| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Melanosis | D008548 | 4 associated lipids |
| Embolism, Fat | D004620 | 4 associated lipids |
| Esophagitis, Peptic | D004942 | 4 associated lipids |
| Dermatitis, Phototoxic | D017484 | 4 associated lipids |
| Biliary Atresia | D001656 | 4 associated lipids |
| Cicatrix, Hypertrophic | D017439 | 4 associated lipids |
| Varicocele | D014646 | 4 associated lipids |
| Epilepsy, Temporal Lobe | D004833 | 4 associated lipids |
| Varicose Ulcer | D014647 | 4 associated lipids |
| Choroidal Neovascularization | D020256 | 5 associated lipids |
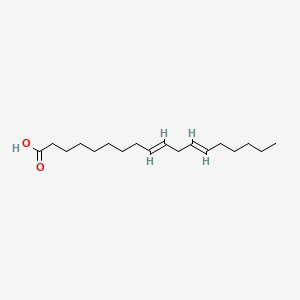
Linoelaidic acid
Linoelaidic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Linoelaidic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease and Metabolic syndrome. The involved functions are known as Metabolic Inhibition, Steroid biosynthesis, Signal Transduction, Insulin Resistance and Inflammation. Linoelaidic acid often locates in Mitochondria, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Linoelaidic acid are FFAR1 gene, C9orf7 gene, TNF gene, CCL2 gene and TLR4 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, octadecadienoic acid, Steroids, methyl linoleate and Cyanoketone.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Linoelaidic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Linoelaidic acid is suspected in Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease, Metabolic syndrome and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Linoelaidic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Linoelaidic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids (1)
- Thorax (1)
- Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (1)
- Others (1)
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Linoelaidic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kelavkar UP et al. | Concordant induction of 15-lipoxygenase-1 and mutant p53 expression in human prostate adenocarcinoma: correlation with Gleason staging. | 2000 | Carcinogenesis | pmid:11023533 |
| Qian SY et al. | EPR detection of lipid-derived free radicals from PUFA, LDL, and cell oxidations. | 2000 | Free Radic. Biol. Med. | pmid:11025200 |
| Van de Velde M et al. | Effects of lipids on the functional and metabolic recovery from global myocardial stunning in isolated rabbit hearts. | 2000 | Cardiovasc. Res. | pmid:11033115 |
| Meaney CM and O'Driscoll CM | A comparison of the permeation enhancement potential of simple bile salt and mixed bile salt:fatty acid micellar systems using the CaCo-2 cell culture model. | 2000 | Int J Pharm | pmid:11036226 |
| Smith HL et al. | Development of a serum-free system for the in vitro cultivation of Brugia malayi infective-stage larvae. | 2000 | Exp. Parasitol. | pmid:11038308 |
| French SJ et al. | The effects of intestinal infusion of long-chain fatty acids on food intake in humans. | 2000 | Gastroenterology | pmid:11040181 |
| Moran JH et al. | Analysis of the cytotoxic properties of linoleic acid metabolites produced by renal and hepatic P450s. | 2000 | Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. | pmid:11042099 |
| Soriano CR et al. | Cutaneous application of vegetable oil as a coadjutant in the nutritional management of preterm infants. | 2000 | J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. | pmid:11045835 |
| Steinkamp G et al. | Energy supplements rich in linoleic acid improve body weight and essential fatty acid status of cystic fibrosis patients. | 2000 | J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. | pmid:11045840 |
| Whigham LD et al. | Conjugated linoleic acid: implications for human health. | 2000 | Pharmacol. Res. | pmid:11058400 |
| Surai PF et al. | Effect of long-term supplementation with arachidonic or docosahexaenoic acids on sperm production in the broiler chicken. | 2000 | J. Reprod. Fertil. | pmid:11058441 |
| Cunnane SC et al. | Specific linoleate deficiency in the rat does not prevent substantial carbon recycling from [(14)C]linoleate into sterols. | 2000 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:11060350 |
| Ferry DR et al. | A phase II study of the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, CV6504, in advanced pancreatic cancer: correlation of clinical data with pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic endpoints. | 2000 | Ann. Oncol. | pmid:11061613 |
| French P et al. | Fatty acid composition, including conjugated linoleic acid, of intramuscular fat from steers offered grazed grass, grass silage, or concentrate-based diets. | 2000 | J. Anim. Sci. | pmid:11063308 |
| Brynes AE et al. | Diet-induced change in fatty acid composition of plasma triacylglycerols is not associated with change in glucagon-like peptide 1 or insulin sensitivity in people with type 2 diabetes. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:11063437 |
| Granot E et al. | Breast-fed and formula-fed infants do not differ in immunocompetent cell cytokine production despite differences in cell membrane fatty acid composition. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:11063450 |
| Sauerwald TU et al. | Polyunsaturated fatty acid supply with human milk. Physiological aspects and in vivo studies of metabolism. | 2000 | Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. | pmid:11065079 |
| Del Prado M et al. | Contribution of dietary and newly formed arachidonic acid to milk secretion in women on low fat diets. | 2000 | Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. | pmid:11065105 |
| Lance A et al. | 13C-linoleic acid oxidation and transfer into milk in lactating women with contrasting body mass index. | 2000 | Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. | pmid:11065106 |
| Cahoon EB et al. | Formation of conjugated delta8,delta10-double bonds by delta12-oleic-acid desaturase-related enzymes: biosynthetic origin of calendic acid. | 2001 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:11067856 |