|
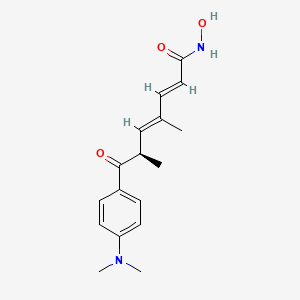
trichostatin A |
Trichostatin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Trichostatin is associated with abnormalities such as Dentatorubral-Pallidoluysian Atrophy, PARAGANGLIOMAS 3, abnormal fragmented structure, Disintegration (morphologic abnormality) and Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal. The involved functions are known as Acetylation, Cell Differentiation process, histone modification, Gene Silencing and Transcriptional Activation. Trichostatin often locates in CD41a, Hematopoietic System, Chromatin Structure, Blood and Endothelium. The associated genes with Trichostatin are SPI1 gene, CELL Gene, Chromatin, CXCR4 gene and DNMT1 gene. The related lipids are Butyrates, Promega, butyrate, Lipopolysaccharides and Steroids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Xenograft Model and Cancer Model. |
5401 |
|
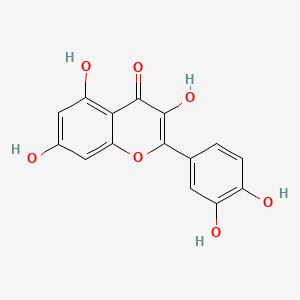
quercetin |
quercetin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Quercetin is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, Myocardial Infarction, Cirrhosis, Coronary Arteriosclerosis and Vascular ring. The involved functions are known as Vasodilation, physiological aspects, Fermentation, Process and Ingredient. Quercetin often locates in Arterial system, Endothelium, Skin, Endothelium, Vascular and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with quercetin are P4HTM gene, SULT gene, UGT1A1 gene, ARHGAP26 gene and PLXNB1 gene. The related lipids are blood lipid, Promega, Steroids, Phosphatidylserines and Fatty Acids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Tissue Model and Cancer Model. |
5377 |
|
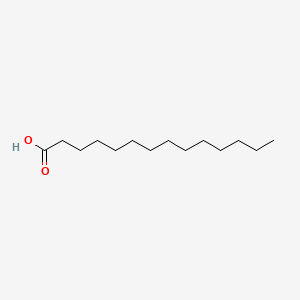
Tetradecanoic acid |
Tetradecanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Tetradecanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Chronic lung disease, Infection, Spastic syndrome, Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases. The involved functions are known as Fatty acid biosynthetic process, Anabolism, lung alveolus development, 5-(carboxyamino)imidazole ribonucleotide mutase activity and Homeostasis. Tetradecanoic acid often locates in Structure of parenchyma of lung, Blood, Head, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Tetradecanoic acid are SLC33A1 gene, SFTPA1 gene, P4HTM gene, Polypeptides and GPR132 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Nonesterified Fatty Acids, palmitoleic acid, Phosphatidylglycerols and Butanols. |
5058 |
|
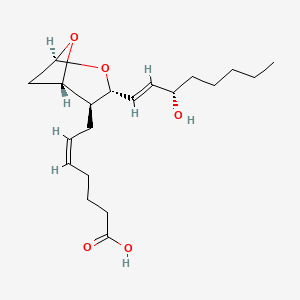
Thromboxane a2 |
Thromboxane a2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Thromboxane a2 is associated with abnormalities such as Asthma, Cardiovascular Diseases, Pulmonary Eosinophilia, ASPIRIN SENSITIVITY and Pneumonia. The involved functions are known as Signal Transduction, paracrine, Binding (Molecular Function), Platelet Activation and Inflammation. Thromboxane a2 often locates in Cell surface, Body tissue, Cell membrane, Blood and Extracellular. The associated genes with Thromboxane a2 are PTPRC gene, ESAM gene and PPBP gene. |
4534 |
|
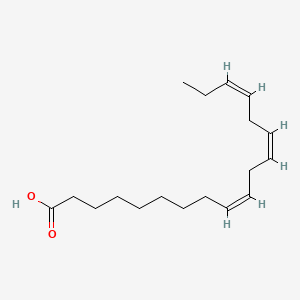
alpha-linolenic acid |
Alpha-linolenic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Alpha-linolenic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, abnormal fragmented structure, Arterial thrombosis and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Signal, Transcription, Genetic, Saturated and Regulation. Alpha-linolenic acid often locates in Blood, Body tissue, Plasma membrane, Hepatic and peroxisome. The associated genes with alpha-linolenic acid are FATE1 gene, volicitin, CYP2U1 gene, CYP1A2 gene and CYP2J2 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Dietary Fatty Acid, stearidonic acid and Fatty Acids, Nonesterified. |
