| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
| Glioma | D005910 | 112 associated lipids |
| Hemolysis | D006461 | 131 associated lipids |
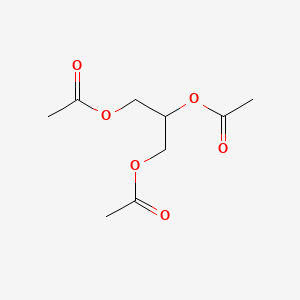
triacetin
triacetin is a lipid of Glycerolipids (GL) class. Triacetin is associated with abnormalities such as Vesicular Exanthema of Swine and Lobomycosis. The involved functions are known as National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (U.S.), Softening, esterase activity, Process and Cell Growth. Triacetin often locates in Tissue fiber, Cell surface and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with triacetin are GRAP2 gene and Immobilized Proteins. The related lipids are Labrafil M 1944 CS, ethyl oleate and glyceryl monostearate.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of triacetin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with triacetin?
triacetin is suspected in Vesicular Exanthema of Swine, Lobomycosis and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with triacetin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with triacetin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with triacetin?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with triacetin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with triacetin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with triacetin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with triacetin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with triacetin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nosko M | [Comparative toxicity of triacetin and diethylene glycol diacetate]. | 1977 | Probl Khig | pmid:614556 |
| Schindler J | TLG medium for pigment detection of staphylococci. | 1977 | Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A | pmid:602515 |
| Shapira J et al. | Acetylated glycerols as dietary constituents: studies on their nutritional adaptation by rats. | 1977 | Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. | pmid:896825 |
| Chandan RC et al. | Bovine pancreatic lipase. III. Lipolysis of oils and fats and fatty acid specificity. | 1976 | J. Dairy Sci. | pmid:944720 |
| Chapus C et al. | Mechanism of pancreatic lipase action. 1. Interfacial activation of pancreatic lipase. | 1976 | Biochemistry | pmid:990257 |
| Shapira J et al. | Adaptation to glycerol and triacetin ingestion in rats: influence of total dietary protein. | 1976 | Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. | pmid:995986 |
| Rakhimov MM et al. | [Substrate specificity of immobilized lipases]. | 1976 | Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR | pmid:964124 |
| Rakhimov MM and Dzhanbaeva NR | [The relationship of cottonseed's triacetinase]. | 1976 | Biokhimiia | pmid:15644 |
| Shapira J et al. | Glycerol, propylene glycol and triacetin as dietary starch substitutes: some effects on rats. | 1975 | Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. | pmid:1178690 |
| Lawrence WH et al. | Development of a toxicity evaluation program for dental materials and products. II. Screening for systemic toxicity. | 1974 | J. Biomed. Mater. Res. | pmid:4819870 |