|
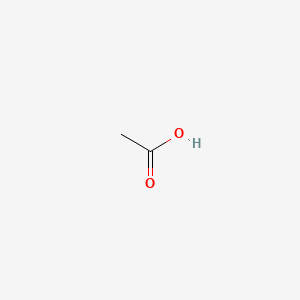
acetic acid |
acetic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Acetic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Vitamin B 12 Deficiency. The involved functions are known as Excretory function. The related lipids are Propionate. |
89633 |
|
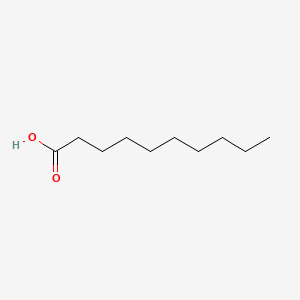
Decanoic acid |
Decanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Decanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Hashimoto Disease, Perisylvian syndrome, Parasitic Diseases, Acute myocardial infarction and Myocardial Infarction. The involved functions are known as Cell Differentiation process, Inflammation, Process, Subtraction process and Pressure- physical agent. Decanoic acid often locates in Epithelium, Tissue membrane, Body tissue, Membrane and Organelles. The associated genes with Decanoic acid are Genome, FATE1 gene, HTR3A wt Allele, FFAR1 gene and O3FAR1 gene. The related lipids are Membrane Lipids, Fatty Acids, Micelles, Stearic acid and rac-glycerol 1-monodecanoate. |
1677 |
|
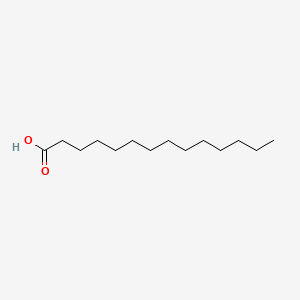
Tetradecanoic acid |
Tetradecanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Tetradecanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Chronic lung disease, Infection, Spastic syndrome, Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases. The involved functions are known as Fatty acid biosynthetic process, Anabolism, lung alveolus development, 5-(carboxyamino)imidazole ribonucleotide mutase activity and Homeostasis. Tetradecanoic acid often locates in Structure of parenchyma of lung, Blood, Head, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Tetradecanoic acid are SLC33A1 gene, SFTPA1 gene, P4HTM gene, Polypeptides and GPR132 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Nonesterified Fatty Acids, palmitoleic acid, Phosphatidylglycerols and Butanols. |
5058 |
|
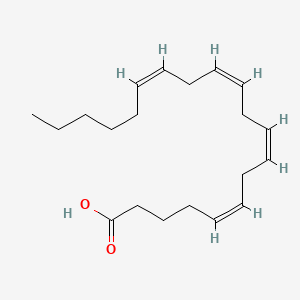
Arachidonic acid |
Arachidonic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Arachidonic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Ischemia, Hypertensive disease, Hypertension induced by pregnancy and Vascular ring of aorta. The involved functions are known as Platelet aggregation, Anabolism, Ion Transport, Signal Transduction Pathways and Signal. Arachidonic acid often locates in Extracellular, Body tissue, Protoplasm, Tissue membrane and soluble. The associated genes with Arachidonic acid are CYP2J2 gene, CYP2E1 gene, Recombinant Proteins, POR gene and P4HTM gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Glycerophospholipids, Steroids, octadecadienoic acid and 9-hydroxy-10,12-octadecadienoic acid. The related experimental models are Mouse Model and Knock-out. |
22864 |
|
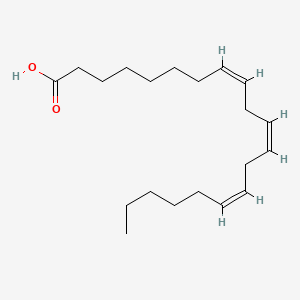
bishomo-gamma-linolenic acid |
Bishomo-gamma-linolenic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Bishomo-gamma-linolenic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Diabetes, Obesity, Hypertensive disease, Cirrhosis and Hepatorenal Syndrome. The involved functions are known as Oxidation, Process, Metabolic Inhibition, epoxide hydrolase activity and Signal Transduction Pathways. Bishomo-gamma-linolenic acid often locates in Protoplasm, Cytoplasmic matrix, soluble, Membrane and Tissue membrane. The associated genes with bishomo-gamma-linolenic acid are P4HTM gene, IMPACT gene, arginine methyl ester, CYP gene and PTGS1 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, 17-octadecynoic acid, Lipopolysaccharides, palmitoleic acid and nervonic acid. The related experimental models are Knock-out and Mouse Model. |
2467 |
|
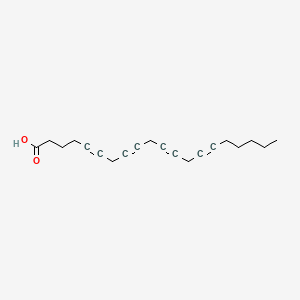
Etya |
Etya is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
1028 |
|
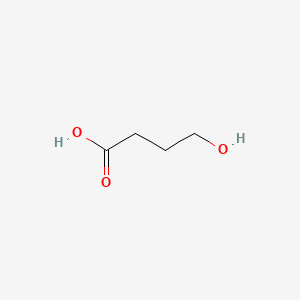
4-hydroxy-butyric acid |
4-hydroxy-butyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
