| MeSH term | MeSH ID | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | D000230 | 166 associated lipids |
| Body Weight | D001835 | 333 associated lipids |
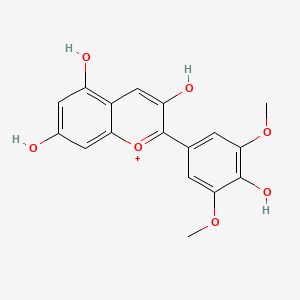
Malvidin
Malvidin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. The involved functions are known as conjugation.
Cross Reference
Introduction
To understand associated biological information of Malvidin, we collected biological information of abnormalities, associated pathways, cellular/molecular locations, biological functions, related genes/proteins, lipids and common seen animal/experimental models with organized paragraphs from literatures.
What diseases are associated with Malvidin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
Possible diseases from mapped MeSH terms on references
We collected disease MeSH terms mapped to the references associated with Malvidin
PubChem Associated disorders and diseases
What pathways are associated with Malvidin
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and Pathways
Link to PubChem Biomolecular Interactions and PathwaysWhat cellular locations are associated with Malvidin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What functions are associated with Malvidin?
Related references are published most in these journals:
| Function | Cross reference | Weighted score | Related literatures |
|---|
What lipids are associated with Malvidin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What genes are associated with Malvidin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
What common seen animal models are associated with Malvidin?
There are no associated biomedical information in the current reference collection.
NCBI Entrez Crosslinks
All references with Malvidin
Download all related citations| Authors | Title | Published | Journal | PubMed Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khandelwal N and Abraham SK | Protective effects of common anthocyanidins against genotoxic damage induced by chemotherapeutic drugs in mice. | 2014 | Planta Med. | pmid:25184891 |
| Harb J et al. | Changes in polyphenols and expression levels of related genes in 'Duke' blueberries stored under high CO2 levels. | 2014 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:24999801 |
| Lin YC et al. | Protective effect of anthocyanidins against sodium dithionite-induced hypoxia injury in C6 glial cells. | 2014 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:24845373 |
| Muñoz C et al. | Relationships among gene expression and anthocyanin composition of Malbec grapevine clones. | 2014 | J. Agric. Food Chem. | pmid:24983916 |
| Vodopivec BM et al. | Differences in the structure of anthocyanins from the two amphibious plants, Lobelia cardinalis and Nesaea crassicaulis. | 2013 | Nat. Prod. Res. | pmid:22694738 |
| Kumar S et al. | Identification of antimutagenic properties of anthocyanins and other polyphenols from rose (Rosa centifolia) petals and tea. | 2013 | J. Food Sci. | pmid:23627876 |
| Quintieri AM et al. | Malvidin, a red wine polyphenol, modulates mammalian myocardial and coronary performance and protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. | 2013 | J. Nutr. Biochem. | pmid:23266283 |
| Bognar E et al. | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in RAW264.7 macrophages of malvidin, a major red wine polyphenol. | 2013 | PLoS ONE | pmid:23755222 |
| Malaj N et al. | Spectrophotometric study of the copigmentation of malvidin 3-O-glucoside with p-coumaric, vanillic and syringic acids. | 2013 | Food Chem | pmid:23993528 |
| Chauthe SK et al. | Quantitative NMR: an applicable method for quantitative analysis of medicinal plant extracts and herbal products. | 2012 Nov-Dec | Phytochem Anal | pmid:22707000 |