| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Reperfusion Injury | D015427 | 65 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Metabolism, Inborn Errors | D008661 | 46 associated lipids |
| Carcinoma, Hepatocellular | D006528 | 140 associated lipids |
| Liver Cirrhosis | D008103 | 67 associated lipids |
| Amino Acid Metabolism, Inborn Errors | D000592 | 16 associated lipids |
| Erectile Dysfunction | D007172 | 19 associated lipids |
| Starvation | D013217 | 47 associated lipids |
| Pregnancy Complications | D011248 | 19 associated lipids |
| Penile Induration | D010411 | 4 associated lipids |
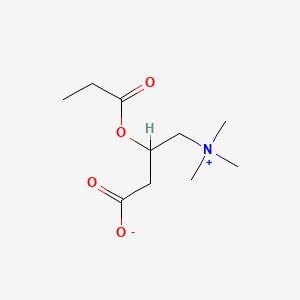
Propionylcarnitine
Propionylcarnitine is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Propionylcarnitine is associated with abnormalities such as Failure to Thrive. The involved functions are known as Functional disorder. Propionylcarnitine often locates in Body tissue.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Propionylcarnitine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Propionylcarnitine?
Propionylcarnitine is suspected in Failure to Thrive and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Propionylcarnitine
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Propionylcarnitine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Propionylcarnitine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Propionylcarnitine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Propionylcarnitine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Propionylcarnitine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with Propionylcarnitine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Propionylcarnitine
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pekkinen J et al. | Betaine supplementation causes increase in carnitine metabolites in the muscle and liver of mice fed a high-fat diet as studied by nontargeted LC-MS metabolomics approach. | 2013 | Mol Nutr Food Res | pmid:23868375 |
| Riccioni C et al. | Rehabilitative treatment in peripheral artery disease: protocol application and follow-up. | 2010 | Minerva Cardioangiol | pmid:20948502 |
| Cotter MA et al. | Effects of acetyl- and proprionyl-L-carnitine on peripheral nerve function and vascular supply in experimental diabetes. | 1995 | Metab. Clin. Exp. | pmid:7666797 |
| Brass EP and Beyerinck RA | Interactions of propionate and carnitine metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes. | 1987 | Metab. Clin. Exp. | pmid:3110541 |
| Ferrari R et al. | Metabolic modulation and optimization of energy consumption in heart failure. | 2003 | Med. Clin. North Am. | pmid:12693736 |
| Barker GA et al. | Effect of propionyl-L-carnitine on exercise performance in peripheral arterial disease. | 2001 | Med Sci Sports Exerc | pmid:11528327 |
| Odiet JA et al. | Carnitine palmitoyl transferase-I activity in the aging mouse heart. | 1995 | Mech. Ageing Dev. | pmid:7616763 |
| Hozyasz KK et al. | Whole blood propionylcarnitine in newborns with orofacial cleft. | 2011 | Matern Child Nutr | pmid:21470367 |
| Gómez-Amores L et al. | Antioxidant activity of propionyl-L-carnitine in liver and heart of spontaneously hypertensive rats. | 2006 | Life Sci. | pmid:16263137 |
| Bueno R et al. | L-carnitine and propionyl-L-carnitine improve endothelial dysfunction in spontaneously hypertensive rats: different participation of NO and COX-products. | 2005 | Life Sci. | pmid:15958269 |
| Mister M et al. | Propionyl-L-carnitine prevents renal function deterioration due to ischemia/reperfusion. | 2002 | Kidney Int. | pmid:11849462 |
| Azzollini N et al. | Propionyl-L-carnitine prevents early graft dysfunction in allogeneic rat kidney transplantation. | 2008 | Kidney Int. | pmid:19008910 |
| Signorelli SS et al. | Propionyl-L-carnitine therapy: effects on endothelin-1 and homocysteine levels in patients with peripheral arterial disease and end-stage renal disease. | 2006 | Kidney Blood Press. Res. | pmid:16809937 |
| Sarafoglou K et al. | Expanded newborn screening for detection of vitamin B12 deficiency. | 2011 | JAMA | pmid:21427371 |
| Cipolla MJ et al. | Propionyl-L-carnitine dilates human subcutaneous arteries through an endothelium-dependent mechanism. | 1999 | J. Vasc. Surg. | pmid:10359944 |
| Loffredo L et al. | Imbalance between nitric oxide generation and oxidative stress in patients with peripheral arterial disease: effect of an antioxidant treatment. | 2006 | J. Vasc. Surg. | pmid:16950429 |
| Alvarez de Sotomayor M et al. | Effect of L-carnitine and propionyl-L-carnitine on endothelial function of small mesenteric arteries from SHR. | 2007 | J. Vasc. Res. | pmid:17483601 |
| Safarinejad MR et al. | Comparison of vitamin E and propionyl-L-carnitine, separately or in combination, in patients with early chronic Peyronie's disease: a double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized study. | 2007 | J. Urol. | pmid:17706714 |
| Cunningham VJ et al. | Uptake of [N-methyl-11C]propionyl-L-carnitine (PLC) in human myocardium. | 1996 | J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. | pmid:8613961 |
| Hotta N et al. | Effect of propionyl-L-carnitine on motor nerve conduction, autonomic cardiac function, and nerve blood flow in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes: comparison with an aldose reductase inhibitor. | 1996 | J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. | pmid:8558455 |