3927 |

|
3-hydroxymyristic acid |
3-hydroxymyristic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, RNA Interference and photorespiration. 3-hydroxymyristic acid often locates in chloroplast starch grain. The related lipids are Fatty Acids. |
165 |
|
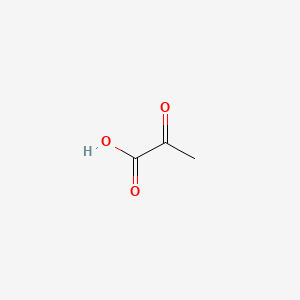
Pyruvic acid |
Pyruvic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
27047 |
|
4-aminobutyric acid |
4-aminobutyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 4-aminobutyric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Epilepsy and Premenstrual syndrome. The involved functions are known as Binding (Molecular Function), neuron survival, Process, Uptake and physiological aspects. 4-aminobutyric acid often locates in Microglial, Neurofilament, Neuraxis, Brain region and Neurites. The associated genes with 4-aminobutyric acid are arginine methyl ester, SLC33A1 gene, NKS1 gene, P4HTM gene and ITSN2 gene. The related lipids are pregnenolone sulfate, pregnane-20-one, Pregnanes, Steroids and endogenous steroids. |
19702 |

|
2,5-diaminopentanoic acid |
2,5-diaminopentanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Vasodilation, Intestinal Absorption and Pinocytosis. 2,5-diaminopentanoic acid often locates in Mitochondria, Microfilaments, NADH dehydrogenase complex and respiratory chain complex III location sensu Eukarya. The associated genes with 2,5-diaminopentanoic acid are GAPDH gene and iberiotoxin. |
8868 |
|
Lipoic acid |
Lipoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
7940 |
|
Malonic acid |
Malonic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Malonic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Malonic aciduria. The involved functions are known as Vmax, Regulation, Biochemical Pathway, Citric Acid Cycle and intermediary metabolism. Malonic acid often locates in Body tissue, Mitochondria, soluble and NADH dehydrogenase complex. The associated genes with Malonic acid are ACACA gene, ACSF3 gene, Recombinant Proteins, NKS1 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids and Butyric Acid. |
3587 |
|
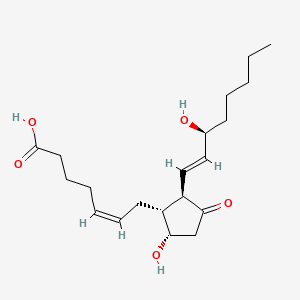
Prostaglandin E2 |
Prostaglandin E2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Prostaglandin e2 is associated with abnormalities such as Renal glomerular disease, Arthritis, Degenerative polyarthritis, Pancreatitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. The involved functions are known as enzyme pathway, Atherogenesis, Anabolism, inhibitors and Oxidants. Prostaglandin e2 often locates in Tissue membrane, Blood, Extracellular, Membrane and Protoplasm. The associated genes with Prostaglandin E2 are PTGS2 gene, TP53 gene, TNFRSF5 gene, FASTK Gene and TNF gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Steroids, monooxyethylene trimethylolpropane tristearate, Fatty Acids, Unsaturated and Promega. The related experimental models are Arthritis, Adjuvant-Induced, Xenograft Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis, Cancer Model and Knock-out. |
49278 |
|
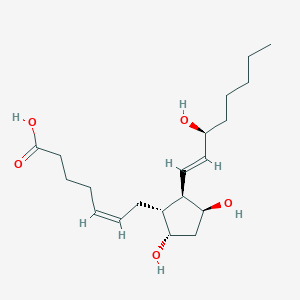
PGD2 |
Pgd2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Pgd2 is associated with abnormalities such as Inflammatory disorder, Pleurisy, Rhinitis, Dehydration and Pneumonia. The involved functions are known as antagonists, fat cell differentiation, Phosphorylation, Process and Gene Expression. Pgd2 often locates in Cell surface, Body tissue, Extracellular, Bone Marrow and Membrane. The associated genes with PGD2 are oxytocin, 1-desamino-(O-Et-Tyr)(2)-, P4HTM gene, PTGS2 gene, PTGDS gene and IL3 gene. The related lipids are 15-deoxyprostaglandin J2, Nonesterified Fatty Acids, Lipopolysaccharides, Steroids and Liposomes. The related experimental models are Knock-out and Rodent Model. |
6464 |
|
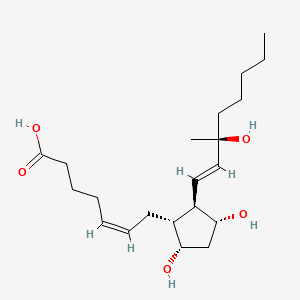
11beta-PGF2 |
11beta-pgf2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
