| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classen-Houben D et al. | Selective inhibition of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 by 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid but not 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid. | 2009 | J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. | pmid:19429429 |
| Lee CS et al. | 18beta-Glycyrrhetinic acid induces apoptotic cell death in SiHa cells and exhibits a synergistic effect against antibiotic anti-cancer drug toxicity. | 2008 | Life Sci. | pmid:18721818 |
| Nishida S and Satoh H | Role of gap junction involved with endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor for the quercetin-induced vasodilatation in rat mesenteric artery. | 2013 | Life Sci. | pmid:23435092 |
| Kamioka H et al. | Primary cultures of chick osteocytes retain functional gap junctions between osteocytes and between osteocytes and osteoblasts. | 2007 | Microsc. Microanal. | pmid:17367550 |
| Li L et al. | Myoendothelial coupling is unidirectional in guinea pig spiral modiolar arteries. | 2012 | Microvasc. Res. | pmid:22580342 |
| Yu J et al. | Gap junction uncouplers attenuate arteriolar response to distal capillary stimuli. | 2000 | Microvasc. Res. | pmid:10625583 |
| Chen H et al. | Metabolism of ginger component [6]-shogaol in liver microsomes from mouse, rat, dog, monkey, and human. | 2013 | Mol Nutr Food Res | pmid:23322474 |
| Zhao K et al. | Inhibition of gap junction channel attenuates the migration of breast cancer cells. | 2012 | Mol. Biol. Rep. | pmid:21674188 |
| Trepel M et al. | A heterotypic bystander effect for tumor cell killing after adeno-associated virus/phage-mediated, vascular-targeted suicide gene transfer. | 2009 | Mol. Cancer Ther. | pmid:19671758 |
| Yang JC et al. | 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid potentiates Hsp90 inhibition-induced apoptosis in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells via activation of death receptor and mitochondrial pathway. | 2012 | Mol. Cell. Biochem. | pmid:22865487 |
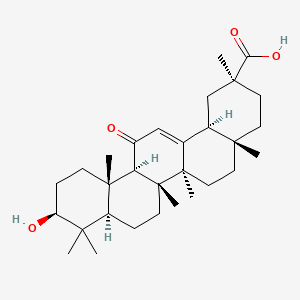
18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid
18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, salivary gland development and branching morphogenesis.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid?
18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.