| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas Infections | D011552 | 25 associated lipids |
| Genetic Predisposition to Disease | D020022 | 24 associated lipids |
| Cattle Diseases | D002418 | 24 associated lipids |
| Breast Neoplasms | D001943 | 24 associated lipids |
| Stomach Neoplasms | D013274 | 24 associated lipids |
| Pulmonary Edema | D011654 | 23 associated lipids |
| Hypoxia | D000860 | 23 associated lipids |
| Cholestasis | D002779 | 23 associated lipids |
| Birth Weight | D001724 | 23 associated lipids |
| Neoplasms, Hormone-Dependent | D009376 | 23 associated lipids |
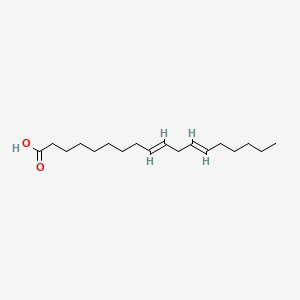
Linoelaidic acid
Linoelaidic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Linoelaidic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease and Metabolic syndrome. The involved functions are known as Metabolic Inhibition, Steroid biosynthesis, Signal Transduction, Insulin Resistance and Inflammation. Linoelaidic acid often locates in Mitochondria, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Linoelaidic acid are FFAR1 gene, C9orf7 gene, TNF gene, CCL2 gene and TLR4 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, octadecadienoic acid, Steroids, methyl linoleate and Cyanoketone.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Linoelaidic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Linoelaidic acid is suspected in Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease, Metabolic syndrome and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Linoelaidic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Linoelaidic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
- Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids (1)
- Thorax (1)
- Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (1)
- Others (1)
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Linoelaidic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Linoelaidic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bentrad N et al. | Identification and evaluation of antibacterial agents present in lipophilic fractions isolated from sub-products of Phoenix dactilyfera. | 2017 | Nat. Prod. Res. | pmid:28403631 |
| Fan Y et al. | Study of the pH-sensitive mechanism of tumor-targeting liposomes. | 2017 | Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces | pmid:27940165 |
| Zhou Y et al. | UCP2 attenuates apoptosis of tubular epithelial cells in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. | 2017 | Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. | pmid:28424210 |
| Song S et al. | Identification of pork flavour precursors from enzyme-treated lard using Maillard model system assessed by GC-MS and partial least squares regression. | 2017 | Meat Sci. | pmid:27792915 |
| Fujii M | Pathogenesis of Diet-induced Atopic Dermatitis in Hairless Mice. | 2017 | Yakugaku Zasshi | pmid:28049895 |
| Turell L et al. | The Chemical Basis of Thiol Addition to Nitro-conjugated Linoleic Acid, a Protective Cell-signaling Lipid. | 2017 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:27923813 |
| Segal LN et al. | Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with azithromycin selects for anti-inflammatory microbial metabolites in the emphysematous lung. | 2017 | Thorax | pmid:27486204 |
| Matravadia S et al. | LA and ALA prevent glucose intolerance in obese male rats without reducing reactive lipid content, but cause tissue-specific changes in fatty acid composition. | 2016 | Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. | pmid:26764053 |
| Jablonická V et al. | Identification of a secretory phospholipase A2 from Papaver somniferum L. that transforms membrane phospholipids. | 2016 | Phytochemistry | pmid:27473012 |
| Green D et al. | Central activation of TRPV1 and TRPA1 by novel endogenous agonists contributes to mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia after burn injury. | 2016 | Mol Pain | pmid:27411353 |