| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Deficiency Diseases | D003677 | 12 associated lipids |
| Cystic Fibrosis | D003550 | 65 associated lipids |
| Coronary Disease | D003327 | 70 associated lipids |
| Coronary Artery Disease | D003324 | 47 associated lipids |
| Conjunctivitis, Allergic | D003233 | 1 associated lipids |
| Colonic Neoplasms | D003110 | 161 associated lipids |
| Colitis | D003092 | 69 associated lipids |
| Brain Ischemia | D002545 | 89 associated lipids |
| Cattle Diseases | D002418 | 24 associated lipids |
| Cat Diseases | D002371 | 12 associated lipids |
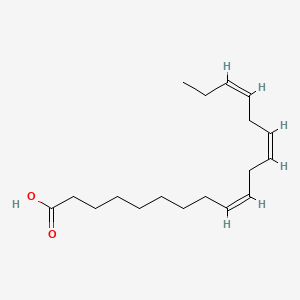
alpha-linolenic acid
Alpha-linolenic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Alpha-linolenic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, abnormal fragmented structure, Arterial thrombosis and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Signal, Transcription, Genetic, Saturated and Regulation. Alpha-linolenic acid often locates in Blood, Body tissue, Plasma membrane, Hepatic and peroxisome. The associated genes with alpha-linolenic acid are FATE1 gene, volicitin, CYP2U1 gene, CYP1A2 gene and CYP2J2 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Dietary Fatty Acid, stearidonic acid and Fatty Acids, Nonesterified.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of alpha-linolenic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
alpha-linolenic acid is suspected in Coronary heart disease, Arterial thrombosis, Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with alpha-linolenic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with alpha-linolenic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with alpha-linolenic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with alpha-linolenic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vos E et al. | alpha-Linolenic acid and fish oil n-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease risk. | 2007 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:17344517 |
| Kelley DS et al. | Dietary alpha-linolenic acid and immunocompetence in humans. | 1991 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:1670594 |
| Wang C et al. | n-3 Fatty acids from fish or fish-oil supplements, but not alpha-linolenic acid, benefit cardiovascular disease outcomes in primary- and secondary-prevention studies: a systematic review. | 2006 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:16825676 |
| Renaud SC and Lanzmann-Petithory D | The beneficial effect of alpha-linolenic acid in coronary artery disease is not questionable. | 2002 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12324307 |
| Cunnane SC et al. | Nutritional attributes of traditional flaxseed in healthy young adults. | 1995 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:7825540 |
| Devore EE et al. | Dietary intake of fish and omega-3 fatty acids in relation to long-term dementia risk. | 2009 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:19474131 |
| Pan A et al. | α-Linolenic acid and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. | 2012 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:23076616 |
| Innis SM and Elias SL | Intakes of essential n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids among pregnant Canadian women. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12540410 |
| Vos E and Cunnane SC | Alpha-linolenic acid, linoleic acid, coronary artery disease, and overall mortality. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12540417 |
| Finnegan YE et al. | Plant- and marine-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids have differential effects on fasting and postprandial blood lipid concentrations and on the susceptibility of LDL to oxidative modification in moderately hyperlipidemic subjects. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12663273 |
| Jeppesen PB et al. | Differences in essential fatty acid requirements by enteral and parenteral routes of administration in patients with fat malabsorption. | 1999 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10393142 |
| James MJ et al. | Metabolism of stearidonic acid in human subjects: comparison with the metabolism of other n-3 fatty acids. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12716664 |
| Kew S et al. | Lack of effect of foods enriched with plant- or marine-derived n-3 fatty acids on human immune function. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12716684 |
| de Groot RH et al. | Effect of alpha-linolenic acid supplementation during pregnancy on maternal and neonatal polyunsaturated fatty acid status and pregnancy outcome. | 2004 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:14749231 |
| Lemaitre RN et al. | n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids, fatal ischemic heart disease, and nonfatal myocardial infarction in older adults: the Cardiovascular Health Study. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12540389 |
| Pawlosky RJ et al. | Effects of beef- and fish-based diets on the kinetics of n-3 fatty acid metabolism in human subjects. | 2003 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12600844 |
| Vedtofte MS et al. | Dietary α-linolenic acid, linoleic acid, and n-3 long-chain PUFA and risk of ischemic heart disease. | 2011 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:21865326 |
| Kestin M et al. | n-3 fatty acids of marine origin lower systolic blood pressure and triglycerides but raise LDL cholesterol compared with n-3 and n-6 fatty acids from plants. | 1990 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:1971991 |
| Carlson SE et al. | Effect of long-chain n-3 fatty acid supplementation on visual acuity and growth of preterm infants with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia. | 1996 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:8615350 |
| Connor WE | Alpha-linolenic acid in health and disease. | 1999 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10232618 |