15009 |
|
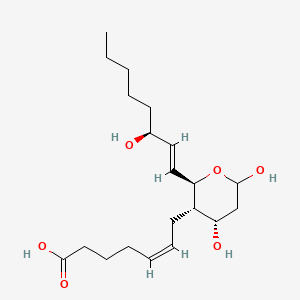
Carboprost |
Carboprost is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
289 |
|
Thromboxane b2 |
Thromboxane b2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Thromboxane b2 is associated with abnormalities such as endothelial dysfunction, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Diabetes Mellitus, Ischemia and Thrombocytosis. The involved functions are known as Platelet Activation, Excretory function, Anabolism, Inflammation and mRNA Expression. Thromboxane b2 often locates in Endothelium, Hepatic and Microsomes, Liver. The associated genes with Thromboxane b2 are PTGS2 gene, prothrombin fragment 2 and CCL14 wt Allele. |
10175 |
|
Stearaldehyde |
Stearaldehyde is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
457 |
|
Anandamide |
Anandamide is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Anandamide is associated with abnormalities such as Dehydration. The involved functions are known as Process, Phenomenon, Phosphorylation, Catabolic Process and Gene Expression. Anandamide often locates in Nuchal region, Microglial and Hepatic. The associated genes with Anandamide are SGPL1 gene, SPTLC1 gene, RPSA gene, KDSR gene and SMPD1 gene. The related lipids are Sphingolipids, Lipopolysaccharides, Lysophospholipids, LYSO-PC and lysophosphatidylethanolamine. |
4747 |
|
Hexane |
Hexane is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
9183 |
|
Platelet activating factor |
Platelet activating factor is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Platelet activating factor is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Acute cholecystitis without calculus, Cholecystitis, Colitis and Cholecystitis, Acute. The involved functions are known as Cell Survival, Metabolic Inhibition, lipid oxidation, Apoptosis and Oxidation. Platelet activating factor often locates in soluble, Cellular Membrane, Smooth muscle (tissue), Intima and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with Platelet activating factor are apolipoprotein A-I Milano, Homologous Gene, TSPO gene, HBEGF gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are Hydroxycholesterols, Liposomes, 25-hydroxycholesterol, Lysophosphatidylcholines and Lipopolysaccharides. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model and Transgenic Model. |
7383 |
|
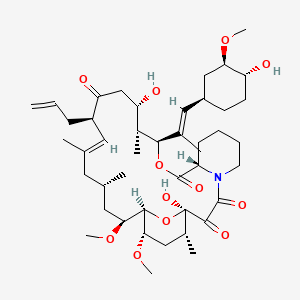
tacrolimus |
Tacrolimus is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Tacrolimus is associated with abnormalities such as Renal glomerular disease. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Fungicidal activity, Metabolic Inhibition, Excretory function and Dephosphorylation. Tacrolimus often locates in Hepatic, Mitochondrial matrix and Inner mitochondrial membrane. The associated genes with Tacrolimus are RHOA gene and BGN gene. |
12730 |
|
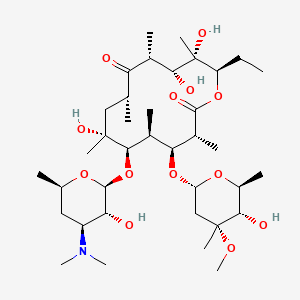
erythromycin |
erythromycin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Erythromycin is associated with abnormalities such as Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, Pneumonia, Infection, Pneumococcal Infections and Exanthema. The involved functions are known as Pharmacodynamics, Sterility, Agent, Drug Kinetics and Adjudication. Erythromycin often locates in Blood, peritoneal, Extracellular, Ribosomes and apicoplast. The associated genes with erythromycin are P4HTM gene, SLC33A1 gene, FAM3B gene, Operon and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Hydroxytestosterones, Steroids, Propionate, Mycolic Acids and campesterol. The related experimental models are Mouse Model and Knock-out. |
19871 |
|
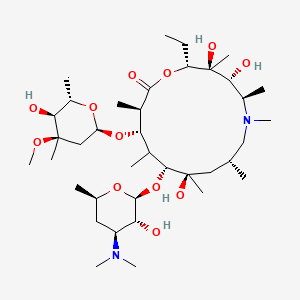
Azithramycine |
