| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Irritable Bowel Syndrome | D043183 | 8 associated lipids |
| Overweight | D050177 | 11 associated lipids |
| Atherosclerosis | D050197 | 85 associated lipids |
| Carcinogenesis | D063646 | 3 associated lipids |
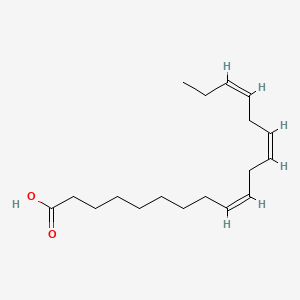
alpha-linolenic acid
Alpha-linolenic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Alpha-linolenic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, abnormal fragmented structure, Arterial thrombosis and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Signal, Transcription, Genetic, Saturated and Regulation. Alpha-linolenic acid often locates in Blood, Body tissue, Plasma membrane, Hepatic and peroxisome. The associated genes with alpha-linolenic acid are FATE1 gene, volicitin, CYP2U1 gene, CYP1A2 gene and CYP2J2 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Dietary Fatty Acid, stearidonic acid and Fatty Acids, Nonesterified.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of alpha-linolenic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
alpha-linolenic acid is suspected in Coronary heart disease, Arterial thrombosis, Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with alpha-linolenic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with alpha-linolenic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with alpha-linolenic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caligiuri SP et al. | The HYPERFlax trial for determining the anti-HYPERtensive effects of dietary flaxseed in newly diagnosed stage 1 hypertensive patients: study protocol for a randomized, double-blinded, controlled clinical trial. | 2014 | Trials | pmid:24938224 |
| Baumgartner J et al. | Providing male rats deficient in iron and n-3 fatty acids with iron and alpha-linolenic acid alone affects brain serotonin and cognition differently from combined provision. | 2014 | Lipids Health Dis | pmid:24928171 |
| Herchi W et al. | Flaxseed hull: Chemical composition and antioxidant activity during development. | 2014 | J Oleo Sci | pmid:24919478 |
| Mariutto M et al. | Reprogramming of fatty acid and oxylipin synthesis in rhizobacteria-induced systemic resistance in tomato. | 2014 | Plant Mol. Biol. | pmid:24146221 |
| Matravadia S et al. | Both linoleic and α-linolenic acid prevent insulin resistance but have divergent impacts on skeletal muscle mitochondrial bioenergetics in obese Zucker rats. | 2014 | Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. | pmid:24844257 |
| Hudson BD et al. | The molecular basis of ligand interaction at free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFA4/GPR120). | 2014 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:24860101 |
| Berasategi I et al. | Reduced-fat bologna sausages with improved lipid fraction. | 2014 | J. Sci. Food Agric. | pmid:24105447 |
| Vedtofte MS et al. | Association between the intake of α-linolenic acid and the risk of CHD. | 2014 | Br. J. Nutr. | pmid:24964401 |
| Yavin E et al. | Metabolic conversion of intra-amniotically-injected deuterium-labeled essential fatty acids by fetal rats following maternal n-3 fatty acid deficiency. | 2014 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:24960100 |
| Liang CH et al. | Synthesis of doxorubicin α-linolenic acid conjugate and evaluation of its antitumor activity. | 2014 | Mol. Pharm. | pmid:24720787 |