| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanley TP et al. | The serine/threonine phosphatase, PP2A: endogenous regulator of inflammatory cell signaling. | 2001 | J. Immunol. | pmid:11145674 |
| Li SJ et al. | Effect of electrostatic interactions on phase stability of cubic phases of membranes of monoolein/dioleoylphosphatidic acid mixtures. | 2001 | Biophys. J. | pmid:11463640 |
| Baenziger JE et al. | Effect of membrane lipid composition on the conformational equilibria of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. | 2000 | J. Biol. Chem. | pmid:10625607 |
| Kostrzewa A et al. | Membrane location of spin-labeled cytochrome c determined by paramagnetic relaxation agents. | 2000 | Biochemistry | pmid:10821679 |
| Holopainen JM et al. | Evidence for the extended phospholipid conformation in membrane fusion and hemifusion. | 1999 | Biophys. J. | pmid:10096906 |
| Dalton KA et al. | Anionic phospholipids decrease the rate of slippage on the Ca(2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. | 1999 | Biochem. J. | pmid:10455031 |
| Raines DE and Krishnan NS | Agonist binding and affinity state transitions in reconstituted nicotinic acetylcholine receptors revealed by single and sequential mixing stopped-flow fluorescence spectroscopies. | 1998 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:9814855 |
| Dalton KA et al. | Anionic lipids and accumulation of Ca2+ by a Ca(2+)-ATPase. | 1998 | Biochem. Soc. Trans. | pmid:9765953 |
| Hixon MS et al. | Calcium-dependent and -independent interfacial binding and catalysis of cytosolic group IV phospholipase A2. | 1998 | Biochemistry | pmid:9622504 |
| Oja CD et al. | Influence of dose on liposome clearance: critical role of blood proteins. | 1996 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | pmid:8652601 |
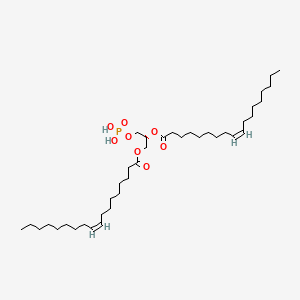
PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. The involved functions are known as adenylate cyclase activity, inhibitors, Drug Interactions, Membrane Fluidity and Force. Pa(18:1(9z)/18:1(9z)) often locates in Cell membrane, Tissue membrane, Epidermis, Connective Tissue and Back. The associated genes with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) are growth promoting activity and RAF1 gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidic Acid, Lysophospholipids, lysophosphatidic acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines and dioleoyl phosphate.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)), we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with PA(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z))?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.