Azithramycine is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Azithramycine is associated with abnormalities such as Respiratory Tract Infections, Pneumonia, Lower respiratory tract infection, Infection and Nonspecific urethritis. The involved functions are known as Lysis, Selection, Genetic, Mutation, Relapse and Adaptation. Azithramycine often locates in Blood, Respiratory System, Genitourinary system, Back and Chest. The associated genes with Azithramycine are Genes, rRNA, Genome, RPL22 gene, OPRM1 gene and tryptic soy broth. The related lipids are Liposomes, Phosphatidylserines, Promega, Lipopolysaccharides and Steroids. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out and Tissue Model. |
7835 |
|
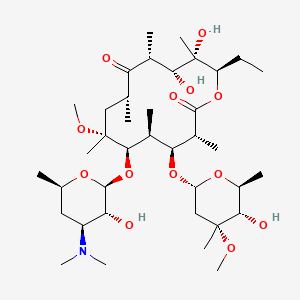
clarithromycin |
clarithromycin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Clarithromycin is associated with abnormalities such as Helicobacter Pylori Infection, Infection, Coinfection, Gastritis and Peptic Ulcer. The involved functions are known as Point Mutation, Increased Sensitivy, Bacterial resistance, urease activity and Mutation. Clarithromycin often locates in Blood, Gastric mucosa, Biopsy sample, Respiratory System and Entire gastrointestinal tract. The associated genes with clarithromycin are Genes, rRNA, rRNA Operon, Genome, HM13 gene and GDF15 gene. The related lipids are 9,11-linoleic acid, Steroids, Lysophosphatidylcholines, Lipopolysaccharides and 4-hydroxycholesterol. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out and Experimental Pneumococcal Meningitis. |
10449 |

|
ZEARALENONE |
ZEARALENONE is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Zearalenone is associated with abnormalities such as HYPOTRICHOSIS, LOCALIZED, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE, 2, Estrogen excess, Food-Drug Interactions, Osteomalacia and Osteoporosis. The involved functions are known as mRNA Expression, Metabolic Inhibition, Phosphorylation, Agent and Transcriptional Activation. Zearalenone often locates in Gastrointestinal tract structure, soluble, viral nucleocapsid location, Spindle and Hepatic. The associated genes with ZEARALENONE are Candidate Disease Gene, Genome, Genes, Reporter, P4HTM gene and Open Reading Frames. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Steroids, Fatty Acids and Promega. The related experimental models are Transgenic Model. |
2573 |
|
minocycline |
minocycline is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Minocycline is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Soft Tissue Infections, Septicemia, Chronic hyponatremia and Lesion of brain. The involved functions are known as Pharmacodynamics, Gene Expression, Transcriptional Activation, Regulation and Process. Minocycline often locates in Ribosomes, 50S ribosomal subunit, Blood, Skin and Immune system. The associated genes with minocycline are THEMIS gene, KCNK2 gene, RBFOX3 gene, PIWIL2 gene and P4HTM gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Promega, Steroids, Liposomes and Octanols. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis, Genetically Engineered Mouse, Disease model and spinal model. |
9780 |
|
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate |
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. (-)-epigallocatechin gallate is associated with abnormalities such as IMMUNE SUPPRESSION, Infection, Nodule, Lymphopenia and Tumor Immunity. The involved functions are known as Apoptosis, Cellular Immune Response, Specific immune response, Signal and Infiltration. (-)-epigallocatechin gallate often locates in Immune system, Cytoplasmic Granules, Skin, Protoplasm and Body tissue. The associated genes with (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate are C8orf4 gene, Genes, vpr, MAPK8 gene, P4HTM gene and GAG Gene. The related lipids are Promega, Lipopolysaccharides, Palmitates, Fatty Acids and Sphingolipids. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Transgenic Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Arthritis, Collagen-Induced. |
