| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Dermatitis, Contact | D003877 | 59 associated lipids |
| Edema | D004487 | 152 associated lipids |
| Occupational Diseases | D009784 | 42 associated lipids |
| Asthma | D001249 | 52 associated lipids |
| Weight Gain | D015430 | 101 associated lipids |
| Cell Transformation, Neoplastic | D002471 | 126 associated lipids |
| Ulcer | D014456 | 16 associated lipids |
| Psoriasis | D011565 | 47 associated lipids |
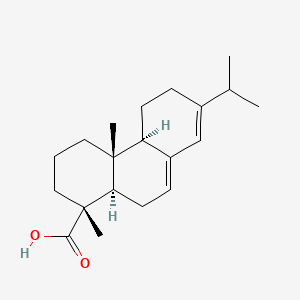
Abietic acid
Abietic acid is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Abietic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Hand eczema, Dermatitis, Vitelliform dystrophy, Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome and Dehydration. The involved functions are known as Process, Oxidation, Anabolism, Transmembrane Transport and physiological aspects. Abietic acid often locates in Membrane, Protoplasm, Microsomes and Cellular Membrane. The associated genes with Abietic acid are SLC33A1 gene and ABCG2 gene. The related lipids are Pinene.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Abietic acid, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Abietic acid?
Abietic acid is suspected in Hand eczema, Dermatitis, Dehydration and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Abietic acid
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Abietic acid
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Abietic acid?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Abietic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Abietic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Lipid concept | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What genes are associated with Abietic acid?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Gene | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What common seen animal models are associated with Abietic acid?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Abietic acid
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitani K et al. | Analysis of abietic acid and dehydroabietic acid in food samples by in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. | 2007 | J Chromatogr A | pmid:17306277 |
| Smith DJ et al. | A large gene cluster in Burkholderia xenovorans encoding abietane diterpenoid catabolism. | 2007 | J. Bacteriol. | pmid:17586638 |
| Anderson KB | The nature and fate of natural resins in the geosphere. XII. Investigation of C-ring aromatic diterpenoids in Raritan amber by pyrolysis-GC-matrix isolation FTIR-MS. | 2006 | Geochem. Trans. | pmid:16759406 |
| Shaneyfelt ME et al. | Natural products that reduce rotavirus infectivity identified by a cell-based moderate-throughput screening assay. | 2006 | Virol. J. | pmid:16948846 |
| Sakamoto K et al. | Molecular mechanisms for large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel activation by a novel opener, 12,14-dichlorodehydroabietic acid. | 2006 | J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. | pmid:16195419 |
| Justino GC et al. | Antioxidant activity of a catechol derived from abietic acid. | 2006 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:16417289 |
| Oppel T and Schnuch A | [The most frequent allergens in allergic contact dermatitis]. | 2006 | Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. | pmid:16823706 |
| Ozaki A et al. | Migration of dehydroabietic and abietic acids from paper and paperboard food packaging into food-simulating solvents and Tenax TA. | 2006 | Food Addit Contam | pmid:16807212 |
| Keeling CI and Bohlmann J | Genes, enzymes and chemicals of terpenoid diversity in the constitutive and induced defence of conifers against insects and pathogens. | 2006 | New Phytol. | pmid:16684230 |
| Belmonte M et al. | Effect of aerobic sludge with increasing level of adaptation on abietic acid biodegradation. | 2006 | Bull Environ Contam Toxicol | pmid:17219306 |