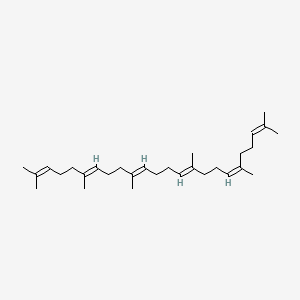
(e,e,e,e)-squalene
(e,e,e,e)-squalene is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. (e,e,e,e)-squalene is associated with abnormalities such as Hypercholesterolemia and Cataract. The involved functions are known as Process, metaplastic cell transformation, Protein Overexpression, Anabolism and Biosynthetic Pathways. (e,e,e,e)-squalene often locates in Membrane, Protoplasm, Plasma membrane, Tissue membrane and Back. The associated genes with (e,e,e,e)-squalene are Genome, IMPACT gene, GAPDH gene, GTF2I gene and Chromatin. The related lipids are Membrane Lipids, cycloartenol, Sterols, Fatty Acids and Nonesterified Fatty Acids.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of (e,e,e,e)-squalene, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with (e,e,e,e)-squalene?
(e,e,e,e)-squalene is suspected in Hypercholesterolemia, Cataract and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with (e,e,e,e)-squalene
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with (e,e,e,e)-squalene
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with (e,e,e,e)-squalene?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with (e,e,e,e)-squalene?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with (e,e,e,e)-squalene?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with (e,e,e,e)-squalene?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with (e,e,e,e)-squalene?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with (e,e,e,e)-squalene
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim ES et al. | Squalene-induced exogenous lipoid pneumonia in an infant. | 2009 | Pediatr Int | pmid:19799746 |
| Lee KH et al. | Squalene aspiration pneumonia in children: radiographic and CT findings as the first clue to diagnosis. | 2005 | Pediatr Radiol | pmid:15806404 |
| Gavaldà J et al. | Immunogenicity of pandemic influenza A H1N1/2009 adjuvanted vaccine in pediatric solid organ transplant recipients. | 2013 | Pediatr Transplant | pmid:23692602 |
| Vesikari T et al. | Enhanced immunogenicity of seasonal influenza vaccines in young children using MF59 adjuvant. | 2009 | Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. | pmid:19561422 |
| Huber VC and McCullers JA | Vaccines against pandemic influenza: what can be done before the next pandemic? | 2008 | Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. | pmid:18820570 |
| Langley JM et al. | Randomized, multicenter trial of a single dose of AS03-adjuvanted or unadjuvanted H1N1 2009 pandemic influenza vaccine in children 6 months to <9 years of age: safety and immunogenicity. | 2012 | Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. | pmid:22801094 |
| Block SL et al. | Dose-range study of MF59-adjuvanted versus nonadjuvanted monovalent A/H1N1 pandemic influenza vaccine in six- to less than thirty-six-month-old children. | 2012 | Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. | pmid:22481427 |
| Mitchell DK et al. | Immunogenicity of a recombinant human cytomegalovirus gB vaccine in seronegative toddlers. | 2002 | Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. | pmid:11840080 |
| Nassim C et al. | Identification of antigen and adjuvant doses resulting in optimal immunogenicity and antibody persistence up to 1 year after immunization with a pandemic A/H1N1 influenza vaccine in children 3 to < 9 years of age. | 2012 | Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. | pmid:22418661 |
| Ketomäki A et al. | Squalene and noncholesterol sterols in serum and lipoproteins of children with and without familial hypercholesterolemia. | 2003 | Pediatr. Res. | pmid:12612218 |
| Vesikari T et al. | Immunogenicity and safety of MF59-adjuvanted H5N1 influenza vaccine from infancy to adolescence. | 2010 | Pediatrics | pmid:20819892 |
| Esposito S et al. | Influenza A/H1N1 MF59-adjuvanted vaccine in preterm and term children aged 6 to 23 months. | 2011 | Pediatrics | pmid:21464195 |
| Adrangui M et al. | [Water-surfactant-oil diagrams based on perhydrosqualene and triglycerides (Miglyol 812). Study of emulsion phases and stability]. | 1979 | Pharm Acta Helv | pmid:515109 |
| Ott G et al. | MF59. Design and evaluation of a safe and potent adjuvant for human vaccines. | 1995 | Pharm Biotechnol | pmid:7551221 |
| Fox CB et al. | Effects of emulsifier concentration, composition, and order of addition in squalene-phosphatidylcholine oil-in-water emulsions. | 2011 | Pharm Dev Technol | pmid:20550484 |
| Baudner BC et al. | MF59 emulsion is an effective delivery system for a synthetic TLR4 agonist (E6020). | 2009 | Pharm. Res. | pmid:19255727 |
| Lin YK et al. | Squalene-containing nanostructured lipid carriers promote percutaneous absorption and hair follicle targeting of diphencyprone for treating alopecia areata. | 2013 | Pharm. Res. | pmid:23070602 |
| Morin RJ and Srikantaiah MV | Inhibition of rat liver sterol formation by isoprenoid and conjugated ene compounds. | 1982 | Pharmacol Res Commun | pmid:7156175 |
| Sabeena Farvin KH et al. | Effect of squalene on tissue defense system in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. | 2004 | Pharmacol. Res. | pmid:15225664 |
| Dennis KJ and Shibamoto T | Production of malonaldehyde from squalene, a major skin surface lipid, during UV-irradiation. | 1989 | Photochem. Photobiol. | pmid:2756005 |
