| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Refeeding Syndrome | D055677 | 1 associated lipids |
| Acute Coronary Syndrome | D054058 | 11 associated lipids |
| Mucositis | D052016 | 7 associated lipids |
| Renal Insufficiency, Chronic | D051436 | 9 associated lipids |
| Atherosclerosis | D050197 | 85 associated lipids |
| Micronuclei, Chromosome-Defective | D048629 | 33 associated lipids |
| Genetic Diseases, X-Linked | D040181 | 2 associated lipids |
| Pulmonary Disease, Chronic Obstructive | D029424 | 16 associated lipids |
| Metabolic Syndrome | D024821 | 44 associated lipids |
| Coronary Restenosis | D023903 | 10 associated lipids |
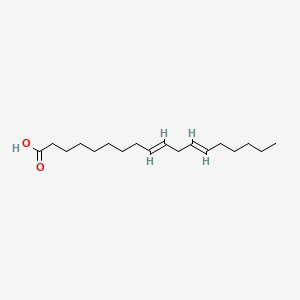
Linoelaidic acid
Linoelaidic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Linoelaidic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease and Metabolic syndrome. The involved functions are known as Metabolic Inhibition, Steroid biosynthesis, Signal Transduction, Insulin Resistance and Inflammation. Linoelaidic acid often locates in Mitochondria, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Linoelaidic acid are FFAR1 gene, C9orf7 gene, TNF gene, CCL2 gene and TLR4 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, octadecadienoic acid, Steroids, methyl linoleate and Cyanoketone.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Linoelaidic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Linoelaidic acid is suspected in Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease, Metabolic syndrome and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Linoelaidic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Linoelaidic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- J. Lipid Res. (1)
- Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids (1)
- Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. (1)
- Others (3)
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (1)
- Plant Cell (1)
- Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids (1)
- Others (1)
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Linoelaidic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHRISTAKIS GJ et al. | EFFECT OF A SERUM CHOLESTEROL-LOWERING DIET ON COMPOSITION OF DEPOT FAT IN MAN. | 1965 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:14253897 |
| ZUKEL MC | FAT-CONTROLLED DIETS. | 1965 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:14253901 |
| Brynes AE et al. | Diet-induced change in fatty acid composition of plasma triacylglycerols is not associated with change in glucagon-like peptide 1 or insulin sensitivity in people with type 2 diabetes. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:11063437 |
| Higdon JV et al. | Supplementation of postmenopausal women with fish oil rich in eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid is not associated with greater in vivo lipid peroxidation compared with oils rich in oleate and linoleate as assessed by plasma malondialdehyde and F(2)-isoprostanes. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10966889 |
| Tokede OA et al. | Plasma phospholipid trans fatty acids and risk of heart failure. | 2013 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:23446892 |
| Hennig B et al. | Linoleic acid activates nuclear transcription factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) and induces NF-kappa B-dependent transcription in cultured endothelial cells. | 1996 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:8602587 |
| Kark JD et al. | Adipose tissue n-6 fatty acids and acute myocardial infarction in a population consuming a diet high in polyunsaturated fatty acids. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12663274 |
| Djoussé L et al. | Dietary linolenic acid and carotid atherosclerosis: the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Family Heart Study. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12663278 |
| KRAUSE RF | LIVER LIPIDS IN A CASE OF HYPERVITAMINOSIS A. | 1965 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:14301352 |
| Hennig B and Watkins BA | Linoleic acid and linolenic acid: effect on permeability properties of cultured endothelial cell monolayers. | 1989 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:2563626 |
| Mantzioris E et al. | Differences exist in the relationships between dietary linoleic and alpha-linolenic acids and their respective long-chain metabolites. | 1995 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:7840069 |
| Siguel E | Does linoleic acid contribute to coronary artery disease? | 1995 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:7840081 |
| Innis SM and Elias SL | Intakes of essential n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids among pregnant Canadian women. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12540410 |
| Vos E and Cunnane SC | Alpha-linolenic acid, linoleic acid, coronary artery disease, and overall mortality. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12540417 |
| O'Connell ED et al. | Diet and risk factors for age-related maculopathy. | 2008 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:18326611 |
| Hayes KC | The linoleic acid content of test diets must be carefully monitored in cholesterol studies. | 1997 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:9094899 |
| Decsi T et al. | Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in children with severe protein-energy malnutrition with and without human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection. | 1995 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:7491893 |
| Hrboticky N et al. | Retina fatty acid composition of piglets fed from birth with a linoleic acid-rich vegetable-oil formula for infants. | 1991 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:1989416 |
| Carnielli VP et al. | Medium-chain triacylglycerols in formulas for preterm infants: effect on plasma lipids, circulating concentrations of medium-chain fatty acids, and essential fatty acids. | 1996 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:8694014 |
| Rudel LL et al. | Dietary polyunsaturated fat modifies low-density lipoproteins and reduces atherosclerosis of nonhuman primates with high and low diet responsiveness. | 1995 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:7625361 |
