| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Hemolysis | D006461 | 131 associated lipids |
| Tuberculosis | D014376 | 20 associated lipids |
| Diabetes Mellitus | D003920 | 90 associated lipids |
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Otitis Externa | D010032 | 8 associated lipids |
| Pain | D010146 | 64 associated lipids |
| Lung Neoplasms | D008175 | 171 associated lipids |
| Inflammation | D007249 | 119 associated lipids |
| Colitis | D003092 | 69 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
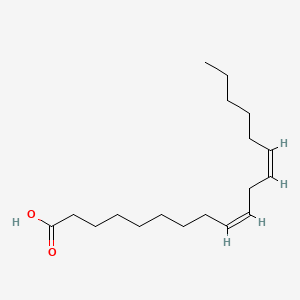
Linoleic acid
Linoleic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Linoleic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Metabolic syndrome, Obesity, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease and Pneumonia. The involved functions are known as Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, Synthesis, Pathological accumulation of air in tissues and cytokine biosynthesis. The associated genes with Linoleic acid are TNF gene, CCL2 gene and TLR4 gene. The related lipids are palmitoleic acid, nervonic acid and Sphingolipids.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Linoleic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Linoleic acid?
Linoleic acid is suspected in Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Metabolic syndrome, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease, Pneumonia and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Linoleic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Linoleic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Linoleic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with Linoleic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Linoleic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Linoleic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Linoleic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Linoleic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spaide RF et al. | Characterization of peroxidized lipids in Bruch's membrane. | 1999 | Retina (Philadelphia, Pa.) | pmid:10213241 |
| Minich DM et al. | Bile diversion in rats leads to a decreased plasma concentration of linoleic acid which is not due to decreased net intestinal absorption of dietary linoleic acid. | 1999 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:10216285 |
| Cortez-Pinto H et al. | Lipids up-regulate uncoupling protein 2 expression in rat hepatocytes. | 1999 | Gastroenterology | pmid:10220511 |
| Banni S et al. | An increase in vitamin A status by the feeding of conjugated linoleic acid. | 1999 | Nutr Cancer | pmid:10227044 |
| Szitanyi P et al. | Metabolism of 13C-labeled linoleic acid in newborn infants during the first week of life. | 1999 | Pediatr. Res. | pmid:10231862 |
| Iuliano L et al. | Protection of low density lipoprotein oxidation by the antioxidant agent IRFI005, a new synthetic hydrophilic vitamin E analogue. | 1999 | Free Radic. Biol. Med. | pmid:10232829 |
| Burke PA et al. | Conditionally essential fatty acid deficiencies in end-stage liver disease. | 1999 | Nutrition | pmid:10319364 |
| Geetha T and Varalakshmi P | Anticomplement activity of triterpenes from Crataeva nurvala stem bark in adjuvant arthritis in rats. | 1999 | Gen. Pharmacol. | pmid:10323491 |
| Haggarty P et al. | Effect of maternal polyunsaturated fatty acid concentration on transport by the human placenta. | 1999 | Biol. Neonate | pmid:10325438 |
| Wei T et al. | Antioxidant properties of EPC-K1: a study on mechanisms. | 1999 | Biophys. Chem. | pmid:10326248 |