|
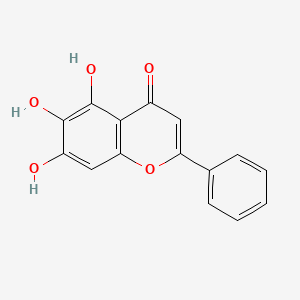
baicalein |
baicalein is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Baicalein is associated with abnormalities such as Neurodegenerative Disorders, Fibrillation, Hypertensive disease, Aortic coarctation and Coronary Occlusion. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Polymerization, Process, inhibitors and Pathogenesis. Baicalein often locates in Membrane, Lipid Bilayers, soluble, Cell-Free System and Protoplasm. The associated genes with baicalein are P4HTM gene, BIRC5 gene, TSPO gene, SHOC2 gene and XIAP gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Nonesterified Fatty Acids, iodoresiniferatoxin, Lipopolysaccharides and 17-octadecynoic acid. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model and Parkinsonism, Experimental. |
1997 |
|
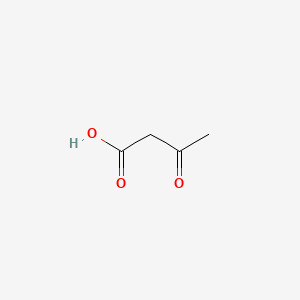
Acetoacetic acid |
Acetoacetic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class.Acetoacetic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Dehydration. The involved functions are known as Biochemical Reaction, intracellular signal transduction, fatty acid elongation, Cytokinesis and Mass-to-Charge Ratio. The associated genes with Acetoacetic acid are CFB gene and mersacidin. Acetoacetic acidis associated with Carbon, Acids, Potassium, Acetoacetic acid and Oximes. The related lipids are Nonesterified Fatty Acids and Stearates. |
2523 |

|
(r)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid |
(r)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
2710 |
|
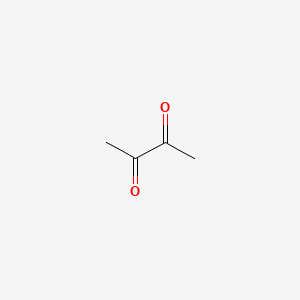
2,3-butanedione |
2,3-butanedione is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Physiologic Organization, Biochemical Pathway, physiological aspects, establishment and maintenance of localization and Phosphorylation. 2,3-butanedione often locates in Membrane, Microfilaments, Microtubules, Cell body of neuron and filamentous actin location. The associated genes with 2,3-butanedione are SLC33A1 gene and WASF1 gene. |
2715 |
|
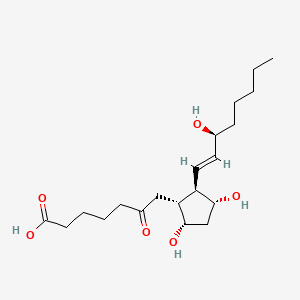
6-keto-pgf1alpha |
6-keto-pgf1alpha is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
3430 |
|
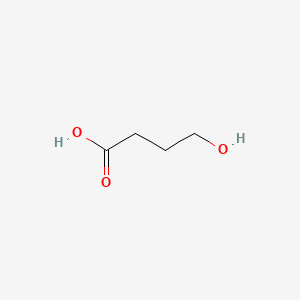
4-hydroxy-butyric acid |
4-hydroxy-butyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
3927 |
|
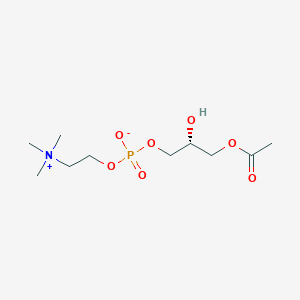
Lysophosphatidylcholine |
Lysophosphatidylcholine is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Lysophosphatidylcholine is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Fatty Liver and Atherosclerosis. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, antagonists, Signal Transduction, Signal Pathways and Saturated. Lysophosphatidylcholine often locates in Body tissue, Head, integral to membrane, Membrane and Extracellular. The associated genes with Lysophosphatidylcholine are RHOA gene, Homologous Gene, GPR4 gene, GPR68 gene and TRPV2 gene. The related lipids are Nonesterified Fatty Acids, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, Lysophosphatidylcholines, Phosphatidylserines and 25-hydroxycholesterol. The related experimental models are Knock-out and Disease model. |
4395 |
|
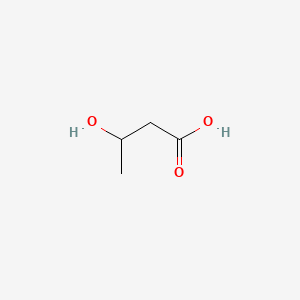
3-hydroxybutyric acid |
3-hydroxybutyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 3-hydroxybutyric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Ketosis. The involved functions are known as fatty acid oxidation, Oxidation, Synthesis, inhibitors and glucose metabolism. 3-hydroxybutyric acid often locates in Blood, Adipose tissue, Protoplasm, Hepatic and Extracellular. The associated genes with 3-hydroxybutyric acid are Genes, Developmental and Oncogene, RET. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Nonesterified, 6-hydroxyhexanoate, tributyrin, 3-Hydroxyvalerate and Valerates. |
4735 |
|
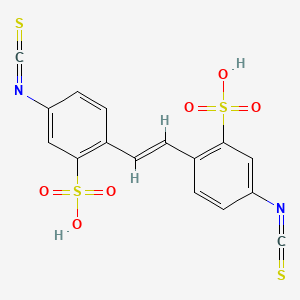
dids |
dids is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Dids is associated with abnormalities such as Cystic Fibrosis, Cardiovascular Diseases, Hypercholesterolemia, Senile Plaques and Tangier Disease. The involved functions are known as Cell Survival, exchanger, Uptake, Increased Sensitivy and inhibitors. Dids often locates in Extracellular, Cell surface, Tissue membrane, apical membrane and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with dids are P4HTM gene, GAPDH gene, SLC4A1 gene, ME1 gene and THOC4 gene. The related lipids are Total cholesterol and Butyrates. |
5017 |
|
quercetin |
quercetin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Quercetin is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, Myocardial Infarction, Cirrhosis, Coronary Arteriosclerosis and Vascular ring. The involved functions are known as Vasodilation, physiological aspects, Fermentation, Process and Ingredient. Quercetin often locates in Arterial system, Endothelium, Skin, Endothelium, Vascular and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with quercetin are P4HTM gene, SULT gene, UGT1A1 gene, ARHGAP26 gene and PLXNB1 gene. The related lipids are blood lipid, Promega, Steroids, Phosphatidylserines and Fatty Acids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Tissue Model and Cancer Model. |
5377 |