4231 |
|
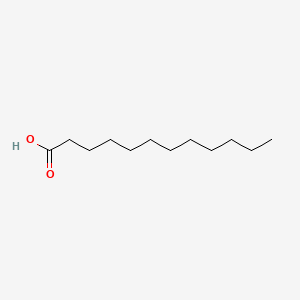
lauric acid |
lauric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Lauric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Renal tubular disorder, Hypertensive disease, Obesity and Mycoses. The involved functions are known as Transcription, Genetic, Signal Transduction, Mutation, metaplastic cell transformation and Anabolism. Lauric acid often locates in Skin, Plasma membrane, Cytoplasmic matrix, Body tissue and Palmar surface. The associated genes with lauric acid are Gene Family, SLC33A1 gene, Homologous Gene, Open Reading Frames and P4HTM gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Oleic Acids, Palmitates, Stearates and 9,11-linoleic acid. |
3691 |
|
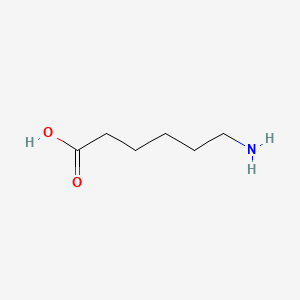
6-aminohexanoic acid |
6-aminohexanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 6-aminohexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular accident, Renal impairment and Scoliosis, unspecified. The involved functions are known as Fibrinolysis, Agent, Hemorrhage, plasminogen activation and inhibitors. 6-aminohexanoic acid often locates in Chest, Blood, Body tissue, peritoneal and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 6-aminohexanoic acid are P4HTM gene, BSND gene, MTPN gene, NDUFS4 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidylserines and Butyric Acid. |
3685 |
|
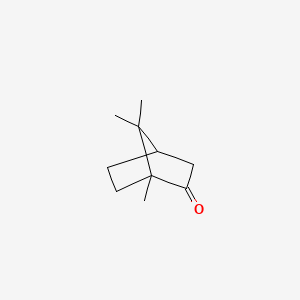
(+)-Camphor |
(+)-camphor is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. (+)-camphor is associated with abnormalities such as Athetoid cerebral palsy. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Synthesis, Feedback and Competitive inhibition. The associated genes with (+)-Camphor are 4S-limonene synthase. The related lipids are palmitoleic acid, pentadecanoic acid, stearic acid and erucic acid. |
3660 |
|
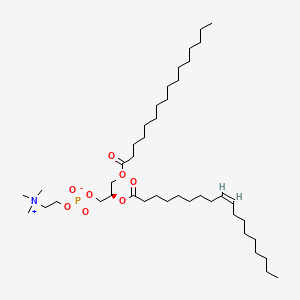
POPC |
POPC is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Popc is associated with abnormalities such as Hyperlipidemia, Atherosclerosis, Type I Mucolipidosis, Coronary Arteriosclerosis and Coronary Artery Disease. The involved functions are known as phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase activity, Denaturation, immunoreactivity, high-density lipoprotein particle remodeling and Process. Popc often locates in high-density lipoprotein particle, viral nucleocapsid location, Plasma membrane, spherical high-density lipoprotein particle and Face. The associated genes with POPC are Mutant Proteins, SCARB1 gene, SPEN gene, Polypeptides and globular protein. The related lipids are Total cholesterol, i-cholesterol, Fatty Acids, cholesteryl oleate and Cholesterol/Phospholipid. The related experimental models are Genetically Engineered Mouse. |
3550 |
|
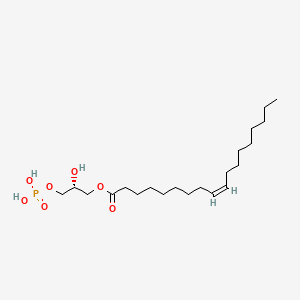
1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid |
1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. 1-oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Myocardial Infarction, early pregnancy, Scleroderma, Blind Vision and Hyperlipidemia. The involved functions are known as Agent, Blood coagulation, Selection, Genetic, Analyte and Biological Processes. 1-oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid often locates in Tissue specimen, Body tissue, Blood, Membrane and Skin. The associated genes with 1-Oleoyl Lysophosphatidic Acid are Mucin-16, Peptides, SMAD4 gene, RND1 gene and Polypeptides. The related lipids are lysophosphatidic acid, A(2)C, Lysophospholipids, Fatty Acids and sphingosine 1-phosphate. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out, Cancer Model, Xenograft Model and Arthritis, Adjuvant-Induced. |
3463 |









