|
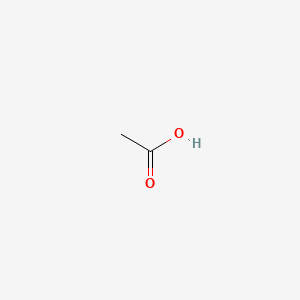
acetic acid |
acetic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Acetic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Vitamin B 12 Deficiency. The involved functions are known as Excretory function. The related lipids are Propionate. |
89633 |
|
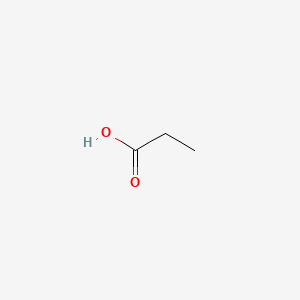
propionic acid |
propionic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Propionic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Epilepsy, Infection, Tuberculosis, Alkalosis and Ischemia. The involved functions are known as Uptake, Biosynthetic Pathways, Methylation, Protein Overexpression and Biochemical Pathway. Propionic acid often locates in Body tissue, Cytoplasmic matrix, Membrane, Protoplasm and Extracellular. The associated genes with propionic acid are TRIO gene, TRRAP gene, SLC5A8 gene, SLC33A1 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Propionate, butyrate, Valerates and mycocerosic acid. |
7360 |
|
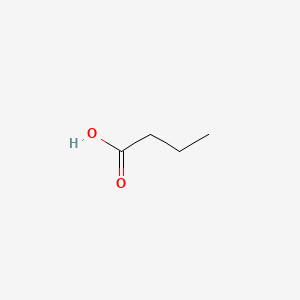
butyric acid |
butyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Butyric acid is associated with abnormalities such as PARKINSON DISEASE, LATE-ONSET, Colitis, Autoimmune Diseases, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and PARAGANGLIOMAS 2. The involved functions are known as DNA Methylation, Transcription, Genetic, chromatin modification, Gene Expression and Gene Silencing. Butyric acid often locates in Membrane, Chromatin Structure, Chromosomes, viral nucleocapsid location and Ribosomes. The associated genes with butyric acid are Locus, Genes, Dominant, Genes, rRNA, Genome and Chromatin. The related lipids are Butyrates, butyrate, Promega, Butyric Acids and Butyric Acid. |
9358 |
|
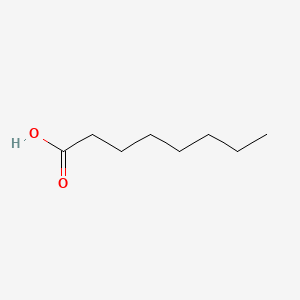
octanoic acid |
octanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Octanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Ischemia, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Diabetes, Cardiomyopathies and Obesity. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, 5-(carboxyamino)imidazole ribonucleotide mutase activity, Citric Acid Cycle, Metabolic Inhibition and Excretory function. Octanoic acid often locates in Pore, Protoplasm, Endothelium, Mitochondria and Muscle. The associated genes with octanoic acid are P4HTM gene, CPT1A gene, HADH gene, ACSL1 Gene and CD36 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Nonesterified Fatty Acids, Oleates, Palmitates and hexanoic acid. |
3349 |
|
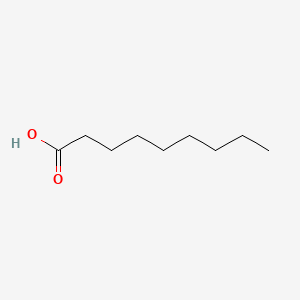
NONANOIC ACID |
NONANOIC ACID is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Nonanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as megalocytosis, Hypos, Renal tubular disorder, Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Adult and Little's Disease. The involved functions are known as Gene Expression, Signal Transduction, Regulation, Cell Cycle and Force. Nonanoic acid often locates in Membrane, Protoplasm, Body tissue, Extracellular and Cell membrane. The associated genes with NONANOIC ACID are cysteinylglycine, glycylsarcosine, arginine methyl ester, GLI3 gene and ADRBK1 gene. The related lipids are 1-octen-3-ol, Butyric Acids, palmitoleic acid, pentadecanoic acid and stearic acid. |
541 |

|
4-Methyloctanoic acid |
4-Methyloctanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 4-methyloctanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Epilepsy, Migraine Disorders, Alzheimer's Disease and Little's Disease. The involved functions are known as Signal Transduction, inhibitors, Synthesis, PI3K activity and Anabolism. 4-methyloctanoic acid often locates in Head and Growth Cones. The associated genes with 4-Methyloctanoic acid are PTEN gene, Homologous Gene and Genome. The related lipids are Saponin and branched chain fatty acid. |