| Li D et al. | Effect of dietary alpha-linolenic acid on thrombotic risk factors in vegetarian men. | 1999 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10232625 |
| Hu FB et al. | Dietary intake of alpha-linolenic acid and risk of fatal ischemic heart disease among women. | 1999 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10232627 |
| Lin YH et al. | Compartmental analyses of 2H5-alpha-linolenic acid and C-U-eicosapentaenoic acid toward synthesis of plasma labeled 22:6n-3 in newborn term infants. | 2010 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:20534748 |
| Bursztyn P | Does dietary linolenic acid influence blood pressure? | 1987 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:2884863 |
| Bozian RC and Moussavian SN | Human linolenic acid deficiency. | 1982 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:6293298 |
| Marshall LA et al. | Dietary alpha-linolenic acid and prostaglandin synthesis: a time course study. | 1983 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:6316775 |
| Decsi T and Kennedy K | Sex-specific differences in essential fatty acid metabolism. | 2011 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:22089435 |
| Sanders TA | Polyunsaturated fatty acids in the food chain in Europe. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617968 |
| Uauy R and Hoffman DR | Essential fat requirements of preterm infants. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617979 |
| Gibson RA and Makrides M | n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid requirements of term infants. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617980 |
| Baylin A et al. | Adipose tissue biomarkers of fatty acid intake. | 2002 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:12324287 |
| Crawford M | Placental delivery of arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acids: implications for the lipid nutrition of preterm infants. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617983 |
| Dutta-Roy AK | Transport mechanisms for long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the human placenta. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617989 |
| Wilk JB et al. | Plasma and dietary omega-3 fatty acids, fish intake, and heart failure risk in the Physicians' Health Study. | 2012 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:22952185 |
| Horrobin DF | Essential fatty acid metabolism and its modification in atopic eczema. | 2000 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:10617999 |
| Koletzko B and Cunnane S | Human alpha-linolenic acid deficiency. | 1988 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:2897782 |
| Lucas M et al. | Dietary intake of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids and the risk of clinical depression in women: a 10-y prospective follow-up study. | 2011 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:21471279 |
| Oomen CM et al. | alpha-Linolenic acid intake is not beneficially associated with 10-y risk of coronary artery disease incidence: the Zutphen Elderly Study. | 2001 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:11566643 |
| Chiu CC et al. | Associations between n-3 PUFA concentrations and cognitive function after recovery from late-life depression. | 2012 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:22218153 |
| Welch AA et al. | Dietary intake and status of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in a population of fish-eating and non-fish-eating meat-eaters, vegetarians, and vegans and the product-precursor ratio [corrected] of α-linolenic acid to long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: results from the EPIC-Norfolk cohort. | 2010 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:20861171 |
| Kwon JS et al. | Effects of diets high in saturated fatty acids, canola oil, or safflower oil on platelet function, thromboxane B2 formation, and fatty acid composition of platelet phospholipids. | 1991 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:1677525 |
| Baylin A et al. | alpha-Linolenic acid, Delta6-desaturase gene polymorphism, and the risk of nonfatal myocardial infarction. | 2007 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:17284757 |
| Sanders TA et al. | Effect of varying the ratio of n-6 to n-3 fatty acids by increasing the dietary intake of alpha-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid, or both on fibrinogen and clotting factors VII and XII in persons aged 45-70 y: the OPTILIP study. | 2006 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:16960164 |
| Salem N and Kuratko CN | Lack of evidence for increased α-linolenic acid metabolism in vegetarians. | 2011 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:21430120 |
| Djoussé L et al. | Plasma omega-3 fatty acids and incident diabetes in older adults. | 2011 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:21593500 |
| Heskey CE et al. | Adipose tissue α-linolenic acid is inversely associated with insulin resistance in adults. | 2016 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:26912497 |
| Goyens PL et al. | Conversion of alpha-linolenic acid in humans is influenced by the absolute amounts of alpha-linolenic acid and linoleic acid in the diet and not by their ratio. | 2006 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:16825680 |
| Venäläinen TM et al. | Effect of a 2-y dietary and physical activity intervention on plasma fatty acid composition and estimated desaturase and elongase activities in children: the Physical Activity and Nutrition in Children Study. | 2016 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:27581473 |
| Zhao G et al. | Dietary alpha-linolenic acid inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in hypercholesterolemic subjects. | 2007 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:17284733 |
| Chan JK et al. | Dietary alpha-linolenic acid is as effective as oleic acid and linoleic acid in lowering blood cholesterol in normolipidemic men. | 1991 | Am. J. Clin. Nutr. | pmid:1673589 |