6551 |

|
SCHEMBL105486 |
Kakonein is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Kakonein is associated with abnormalities such as Fatty Liver, Chronic liver disease, Morphologically altered structure, Hypertensive disease and Cardiovascular Diseases. The involved functions are known as protein expression, Extravasation, Liver damage, mRNA Expression and cell activation. Kakonein often locates in Body tissue, Hepatic, Microvilli, Cytoplasm and Membrane. The associated genes with Kakonein are TJP1 gene, CD14 gene, iberiotoxin, AT-Rich Interactive Domain-Containing Protein 1A and NKS1 gene. The related lipids are dehydrosoyasaponin I and Steroids. The related experimental models are Knock-out. |
1391 |
|
quercetin |
quercetin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Quercetin is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, Myocardial Infarction, Cirrhosis, Coronary Arteriosclerosis and Vascular ring. The involved functions are known as Vasodilation, physiological aspects, Fermentation, Process and Ingredient. Quercetin often locates in Arterial system, Endothelium, Skin, Endothelium, Vascular and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with quercetin are P4HTM gene, SULT gene, UGT1A1 gene, ARHGAP26 gene and PLXNB1 gene. The related lipids are blood lipid, Promega, Steroids, Phosphatidylserines and Fatty Acids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Tissue Model and Cancer Model. |
5377 |
|
doxorubicin |
Adriamycin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Adriamycin is associated with abnormalities such as Cardiomyopathies. The involved functions are known as Transcription, Genetic, Process, Drug effect disorder, Diastasis and Oxidation-Reduction. Adriamycin often locates in Muscle, Myocardium and Entire gastrointestinal tract. |
54913 |
|
Parthenolide |
Parthenolide is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Parthenolide is associated with abnormalities such as Migraine Disorders, abnormal fragmented structure, Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal, Consumption-archaic term for TB and Infection. The involved functions are known as Apoptosis, Cell Proliferation, Inflammation, pathologic cytolysis and Membrane Potentials. Parthenolide often locates in Mitochondria, Tissue membrane, Cytoplasmic matrix, Cytoplasm and Body tissue. The associated genes with Parthenolide are IGKJ1 gene, BCL2 gene, DDIT3 gene, Procaspase 7 and GAPDH gene. The related lipids are A(2)C. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Breast Cancer Model and Cancer Model. |
925 |
|
N-acetylsphingosine |
N-acetylsphingosine is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. N-acetylsphingosine is associated with abnormalities such as Morphologically altered structure, Atherosclerosis, Cardiovascular Diseases, Hyperinsulinism and Gigantism. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, anti-apoptosis, Apoptosis, Dephosphorylation and immunoreactivity. N-acetylsphingosine often locates in Plasma membrane, Mitochondria, Pore, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with N-acetylsphingosine are EGR3 gene, CFB gene, FATE1 gene, P4HTM gene and PFDN4 gene. The related lipids are Sphingolipids, Cardiolipins, Glycerophospholipids, dihydroceramide and Phosphatidic Acid. |
633 |
|
prednisone |
Prednisone is a lipid of Sterol Lipids (ST) class. Prednisone is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Hyperbilirubinemia, Aspergillosis, Allergic Bronchopulmonary, Asthma and Pulmonary infiltrates. The involved functions are known as Relapse, Recurrence, Obstruction, continuance and Philadelphia Chromosome. Prednisone often locates in Bone Marrow. The associated genes with prednisone are MLLT2 wt Allele, BCR-ABL Fusion Gene, TCF3 gene, PBX1 gene and ABCB1 gene. |
27879 |


