18 |
|
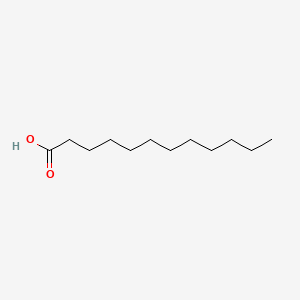
lauric acid |
lauric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Lauric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Renal tubular disorder, Hypertensive disease, Obesity and Mycoses. The involved functions are known as Transcription, Genetic, Signal Transduction, Mutation, metaplastic cell transformation and Anabolism. Lauric acid often locates in Skin, Plasma membrane, Cytoplasmic matrix, Body tissue and Palmar surface. The associated genes with lauric acid are Gene Family, SLC33A1 gene, Homologous Gene, Open Reading Frames and P4HTM gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Oleic Acids, Palmitates, Stearates and 9,11-linoleic acid. |
3691 |
|
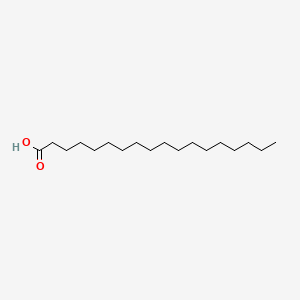
stearic acid |
stearic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Stearic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Helminthiasis, Exanthema, Chronic disease, Obesity and Dyslipidemias. The involved functions are known as acyltransferase activity, Mutation, Cell division, cell fate and Fatty Acid Metabolism. Stearic acid often locates in membrane fraction, Mouse Liver, Membrane, Body tissue and Endoplasmic reticulum, membrane. The associated genes with stearic acid are Homologous Gene, ACLY gene, Transgenes, FATE1 gene and Alleles. The related lipids are Lysophospholipids, Stearic acid, Fatty Acids, cis-vaccenic acid and Phosphatidylserines. The related experimental models are Knock-out. |
5692 |
|
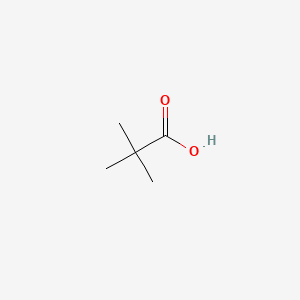
Pivalic acid |
Pivalic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Pivalic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Renal carnitine transport defect, Carnitine deficiency, Urinary tract infection, Otitis Media and Chronic infectious disease. The involved functions are known as carnitine transport, Uptake, inhibitors, Oxidation and Intestinal Absorption. Pivalic acid often locates in Grey line. The related lipids are pivalic acid and Fatty Acids. |
411 |
|
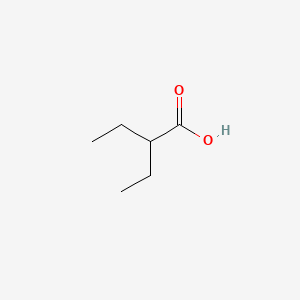
2-ETHYLBUTYRIC ACID |
2-ETHYLBUTYRIC ACID is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
26 |
|
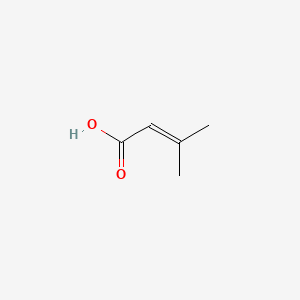
3-methylbut-2-enoic acid |
3-methylbut-2-enoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as volatile substances, Anabolism, Pressure- physical agent, Adaptation and mevalonate pathway. 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid often locates in Cell membrane and Membrane. The associated genes with 3-methylbut-2-enoic acid are tryptones. The related lipids are Butyric Acids. |
88 |
|
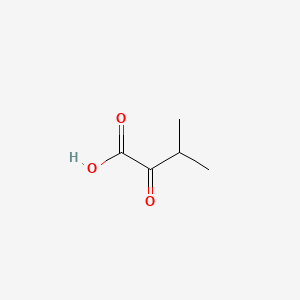
3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid |
3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Maple Syrup Urine Disease and Kidney Failure, Chronic. The involved functions are known as Phosphorylation, Citric Acid Cycle, inhibitors, Process and Metabolic Control. 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid often locates in Mitochondria, BL21, Cytoplasm, Ribosomes and Head. The associated genes with 3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid are Genome, Homologous Gene, Operon, Alleles and Oxidoreductase Gene. The related lipids are dimyristoylphosphatidylglycerol, 9-oxononanoic acid, Valerates and alpha-ketocaproic acid. |
1021 |
|
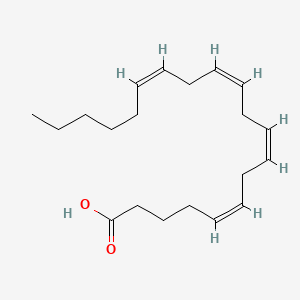
Arachidonic acid |
