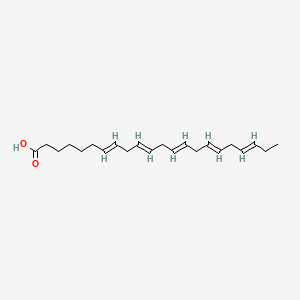
| Okuda N et al. |
Relation of long chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake to serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol among Japanese men in Japan and Japanese-American men in Hawaii: the INTERLIPID study. |
2005 |
Atherosclerosis |
pmid:15694947
|
| GarcÃa-Calatayud S et al. |
Brain docosahexaenoic acid status and learning in young rats submitted to dietary long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency and supplementation limited to lactation. |
2005 |
Pediatr. Res. |
pmid:15718358
|
| Kojima M et al. |
Serum levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids and risk of colorectal cancer: a prospective study. |
2005 |
Am. J. Epidemiol. |
pmid:15718482
|
| Solakivi T et al. |
Lipoprotein docosapentaenoic acid is associated with serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 concentration. |
2005 |
Lipids Health Dis |
pmid:15826319
|
| Goyens PL et al. |
Compartmental modeling to quantify alpha-linolenic acid conversion after longer term intake of multiple tracer boluses. |
2005 |
J. Lipid Res. |
pmid:15834128
|
| Lin YH and Salem N |
In vivo conversion of 18- and 20-C essential fatty acids in rats using the multiple simultaneous stable isotope method. |
2005 |
J. Lipid Res. |
pmid:15930514
|
| Salem N et al. |
Incomplete replacement of docosahexaenoic acid by n-6 docosapentaenoic acid in the rat retina after an n-3 fatty acid deficient diet. |
2005 |
Exp. Eye Res. |
pmid:15967432
|
| Rosell MS et al. |
Long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in plasma in British meat-eating, vegetarian, and vegan men. |
2005 |
Am. J. Clin. Nutr. |
pmid:16087975
|
| Lim SY et al. |
An extraordinary degree of structural specificity is required in neural phospholipids for optimal brain function: n-6 docosapentaenoic acid substitution for docosahexaenoic acid leads to a loss in spatial task performance. |
2005 |
J. Neurochem. |
pmid:16135079
|
| Llanos A et al. |
Infants with intrauterine growth restriction have impaired formation of docosahexaenoic acid in early neonatal life: a stable isotope study. |
2005 |
Pediatr. Res. |
pmid:16189202
|