| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bertea M et al. | Deoxysphingoid bases as plasma markers in diabetes mellitus. | 2010 | Lipids Health Dis | pmid:20712864 |
| Baird RD et al. | Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacogenomic trial of ES-285, a novel marine cytotoxic agent, administered to adult patients with advanced solid tumors. | 2009 | Mol. Cancer Ther. | pmid:19509256 |
| Sánchez AM et al. | Spisulosine (ES-285) induces prostate tumor PC-3 and LNCaP cell death by de novo synthesis of ceramide and PKCzeta activation. | 2008 | Eur. J. Pharmacol. | pmid:18343365 |
| Pruett ST et al. | Biodiversity of sphingoid bases ("sphingosines") and related amino alcohols. | 2008 | J. Lipid Res. | pmid:18499644 |
| Salcedo M et al. | The marine sphingolipid-derived compound ES 285 triggers an atypical cell death pathway. | 2007 | Apoptosis | pmid:17191124 |
| Den Brok MW et al. | Compatibility and stability of the novel anticancer agent ES-285 x HCl formulated with 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin in infusion devices. | 2006 | Pharmazie | pmid:16454201 |
| Faircloth G and Cuevas C | Kahalalide F and ES285: potent anticancer agents from marine molluscs. | 2006 | Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. | pmid:17153351 |
| Den Brok MW et al. | Pharmaceutical development of a parenteral lyophilised formulation of the investigational anticancer agent ES-285.HCl. | 2005 Jul-Aug | PDA J Pharm Sci Technol | pmid:16218203 |
| Stokvis E et al. | A more sensitive MS detector does not obviously lead to a more sensitive assay: experiences with ES-285. | 2004 | Biomed. Chromatogr. | pmid:15273982 |
| Yun JM et al. | Efficient synthesis of enantiomerically pure 2-acylaziridines: Facile syntheses of N-Boc-safingol, N-Boc-D-erythro-sphinganine, and N-Boc-spisulosine from a common intermediate. | 2003 | J. Org. Chem. | pmid:14510541 |
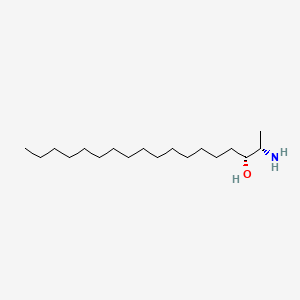
Spisulosine
Spisulosine is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. Spisulosine is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Renal impairment and Lesion of brain. The involved functions are known as Gene Expression, Cell Cycle, Drug Kinetics, Signal Transduction and Cell Cycle Arrest. Spisulosine often locates in Body tissue, Microfilaments, Skin, Stress Fibers and Tissue specimen.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Spisulosine, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Spisulosine?
Spisulosine is suspected in Infection, Renal impairment, Lesion of brain and other diseases in descending order of the highest number of associated sentences.
Related references are mostly published in these journals:
| Disease | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literature |
|---|
No disease MeSH terms mapped to the current reference collection.
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Spisulosine
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Spisulosine?
Visualization in cellular structure
Associated locations are in red color. Not associated locations are in black.
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Location | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What functions are associated with Spisulosine?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Spisulosine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Spisulosine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with Spisulosine?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.