| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 | D003924 | 87 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Hypercholesterolemia | D006937 | 91 associated lipids |
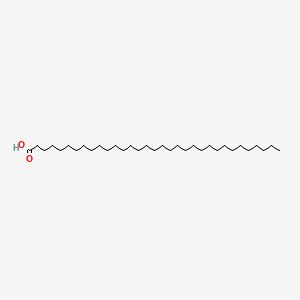
tritriacontanoic acid
tritriacontanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Tritriacontanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as hypercholesterolemia, Metabolic syndrome, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin-Dependent and Parkinson Disease. The involved functions are known as Fermentation, Process, Longterm Effects, Pressure- physical agent and Lipid Metabolism. Tritriacontanoic acid often locates in Blood, Tissue fiber and A Fibers. The associated genes with tritriacontanoic acid are STN gene. The related lipids are Total cholesterol and blood lipid.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of tritriacontanoic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with tritriacontanoic acid?
tritriacontanoic acid is suspected in hypercholesterolemia, Metabolic syndrome, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin-Dependent, Parkinson Disease and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with tritriacontanoic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with tritriacontanoic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with tritriacontanoic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with tritriacontanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with tritriacontanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with tritriacontanoic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with tritriacontanoic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with tritriacontanoic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pare P | The approach to diagnosis and treatment of chronic constipation: suggestions for a general practitioner. | 2011 | Can. J. Gastroenterol. | pmid:22114756 |
| Siahi-Shadbad MR et al. | Release behaviour of propranolol HCl from hydrophilic matrix tablets containing psyllium powder in combination with hydrophilic polymers. | 2011 | AAPS PharmSciTech | pmid:21918920 |
| Halmos EP and Gibson PR | Dried plums, constipation and the irritable bowel syndrome. | 2011 | Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. | pmid:21726250 |
| van der Hagen SJ et al. | Conservative treatment of patients with faecal soiling. | 2011 | Tech Coloproctol | pmid:21720889 |
| McRorie JW | Prunes vs. psyllium for chronic idiopathic constipation. | 2011 | Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. | pmid:21679210 |
| Maurya DP et al. | Formulation and optimization of alkaline extracted ispaghula husk microparticles of isoniazid - in vitro and in vivo assessment. | 2011 | J Microencapsul | pmid:21561399 |
| Al-Hamadani YA et al. | Application of psyllium husk as coagulant and coagulant aid in semi-aerobic landfill leachate treatment. | 2011 | J. Hazard. Mater. | pmid:21507572 |
| Chouinard LE | The role of psyllium fibre supplementation in treating irritable bowel syndrome. | 2011 | Can J Diet Pract Res | pmid:21382232 |
| Mehmood MH et al. | Pharmacological basis for the medicinal use of psyllium husk (Ispaghula) in constipation and diarrhea. | 2011 | Dig. Dis. Sci. | pmid:21082352 |
| Pal S et al. | The effect of a fibre supplement compared to a healthy diet on body composition, lipids, glucose, insulin and other metabolic syndrome risk factors in overweight and obese individuals. | 2011 | Br. J. Nutr. | pmid:20727237 |
| Asnaashari S et al. | Preparation and evaluation of novel metronidazole sustained release and floating matrix tablets. | 2011 | Pharm Dev Technol | pmid:20429828 |
| Ahi S et al. | A bulking agent may lead to adrenal insufficiency crisis: a case report. | 2011 | Acta Med Iran | pmid:22071646 |
| Karhunen LJ et al. | A psyllium fiber-enriched meal strongly attenuates postprandial gastrointestinal peptide release in healthy young adults. | 2010 | J. Nutr. | pmid:20147463 |
| Saeedi M et al. | Evaluation of binding properties of Plantago psyllium seed mucilage. | 2010 | Acta Pharm | pmid:21134867 |
| Bajorek SA and Morello CM | Effects of dietary fiber and low glycemic index diet on glucose control in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. | 2010 | Ann Pharmacother | pmid:20959501 |
| Cannon SJ et al. | Inclusion of psyllium in milk replacer for neonatal calves. 1. Effects on growth, digesta viscosity, rate of passage, nutrient digestibilities, and metabolites in blood. | 2010 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:20655435 |
| Cabré E | Irritable bowel syndrome: can nutrient manipulation help? | 2010 | Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care | pmid:20531176 |
| Timm DA et al. | Wheat dextrin, psyllium, and inulin produce distinct fermentation patterns, gas volumes, and short-chain fatty acid profiles in vitro. | 2010 | J Med Food | pmid:20482283 |
| Giacosa A and Rondanelli M | The right fiber for the right disease: an update on the psyllium seed husk and the metabolic syndrome. | 2010 | J. Clin. Gastroenterol. | pmid:20616745 |
| Cannon SJ et al. | Inclusion of psyllium in milk replacer for neonatal calves. 2. Effects on volatile fatty acid concentrations, microbial populations, and gastrointestinal tract size. | 2010 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:20855009 |