| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Coronary Syndrome | D054058 | 11 associated lipids |
| Renal Insufficiency, Chronic | D051436 | 9 associated lipids |
| Atherosclerosis | D050197 | 85 associated lipids |
| Genetic Diseases, X-Linked | D040181 | 2 associated lipids |
| Metabolic Syndrome | D024821 | 44 associated lipids |
| Coronary Restenosis | D023903 | 10 associated lipids |
| Genetic Predisposition to Disease | D020022 | 24 associated lipids |
| Circoviridae Infections | D018173 | 2 associated lipids |
| Glucose Intolerance | D018149 | 13 associated lipids |
| Community-Acquired Infections | D017714 | 8 associated lipids |
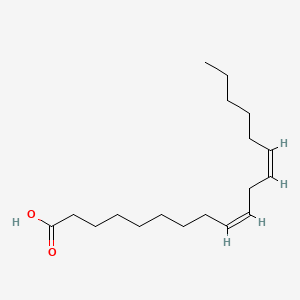
Linoleic acid
Linoleic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Linoleic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Metabolic syndrome, Obesity, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease and Pneumonia. The involved functions are known as Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, Synthesis, Pathological accumulation of air in tissues and cytokine biosynthesis. The associated genes with Linoleic acid are TNF gene, CCL2 gene and TLR4 gene. The related lipids are palmitoleic acid, nervonic acid and Sphingolipids.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Linoleic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Linoleic acid?
Linoleic acid is suspected in Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Metabolic syndrome, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease, Pneumonia and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Linoleic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Linoleic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Linoleic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with Linoleic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Linoleic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Linoleic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Linoleic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Linoleic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu HC et al. | Transcriptome changes in Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. roots induced by methyl jasmonate. | 2015 | J Zhejiang Univ Sci B | pmid:26642186 |
| Grevengoed TJ et al. | Acyl-CoA synthetase 1 deficiency alters cardiolipin species and impairs mitochondrial function. | 2015 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:26136511 |
| Salazar MO et al. | A thin-layer chromatography autographic method for the detection of inhibitors of the Salmonella PhoP-PhoQ regulatory system. | 2014 Mar-Apr | Phytochem Anal | pmid:24185747 |
| Jacob RH et al. | Phenotypic characterisation of colour stability of lamb meat. | 2014 | Meat Sci. | pmid:23415827 |
| Petzinger C et al. | Lipid metabolic dose response to dietary alpha-linolenic acid in monk parrot (Myiopsitta monachus). | 2014 | Lipids | pmid:24293226 |
| Purushothaman D et al. | Flaxseed oil supplementation alters the expression of inflammatory-related genes in dogs. | 2014 | Genet. Mol. Res. | pmid:25078588 |
| van Schalkwijk DB et al. | Dietary medium chain fatty acid supplementation leads to reduced VLDL lipolysis and uptake rates in comparison to linoleic acid supplementation. | 2014 | PLoS ONE | pmid:25049048 |
| Beavers WN et al. | ω-Alkynyl lipid surrogates for polyunsaturated fatty acids: free radical and enzymatic oxidations. | 2014 | J. Am. Chem. Soc. | pmid:25034362 |
| Shimamoto C et al. | Functional characterization of FABP3, 5 and 7 gene variants identified in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder and mouse behavioral studies. | 2014 | Hum. Mol. Genet. | pmid:25027319 |
| Hellstrand S et al. | Genetic variation in FADS1 has little effect on the association between dietary PUFA intake and cardiovascular disease. | 2014 | J. Nutr. | pmid:25008580 |
| Morris JB et al. | Flavonol content, oil%, and fatty acid composition variability in seeds of Teramnus labialis and T. uncinatus accessions with nutraceutical potential. | 2014 | J Diet Suppl | pmid:25054688 |
| Asselin C et al. | Circulating levels of linoleic acid and HDL-cholesterol are major determinants of 4-hydroxynonenal protein adducts in patients with heart failure. | 2014 | Redox Biol | pmid:24494189 |
| Sarath Josh MK et al. | Phthalates efficiently bind to human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor and retinoid X receptor α, β, γ subtypes: an in silico approach. | 2014 | J Appl Toxicol | pmid:23843199 |
| Choque B et al. | Linoleic acid: between doubts and certainties. | 2014 | Biochimie | pmid:23900039 |
| Shimizu N et al. | De novo biosynthesis of linoleic acid and its conversion to the hydrocarbon (Z,Z)-6,9-heptadecadiene in the astigmatid mite, Carpoglyphus lactis: incorporation experiments with 13C-labeled glucose. | 2014 | Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. | pmid:24333472 |
| Chevrot M et al. | Obesity interferes with the orosensory detection of long-chain fatty acids in humans. | 2014 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:24522446 |
| Cho Y et al. | Colon cancer cell apoptosis is induced by combined exposure to the n-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid and butyrate through promoter methylation. | 2014 | Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) | pmid:24495951 |
| Shen J et al. | A 13-lipoxygenase, TomloxC, is essential for synthesis of C5 flavour volatiles in tomato. | 2014 | J. Exp. Bot. | pmid:24453226 |
| Canetti L et al. | Linoleic and alpha linolenic acids ameliorate streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice. | 2014 | Arch. Physiol. Biochem. | pmid:24320056 |
| Paulsen SJ et al. | Expression of the fatty acid receptor GPR120 in the gut of diet-induced-obese rats and its role in GLP-1 secretion. | 2014 | PLoS ONE | pmid:24520357 |