. | pmid:21984653 |
| Tanabe Y et al. | Peroxisomes are involved in biotin biosynthesis in Aspergillus and Arabidopsis. | 2011 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:21730067 |
| Charles H et al. | A genomic reappraisal of symbiotic function in the aphid/Buchnera symbiosis: reduced transporter sets and variable membrane organisations. | 2011 | PLoS ONE | pmid:22229056 |
| Magliano P et al. | Contributions of the peroxisome and β-oxidation cycle to biotin synthesis in fungi. | 2011 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:21998305 |
| Woong Park S et al. | Evaluating the sensitivity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to biotin deprivation using regulated gene expression. | 2011 | PLoS Pathog. | pmid:21980288 |
| Bonde BK et al. | Differential producibility analysis (DPA) of transcriptomic data with metabolic networks: deconstructing the metabolic response of M. tuberculosis. | 2011 | PLoS Comput. Biol. | pmid:21738454 |
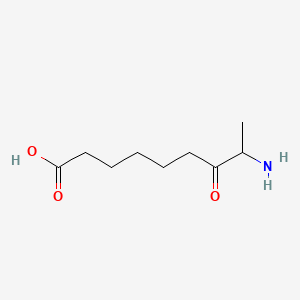
8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid
8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as seed development.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with 8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with 8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with 8-amino-7-oxononanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.