| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Obesity, Abdominal | D056128 | 3 associated lipids |
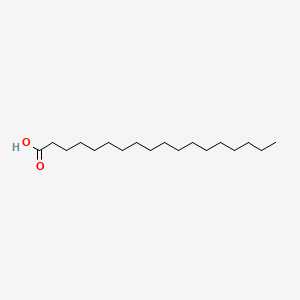
stearic acid
stearic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Stearic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Helminthiasis, Exanthema, Chronic disease, Obesity and Dyslipidemias. The involved functions are known as acyltransferase activity, Mutation, Cell division, cell fate and Fatty Acid Metabolism. Stearic acid often locates in membrane fraction, Mouse Liver, Membrane, Body tissue and Endoplasmic reticulum, membrane. The associated genes with stearic acid are Homologous Gene, ACLY gene, Transgenes, FATE1 gene and Alleles. The related lipids are Lysophospholipids, Stearic acid, Fatty Acids, cis-vaccenic acid and Phosphatidylserines. The related experimental models are Knock-out.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of stearic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with stearic acid?
stearic acid is suspected in Obesity, Diabetes, Fatty Liver, Hyperinsulinism, Cardiovascular Diseases, Infection and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with stearic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with stearic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with stearic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with stearic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with stearic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with stearic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with stearic acid?
Knock-out
Knock-out are used in the study 'Stearic acid accumulation in macrophages induces toll-like receptor 4/2-independent inflammation leading to endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis.' (Anderson EK et al., 2012) and Knock-out are used in the study 'Genome-wide association study identifies novel loci associated with concentrations of four plasma phospholipid fatty acids in the de novo lipogenesis pathway: results from the Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) consortium.' (Wu JH et al., 2013).
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Model | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with stearic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Man TY et al. | Dietary manipulation reveals an unexpected inverse relationship between fat mass and adipose 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. | 2011 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:21406612 |
| Lee WN et al. | Loss of regulation of lipogenesis in the Zucker diabetic (ZDF) rat. | 2000 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:10913044 |
| Brunengraber DZ et al. | Influence of diet on the modeling of adipose tissue triglycerides during growth. | 2003 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:12799315 |
| Hommelberg PP et al. | Fatty acid-induced NF-kappaB activation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle are chain length dependent. | 2009 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:18957619 |
| Montell E et al. | DAG accumulation from saturated fatty acids desensitizes insulin stimulation of glucose uptake in muscle cells. | 2001 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:11158925 |
| Hodson L et al. | Differences in partitioning of meal fatty acids into blood lipid fractions: a comparison of linoleate, oleate, and palmitate. | 2009 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:18940935 |
| Dasu MR and Jialal I | Free fatty acids in the presence of high glucose amplify monocyte inflammation via Toll-like receptors. | 2011 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:20959532 |
| Baldwin AC et al. | A role for aberrant protein palmitoylation in FFA-induced ER stress and β-cell death. | 2012 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:22436701 |
| O'Byrne SM et al. | Multiple pathways ensure retinoid delivery to milk: studies in genetically modified mice. | 2010 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:20040693 |
| Bézaire V et al. | Effects of fasting on muscle mitochondrial energetics and fatty acid metabolism in Ucp3(-/-) and wild-type mice. | 2001 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:11595653 |