| Matsuo I et al. | Possible involvement of oxidation of lipids in inducing griseofulvin photosensitivity. | 1990 | Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed | pmid:2091745 |
| Picardo M et al. | Squalene peroxides may contribute to ultraviolet light-induced immunological effects. | 1991 | Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed | pmid:1804289 |
| Kawada A et al. | In vitro phototoxicity of new quinolones: production of active oxygen species and photosensitized lipid peroxidation. | 1999 | Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed | pmid:10599972 |
| Fujita H and Matsuo I | In vitro phototoxic activities of new quinolone antibacterial agents: lipid peroxidative potentials. | 1994 | Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed | pmid:7880759 |
| Fujita H and Matsuo I | Type I lipid photo-oxidation by the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug suprofen: a possible key to its photosensitivity. | 1992-1993 Oct | Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed | pmid:1342189 |
| Wilson KR et al. | The statistical evolution of multiple generations of oxidation products in the photochemical aging of chemically reduced organic aerosol. | 2012 | Phys Chem Chem Phys | pmid:22158973 |
| King KL et al. | Inelastic scattering of OH radicals from organic liquids: isolating the thermal desorption channel. | 2013 | Phys Chem Chem Phys | pmid:23807737 |
| Packwood DM and Phillips LF | A stochastic, local mode study of neon-liquid surface collision dynamics. | 2011 | Phys Chem Chem Phys | pmid:21042647 |
| Binks BP et al. | How membrane permeation is affected by donor delivery solvent. | 2012 | Phys Chem Chem Phys | pmid:23073464 |
| Liu CL et al. | The direct observation of secondary radical chain chemistry in the heterogeneous reaction of chlorine atoms with submicron squalane droplets. | 2011 | Phys Chem Chem Phys | pmid:21455529 |
| Achitouv E et al. | C31-C34 methylated squalenes from a Bolivian strain of Botryococcus braunii. | 2004 | Phytochemistry | pmid:15541746 |
| Fernández-MartÃn R et al. | ent-Kaurene and squalene synthesis in Fusarium fujikuroi cell-free extracts. | 2000 | Phytochemistry | pmid:10975508 |
| Metzger P et al. | Braunicetals: acetals from condensation of macrocyclic aldehydes and terpene diols in Botryococcus braunii. | 2008 | Phytochemistry | pmid:18639308 |
| Xu R et al. | On the origins of triterpenoid skeletal diversity. | 2004 | Phytochemistry | pmid:14751299 |
| Metzger P et al. | Botryolins A and B, two tetramethylsqualene triethers from the green microalga Botryococcus braunii. | 2002 | Phytochemistry | pmid:11937163 |
| Quang DN et al. | Concentriols B, C and D, three squalene-type triterpenoids from the ascomycete Daldinia concentrica. | 2002 | Phytochemistry | pmid:12359521 |
| Catalán CA et al. | A linear sesterterpene, two squalene derivatives and two peptide derivatives from Croton hieronymi. | 2003 | Phytochemistry | pmid:12943786 |
| Flores-Sánchez IJ et al. | Biosynthesis of sterols and triterpenes in cell suspension cultures of Uncaria tomentosa. | 2002 | Plant Cell Physiol. | pmid:12514247 |
| Suzuki M et al. | Lanosterol synthase in dicotyledonous plants. | 2006 | Plant Cell Physiol. | pmid:16531458 |
| Caligiani A et al. | Characterization of a potential nutraceutical ingredient: pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) seed oil unsaponifiable fraction. | 2010 | Plant Foods Hum Nutr | pmid:20607413 |
| Ryan E et al. | Phytosterol, squalene, tocopherol content and fatty acid profile of selected seeds, grains, and legumes. | 2007 | Plant Foods Hum Nutr | pmid:17594521 |
| Suzuki M et al. | Loss of function of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase 1 (HMG1) in Arabidopsis leads to dwarfing, early senescence and male sterility, and reduced sterol levels. | 2004 | Plant J. | pmid:14871314 |
| Wentzinger LF et al. | Inhibition of squalene synthase and squalene epoxidase in tobacco cells triggers an up-regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase. | 2002 | Plant Physiol. | pmid:12226513 |
| Nguyen HT et al. | Molecular characterization of Glycine max squalene synthase genes in seed phytosterol biosynthesis. | 2013 | Plant Physiol. Biochem. | pmid:24036394 |
| Uchida H et al. | Cloning and characterization of a squalene synthase gene from a petroleum plant, Euphorbia tirucalli L. | 2009 | Planta | pmid:19283408 |
| Wu S et al. | Engineering triterpene metabolism in tobacco. | 2012 | Planta | pmid:22729821 |
| Goff PH et al. | Adjuvants and immunization strategies to induce influenza virus hemagglutinin stalk antibodies. | 2013 | PLoS ONE | pmid:24223176 |
| Oliaro-Bosso S et al. | Characterization of the channel constriction allowing the access of the substrate to the active site of yeast oxidosqualene cyclase. | 2011 | PLoS ONE | pmid:21811565 |
| Puleston R et al. | Multi-centre observational study of transplacental transmission of influenza antibodies following vaccination with AS03(A)-adjuvanted H1N1 2009 vaccine. | 2013 | PLoS ONE | pmid:23372640 |
| Takami T et al. | A genetic and pharmacological analysis of isoprenoid pathway by LC-MS/MS in fission yeast. | 2012 | PLoS ONE | pmid:23145048 |