| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mizuno S et al. | Dioleoyl-phosphatidic acid selectively binds to α-synuclein and strongly induces its aggregation. | 2017 | FEBS Lett. | pmid:28186641 |
| Rivero Berti I et al. | Delivery of fluorophores by calcium phosphate-coated nanoliposomes and interaction with Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. | 2016 | Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces | pmid:26954088 |
| Chen YF et al. | Differential dependencies on [Ca2+] and temperature of the monolayer spontaneous curvatures of DOPE, DOPA and cardiolipin: effects of modulating the strength of the inter-headgroup repulsion. | 2015 | Soft Matter | pmid:25907686 |
| Li J et al. | Calcium phosphate nanoparticles with an asymmetric lipid bilayer coating for siRNA delivery to the tumor. | 2012 | J Control Release | pmid:22056915 |
| Roberts MF et al. | Phospholipid reorientation at the lipid/water interface measured by high resolution 31P field cycling NMR spectroscopy. | 2009 | Biophys. J. | pmid:19580751 |
| Lamberson ER et al. | Path dependence of three-phase or two-phase end points in fluid binary lipid mixtures. | 2009 | J Phys Chem B | pmid:19243147 |
| Chang YJ et al. | Dioleoyl phosphatidic acid induces morphological changes through an endogenous LPA receptor in C6 glioma cells. | 2008 | Arch. Pharm. Res. | pmid:18481020 |
| Stöckl M et al. | Alpha-synuclein selectively binds to anionic phospholipids embedded in liquid-disordered domains. | 2008 | J. Mol. Biol. | pmid:18082181 |
| Andre G et al. | Probing the interaction forces between hydrophobic peptides and supported lipid bilayers using AFM. | 2007 Nov-Dec | J. Mol. Recognit. | pmid:17891753 |
| Kapralov AA et al. | The hierarchy of structural transitions induced in cytochrome c by anionic phospholipids determines its peroxidase activation and selective peroxidation during apoptosis in cells. | 2007 | Biochemistry | pmid:18004876 |
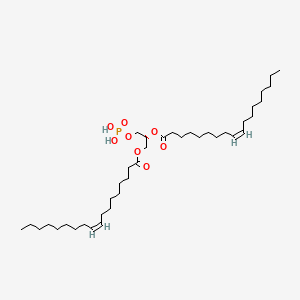
PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. The involved functions are known as adenylate cyclase activity, inhibitors, Drug Interactions, Membrane Fluidity and Force. Pa(18:1(9z)/18:1(9z)) often locates in Cell membrane, Tissue membrane, Epidermis, Connective Tissue and Back. The associated genes with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) are growth promoting activity and RAF1 gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidic Acid, Lysophospholipids, lysophosphatidic acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines and dioleoyl phosphate.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)), we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.