| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Edema | D004487 | 152 associated lipids |
| Hypertension | D006973 | 115 associated lipids |
| Catalepsy | D002375 | 30 associated lipids |
| Hypothermia | D007035 | 19 associated lipids |
| Amnesia | D000647 | 12 associated lipids |
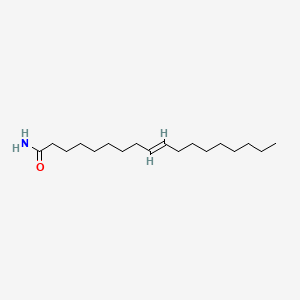
Elaidamide
Elaidamide is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Elaidamide is associated with abnormalities such as Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, salivary gland development and branching morphogenesis.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Elaidamide, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Elaidamide?
Elaidamide is suspected in and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Elaidamide
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Elaidamide
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Elaidamide?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with Elaidamide?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Elaidamide?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Elaidamide?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with Elaidamide?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Elaidamide
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nicholson RA et al. | Anesthetic-like interaction of the sleep-inducing lipid oleamide with voltage-gated sodium channels in mammalian brain. | 2001 | Anesthesiology | pmid:11135731 |
| Schiller PC et al. | Inhibition of gap-junctional communication induces the trans-differentiation of osteoblasts to an adipocytic phenotype in vitro. | 2001 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:11278824 |
| Boger DL et al. | Exceptionally potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase: the enzyme responsible for degradation of endogenous oleamide and anandamide. | 2000 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:10805767 |
| DeLuca DD and Jenkins TC | Feeding oleamide to lactating Jersey cows. 2. Effects on nutrient digestibility, plasma fatty acids, and hormones. | 2000 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:10750115 |
| Jenkins TC et al. | Site of administration and duration of feeding oleamide to cattle on feed intake and ruminal fatty acid concentrations. | 2000 | J. Anim. Sci. | pmid:11048942 |
| Quist AP et al. | Physiological role of gap-junctional hemichannels. Extracellular calcium-dependent isosmotic volume regulation. | 2000 | J. Cell Biol. | pmid:10704454 |
| Egertová M et al. | Fatty acid amide hydrolase expression in rat choroid plexus: possible role in regulation of the sleep-inducing action of oleamide. | 2000 | Neurosci. Lett. | pmid:10713385 |
| Verdon B et al. | Stereoselective modulatory actions of oleamide on GABA(A) receptors and voltage-gated Na(+) channels in vitro: a putative endogenous ligand for depressant drug sites in CNS. | 2000 | Br. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:10694234 |
| Ritenour-Rodgers KJ et al. | Induction of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase in N(18)TG(2) cells: a model for studying oleamide biosynthesis. | 2000 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:10631094 |
| Jenkins TC | Feeding oleamide to lactating Jersey cows 1. Effects on lactation performance and milk fatty acid composition. | 2000 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:10714869 |
| Schweitzer JS et al. | pH Sensitivity of non-synaptic field bursts in the dentate gyrus. | 2000 | J. Neurophysiol. | pmid:10938317 |
| Bannerman P et al. | Early migratory rat neural crest cells express functional gap junctions: evidence that neural crest cell survival requires gap junction function. | 2000 | J. Neurosci. Res. | pmid:10972957 |
| Basile AS et al. | Characterization of the hypnotic properties of oleamide. | 1999 | Neuroreport | pmid:10321465 |
| Hanus LO et al. | A gas chromatographic-mass spectral assay for the quantitative determination of oleamide in biological fluids. | 1999 | Anal. Biochem. | pmid:10328778 |
| Jenkins TC | Lactation performance and fatty acid composition of milk from Holstein cows fed 0 to 5% oleamide. | 1999 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:10416167 |
| Boger DL et al. | Trifluoromethyl ketone inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase: a probe of structural and conformational features contributing to inhibition. | 1999 | Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. | pmid:10021942 |