| Herbel BK et al. | Safflower oil consumption does not increase plasma conjugated linoleic acid concentrations in humans. | 1998 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:9459383 |
| Kinsella JE et al. | Metabolism of trans fatty acids with emphasis on the effects of trans, trans-octadecadienoate on lipid composition, essential fatty acid, and prostaglandins: an overview. | 1981 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:6794350 |
| Gibson RA and Makrides M | n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid requirements of term infants. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617980 |
| Crawford M | Placental delivery of arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acids: implications for the lipid nutrition of preterm infants. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617983 |
| Dutta-Roy AK | Transport mechanisms for long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the human placenta. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617989 |
| Blair IA et al. | Dietary modification of omega 6 fatty acid intake and its effect on urinary eicosanoid excretion. | 1993 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:8424383 |
| Ziboh VA et al. | Metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids by skin epidermal enzymes: generation of antiinflammatory and antiproliferative metabolites. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617998 |
| Horrobin DF | Essential fatty acid metabolism and its modification in atopic eczema. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617999 |
| SINGLETON WS | CHARACTERIZED OILS FOR USE IN INTRAVENOUS FAT EMULSIONS. | 1965 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:14262113 |
| James MJ et al. | Simple relationships exist between dietary linoleate and the n-6 fatty acids of human neutrophils and plasma. | 1993 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:8379505 |
| Reaven P et al. | Feasibility of using an oleate-rich diet to reduce the susceptibility of low-density lipoprotein to oxidative modification in humans. | 1991 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:1897476 |
| Iacono JM and Dougherty RM | Lack of effect of linoleic acid on the high-density-lipoprotein-cholesterol fraction of plasma lipoproteins. | 1991 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:1900384 |
| Jones PJ et al. | Whole body oxidation of dietary fatty acids: implications for energy utilization. | 1985 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:3933323 |
| Thijssen MA and Mensink RP | Small differences in the effects of stearic acid, oleic acid, and linoleic acid on the serum lipoprotein profile of humans. | 2005 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:16155261 |
| Warensjö E et al. | Factor analysis of fatty acids in serum lipids as a measure of dietary fat quality in relation to the metabolic syndrome in men. | 2006 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:16895896 |
| Blasbalg TL et al. | Changes in consumption of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the United States during the 20th century. | 2011 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:21367944 |
| Terpstra AH | Effect of conjugated linoleic acid on body composition and plasma lipids in humans: an overview of the literature. | 2004 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:14985207 |
| Feunekes GI et al. | Relative and biomarker-based validity of a food-frequency questionnaire estimating intake of fats and cholesterol. | 1993 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:8379504 |
| Cunnane SC | Diodoquin and linoleic acid absorption in zinc deficiency. | 1981 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:6792900 |
| Salem N and Kuratko CN | Lack of evidence for increased α-linolenic acid metabolism in vegetarians. | 2011 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:21430120 |
| Goyens PL et al. | Conversion of alpha-linolenic acid in humans is influenced by the absolute amounts of alpha-linolenic acid and linoleic acid in the diet and not by their ratio. | 2006 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:16825680 |
| Venäläinen TM et al. | Effect of a 2-y dietary and physical activity intervention on plasma fatty acid composition and estimated desaturase and elongase activities in children: the Physical Activity and Nutrition in Children Study. | 2016 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:27581473 |
| McMurchie EJ et al. | Dietary-induced changes in the fatty acid composition of human cheek cell phospholipids: correlation with changes in the dietary polyunsaturated/saturated fat ratio. | 1984 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:6720626 |
| Almario RU et al. | Effects of walnut consumption on plasma fatty acids and lipoproteins in combined hyperlipidemia. | 2001 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:11451720 |
| Seidelin KN et al. | Percentage distribution of fatty acids in subcutaneous adipose tissue of patients with peptic ulcer disease. | 1993 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:8416668 |
| Larbi A et al. | Acute in vivo elevation of intravascular triacylglycerol lipolysis impairs peripheral T cell activation in humans. | 2005 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:16280424 |
| Horrobin DF | Fatty acid metabolism in health and disease: the role of delta-6-desaturase. | 1993 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:8386433 |
| OLSON FE et al. | The use of diets containing large amounts of linoleic acid. | 1958 Nov-Dec | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:13594895 |
| Hodge AM et al. | Plasma phospholipid and dietary fatty acids as predictors of type 2 diabetes: interpreting the role of linoleic acid. | 2007 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:17616780 |
| Arca M et al. | Erythrocyte fatty acid composition and gallstone disease: results of an epidemiological survey. | 1987 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:3604961 |