|
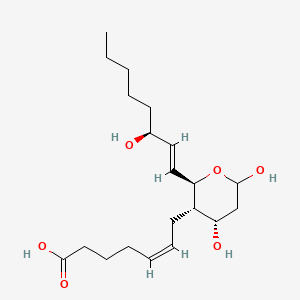
Thromboxane b2 |
Thromboxane b2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Thromboxane b2 is associated with abnormalities such as endothelial dysfunction, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Diabetes Mellitus, Ischemia and Thrombocytosis. The involved functions are known as Platelet Activation, Excretory function, Anabolism, Inflammation and mRNA Expression. Thromboxane b2 often locates in Endothelium, Hepatic and Microsomes, Liver. The associated genes with Thromboxane b2 are PTGS2 gene, prothrombin fragment 2 and CCL14 wt Allele. |
10175 |
|
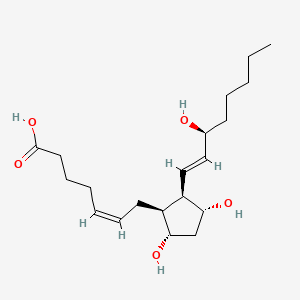
15-F2t-IsoP |
15-f2t-isop is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 15-f2t-isop is associated with abnormalities such as Diabetes Mellitus, Acute coronary syndrome, Risk factor, cardiovascular, thrombocytosis and Chronic ischemic heart disease NOS. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Inflammation, Lipid Peroxidation, Excretory function and Platelet Activation. The associated genes with 15-F2t-IsoP are PTGS2 gene. |
2120 |
|
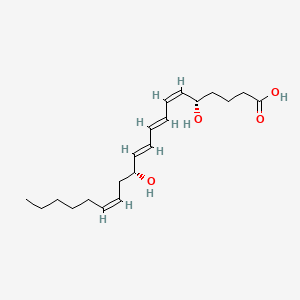
Leukotriene b4 |
Leukotriene b4 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Chemotaxis, release of sequestered calcium ion into cytoplasm and Polymerization. Leukotriene b4 often locates in Protoplasm. The associated genes with Leukotriene b4 are phallacidin. |
9311 |
|
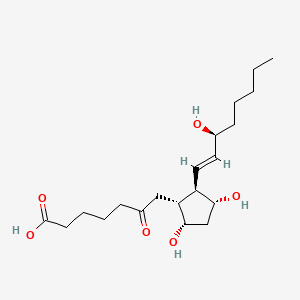
6-keto-pgf1alpha |
6-keto-pgf1alpha is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
3430 |
|
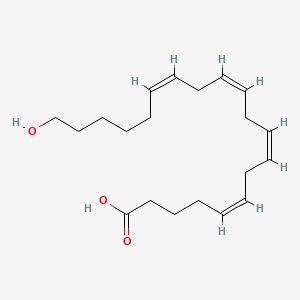
20-HETE |
20-hete is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 20-hete is associated with abnormalities such as Cyst, Kidney Diseases, Kidney Failure, Chronic, Cystic Kidney Diseases and Simple renal cyst. The involved functions are known as Phosphorylation, inhibitors, Hypertrophy, Epithelial Cell Proliferation and Anabolism. 20-hete often locates in Mouse Kidney, Microsomes, Tissue membrane, Body tissue and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with 20-HETE are CYP4F3 gene, PKHD1 gene, Transgenes, P4HTM gene and CYP2E1 gene. The related lipids are Promega, enterodiol, Fatty Acids, hexanoic acid and U 73343. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out, Streptozotocin Diabetes, Transgenic Model and Rodent Model. |
1257 |

|
11-deoxycorticosterone |
11-deoxycorticosterone is a lipid of Sterol Lipids (ST) class. The involved functions are known as Glycogen deposition and tyrosine aminotransferase activity. The associated genes with 11-deoxycorticosterone are PICK1 gene. The related lipids are Steroids. |
5531 |
|
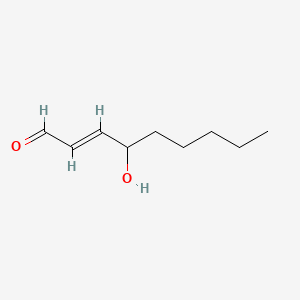
4-hydroxynonenal |
4-hydroxynonenal is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 4-hydroxynonenal is associated with abnormalities such as Chronic disease, Obesity, Diabetes, Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome and Lung diseases. The involved functions are known as protein expression, Glycolysis, mRNA Expression, Regulation and Mitochondrion in division. 4-hydroxynonenal often locates in Muscle, Mitochondria, Adipose tissue, Head and Mouse Muscle. The associated genes with 4-hydroxynonenal are STAT3 gene, SIRT1 gene, PGC gene, IL6 gene and cytochrome c''. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Lipid Peroxides, Promega, Membrane Lipids and oxidized lipid. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out, Transgenic Model, Disease model and Rodent Model. |
5685 |
|
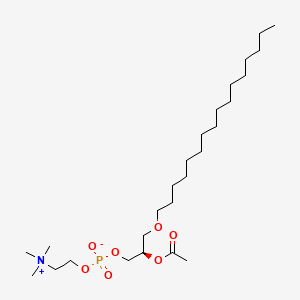
Platelet activating factor |
Platelet activating factor is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Platelet activating factor is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Acute cholecystitis without calculus, Cholecystitis, Colitis and Cholecystitis, Acute. The involved functions are known as Cell Survival, Metabolic Inhibition, lipid oxidation, Apoptosis and Oxidation. Platelet activating factor often locates in soluble, Cellular Membrane, Smooth muscle (tissue), Intima and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with Platelet activating factor are apolipoprotein A-I Milano, Homologous Gene, TSPO gene, HBEGF gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are Hydroxycholesterols, Liposomes, 25-hydroxycholesterol, Lysophosphatidylcholines and Lipopolysaccharides. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model and Transgenic Model. |
7383 |
|
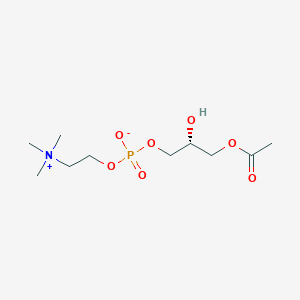
Lysophosphatidylcholine |
Lysophosphatidylcholine is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Lysophosphatidylcholine is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Fatty Liver and Atherosclerosis. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, antagonists, Signal Transduction, Signal Pathways and Saturated. Lysophosphatidylcholine often locates in Body tissue, Head, integral to membrane, Membrane and Extracellular. The associated genes with Lysophosphatidylcholine are RHOA gene, Homologous Gene, GPR4 gene, GPR68 gene and TRPV2 gene. The related lipids are Nonesterified Fatty Acids, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, Lysophosphatidylcholines, Phosphatidylserines and 25-hydroxycholesterol. The related experimental models are Knock-out and Disease model. |
4395 |
|
tacrolimus |
Tacrolimus is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Tacrolimus is associated with abnormalities such as Renal glomerular disease. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Fungicidal activity, Metabolic Inhibition, Excretory function and Dephosphorylation. Tacrolimus often locates in Hepatic, Mitochondrial matrix and Inner mitochondrial membrane. The associated genes with Tacrolimus are RHOA gene and BGN gene. |
12730 |