| Yang JY et al. | Studies on the sedative and hypnotic effects of oleamide in mice. | 1999 | Arzneimittelforschung | pmid:10483511 |
| Thomas EA et al. | The endogenous lipid oleamide activates serotonin 5-HT7 neurons in mouse thalamus and hypothalamus. | 1999 | J. Neurochem. | pmid:10349846 |
| Mendelson WB and Basile AS | The hypnotic actions of oleamide are blocked by a cannabinoid receptor antagonist. | 1999 | Neuroreport | pmid:10574567 |
| Gobbi M et al. | Oleamide-mediated sleep induction does not depend on perturbation of membrane homeoviscosity. | 1999 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:10606738 |
| Hedlund PB et al. | Allosteric regulation by oleamide of the binding properties of 5-hydroxytryptamine7 receptors. | 1999 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | pmid:10571256 |
| Cheer JF et al. | Modification of 5-HT2 receptor mediated behaviour in the rat by oleamide and the role of cannabinoid receptors. | 1999 | Neuropharmacology | pmid:10221757 |
| Jenkins TC | Fatty acid composition of milk from Holstein cows fed oleamide or canola oil. | 1998 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:9565883 |
| Boger DL et al. | Structural requirements for 5-HT2A and 5-HT1A serotonin receptor potentiation by the biologically active lipid oleamide. | 1998 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:9539697 |
| Boger DL et al. | Chemical requirements for inhibition of gap junction communication by the biologically active lipid oleamide. | 1998 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:9560184 |
| Huang GY et al. | Gap junction-mediated cell-cell communication modulates mouse neural crest migration. | 1998 | J. Cell Biol. | pmid:9852163 |
| Bisogno T et al. | Biosynthesis and degradation of bioactive fatty acid amides in human breast cancer and rat pheochromocytoma cells--implications for cell proliferation and differentiation. | 1998 | Eur. J. Biochem. | pmid:9688276 |
| Lees G et al. | Modulation of GABA(A) receptors and inhibitory synaptic currents by the endogenous CNS sleep regulator cis-9,10-octadecenoamide (cOA). | 1998 | Br. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:9692771 |
| Yost CS et al. | Oleamide potentiates benzodiazepine-sensitive gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor activity but does not alter minimum alveolar anesthetic concentration. | 1998 | Anesth. Analg. | pmid:9620523 |
| Thomas EA et al. | Oleamide-induced modulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor-mediated signaling. | 1998 | Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. | pmid:9928256 |
| Thomas EA et al. | Fatty acid amide hydrolase, the degradative enzyme for anandamide and oleamide, has selective distribution in neurons within the rat central nervous system. | 1997 | J. Neurosci. Res. | pmid:9452020 |
| Bisogno T et al. | The sleep inducing factor oleamide is produced by mouse neuroblastoma cells. | 1997 | Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. | pmid:9344854 |
| Lerner RA | A hypothesis about the endogenous analogue of general anesthesia. | 1997 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:9391028 |
| Thomas EA et al. | Unique allosteric regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor-mediated signal transduction by oleamide. | 1997 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:9391162 |
| Mechoulam R et al. | Anandamide may mediate sleep induction. | 1997 | Nature | pmid:9288961 |
| Guan X et al. | The sleep-inducing lipid oleamide deconvolutes gap junction communication and calcium wave transmission in glial cells. | 1997 | J. Cell Biol. | pmid:9412472 |
| Langstein J et al. | cis-9,10-octadecenoamide, an endogenous sleep-inducing CNS compound, inhibits lymphocyte proliferation. | 1996 Jul-Aug | Res. Immunol. | pmid:8903105 |
| Huidobro-Toro JP and Harris RA | Brain lipids that induce sleep are novel modulators of 5-hydroxytrypamine receptors. | 1996 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | pmid:8755606 |
| Cravatt BF et al. | Chemical characterization of a family of brain lipids that induce sleep. | 1995 | Science | pmid:7770779 |
| Osmundsen PE | Contact urticaria from nickel and plastic additives (butylhydroxytoluene, oleylamide). | 1980 | Contact Derm. | pmid:7214887 |
| pmid: | ||||
| pmid:28340410 | ||||
| pmid:27595606 | ||||
| pmid:27152459 | ||||
| pmid:27087645 | ||||
| pmid:27049283 | ||||
| pmid:26711911 | ||||
| pmid:26547872 | ||||
| pmid:26408695 | ||||
| pmid:25660201 | ||||
| pmid:25652184 | ||||
| pmid:25641667 | ||||
| pmid:25171777 |