
|
Ethylcyclohexane |
Ethylcyclohexane is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
26 |

|
N-palmitoyl glycine |
N-palmitoyl glycine is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
40 |
|
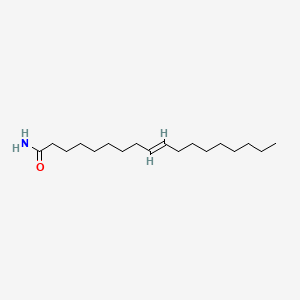
Elaidamide |
Elaidamide is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Elaidamide is associated with abnormalities such as Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, salivary gland development and branching morphogenesis. |
204 |

|
5-aminovaleric acid |
5-aminovaleric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
255 |
|
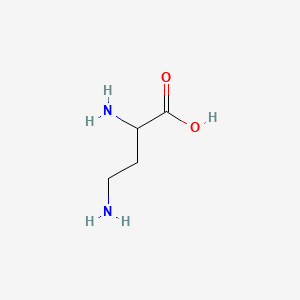
2,4-diamino-butyric acid |
2,4-diamino-butyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
278 |
|
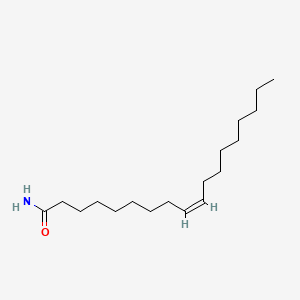
Oleamide |
Oleamide is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Oleamide is associated with abnormalities such as Blepharoptosis, BOSLEY-SALIH-ALORAINY SYNDROME, abnormal fragmented structure, Syndrome and Hashimoto Disease. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Regulation, receptor ligand, Process and Binding (Molecular Function). Oleamide often locates in receptor complex, Tissue membrane, Membrane, annulus and Connexon. The associated genes with Oleamide are Homologous Gene, FAAH gene, FAAH2 gene, P4HTM gene and Integral Membrane Proteins. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Membrane Lipids, N-acylethanolamines, erucyl amide and linoleamide. |
349 |
|
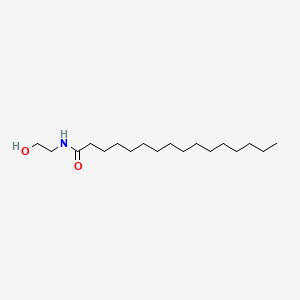
Palmitoyl-EA |
Palmitoyl-ea is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Cytokinesis of the fertilized ovum and phosphatase activity. The related lipids are stearic acid. |
1001 |
|
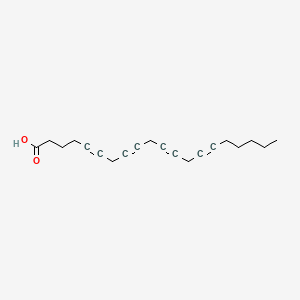
Etya |
Etya is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
1028 |
|
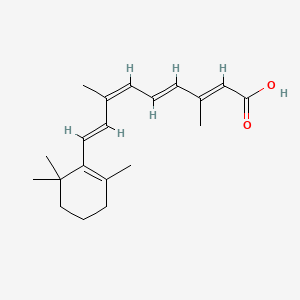
9-cis-retinoic acid |
9-cis-retinoic acid is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. 9-cis-retinoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Cholestasis. The involved functions are known as Enterohepatic Circulation, luciferase activity, Binding (Molecular Function) and inhibitors. The associated genes with 9-cis-retinoic acid are ABCC3 gene, Candidate Disease Gene, NR1H4 gene and GPBAR1 gene. The related lipids are lithocholic acid acetate and Propionate. |
1085 |
|
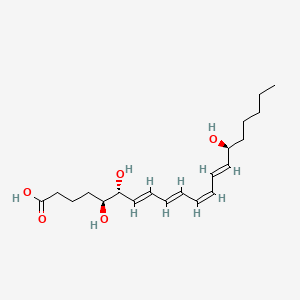
Lipoxin A4 |
Lipoxin a4 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Lipoxin a4 is associated with abnormalities such as Asthma, Cystic Fibrosis, Pneumonia, Obesity and Septicemia. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, Signal, Signal Transduction, Regulation and Metabolic Inhibition. Lipoxin a4 often locates in Immune system, Blood, soluble, Extracellular and Splenic Tissue. The associated genes with Lipoxin A4 are FPR2 gene, Homologous Gene, SAA1 gene, Trp-Lys-Tyr-Met-Val-Met and Annexin 1. The related lipids are Steroids. The related experimental models are Knock-out. |
1240 |









