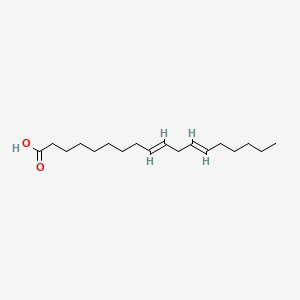
Linoelaidic acid
Linoelaidic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Linoelaidic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease and Metabolic syndrome. The involved functions are known as Metabolic Inhibition, Steroid biosynthesis, Signal Transduction, Insulin Resistance and Inflammation. Linoelaidic acid often locates in Mitochondria, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Linoelaidic acid are FFAR1 gene, C9orf7 gene, TNF gene, CCL2 gene and TLR4 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, octadecadienoic acid, Steroids, methyl linoleate and Cyanoketone.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Linoelaidic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Linoelaidic acid is suspected in Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease, Metabolic syndrome and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Linoelaidic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Linoelaidic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. (1)
- Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (1)
- Hypertension (1)
- Others (3)
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (1)
- Plant Cell (1)
- Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids (1)
- Others (1)
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Linoelaidic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALVAREZ G | [Effect of linoleic acid (vitamin F?) in therapy of infantile eczema]. | 1952 | Sem Med | pmid:13028610 |
| Buchanan MR and Brister SJ | Altering vessel wall fatty acid metabolism: a new strategy for antithrombotic treatment. | 1993 | Semin. Thromb. Hemost. | pmid:8356461 |
| Wang L et al. | [Effects of linoleic acid on intracellular calcium concentration in primarily cultured rat pancreatic β-cells and underlying mechanism]. | 2010 | Sheng Li Xue Bao | pmid:21170499 |
| Wei M et al. | [Kinetics of bioconversion of linoleic acid to conjugated linoleic acid by permeabilized Lactobacillus acidophilus cells]. | 2010 | Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao | pmid:20575439 |
| Zhang Q et al. | [Heteroexpression of Rhizopus arrhizus delta6-fatty acid desaturase gene in Pichia pastoris]. | 2005 | Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao | pmid:16468339 |
| Lu GP et al. | [Establishment of a cell-based high-throughput screening model for PPARdelta agonists]. | 2007 | Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao | pmid:17460914 |
| Amakura Y et al. | Characteristic long-chain fatty acid of Pleurocybella porrigens. | 2006 | Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi | pmid:16984039 |
| NAGAI H et al. | HOST RESPONSE TO THE IMMUNIZATION WITH LIVE ATTENUATED MEASLES VACCINE, OBSERVED IN INFANTS GIVEN LINOLEATE-SUPPLEMENTED DRIED MILK. | 1963 Sep-Oct | Shonika Kiyo | pmid:14115557 |
| Schürer N et al. | Differential utilization of linoleic and arachidonic acid by cultured human keratinocytes. | 1995 | Skin Pharmacol. | pmid:7786523 |
| Blask DE | Melatonin, sleep disturbance and cancer risk. | 2009 | Sleep Med Rev | pmid:19095474 |
| Palta M and Cook T | Some considerations in the analysis of rates of change in longitudinal studies. | 1987 Jul-Aug | Stat Med | pmid:3659670 |
| Viscardi RM and Max SR | Unsaturated fatty acid modulation of glucocorticoid receptor binding in L2 cells. | 1993 | Steroids | pmid:8212085 |
| Cigliano L et al. | Estradiol esterification in the human preovulatory follicle. | 2001 | Steroids | pmid:11711117 |
| Ghosh D et al. | Structure of uncomplexed and linoleate-bound Candida cylindracea cholesterol esterase. | 1995 | Structure | pmid:7788294 |
| Toborek M and Hennig B | The role of linoleic acid in endothelial cell gene expression. Relationship to atherosclerosis. | 1998 | Subcell. Biochem. | pmid:9932524 |
| Alling C et al. | Decreased linoleic acid in serum lecithin after ethanol abuse. | 1980 | Subst Alcohol Actions Misuse | pmid:7302797 |
| Thoresen L and Bjerve KS | [From clinical nursing: long-term tube feeding can cause deficiency diseases]. | 1987 | Sykepleien | pmid:2891206 |
| Okuyama H | [Does food affect brain functions?]. | 1990 | Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso | pmid:1970438 |
| Watanabe S and Okuyama H | [Physiological significance of n-3 fatty acid-containing phospholipids]. | 1991 | Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso | pmid:1673799 |
| SATOMURA K and SODERHJELM L | Deposition of fatty acids in the newborn in relation to the diet of pregnant guinea pigs: a preliminary report. | 1962 | Tex. Rep. Biol. Med. | pmid:13986764 |