Arachidonic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Arachidonic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Ischemia, Hypertensive disease, Hypertension induced by pregnancy and Vascular ring of aorta. The involved functions are known as Platelet aggregation, Anabolism, Ion Transport, Signal Transduction Pathways and Signal. Arachidonic acid often locates in Extracellular, Body tissue, Protoplasm, Tissue membrane and soluble. The associated genes with Arachidonic acid are CYP2J2 gene, CYP2E1 gene, Recombinant Proteins, POR gene and P4HTM gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Glycerophospholipids, Steroids, octadecadienoic acid and 9-hydroxy-10,12-octadecadienoic acid. The related experimental models are Mouse Model and Knock-out. |
22864 |
|
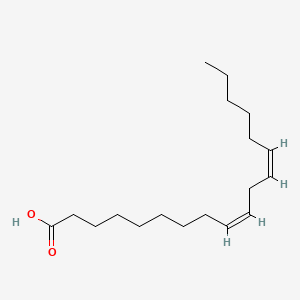
Linoleic acid |
Linoleic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Linoleic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Metabolic syndrome, Obesity, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease and Pneumonia. The involved functions are known as Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, Synthesis, Pathological accumulation of air in tissues and cytokine biosynthesis. The associated genes with Linoleic acid are TNF gene, CCL2 gene and TLR4 gene. The related lipids are palmitoleic acid, nervonic acid and Sphingolipids. |
5699 |
|
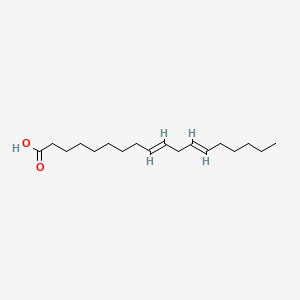
Linoelaidic acid |
Linoelaidic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Linoelaidic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease and Metabolic syndrome. The involved functions are known as Metabolic Inhibition, Steroid biosynthesis, Signal Transduction, Insulin Resistance and Inflammation. Linoelaidic acid often locates in Mitochondria, Membrane and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Linoelaidic acid are FFAR1 gene, C9orf7 gene, TNF gene, CCL2 gene and TLR4 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, octadecadienoic acid, Steroids, methyl linoleate and Cyanoketone. |
10058 |
|
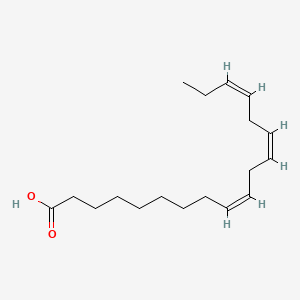
alpha-linolenic acid |
Alpha-linolenic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Alpha-linolenic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, abnormal fragmented structure, Arterial thrombosis and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Signal, Transcription, Genetic, Saturated and Regulation. Alpha-linolenic acid often locates in Blood, Body tissue, Plasma membrane, Hepatic and peroxisome. The associated genes with alpha-linolenic acid are FATE1 gene, volicitin, CYP2U1 gene, CYP1A2 gene and CYP2J2 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Dietary Fatty Acid, stearidonic acid and Fatty Acids, Nonesterified. |
4231 |
|
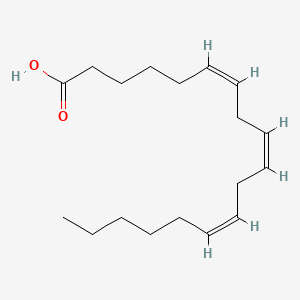
gamma-Linolenic acid |
Gamma-linolenic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Drug Interactions. Gamma-linolenic acid often locates in Articular system. |
1919 |
|
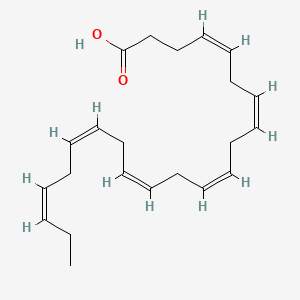
DHA |
Dha is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Dha is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Consumption-archaic term for TB, Chronic disease, Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, Oxidation, fatty acid oxidation, Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Metabolism. Dha often locates in Hepatic, Protoplasm, Mucous Membrane, Epithelium and outer membrane. The associated genes with DHA are IMPACT gene, FATE1 gene, GAPDH gene, THOC4 gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are stearidonic acid, Fatty Acids, Total cholesterol, Lipopolysaccharides and Dietary Fatty Acid. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Transgenic Model, Animal Disease Models and Arthritis, Experimental. |
11054 |
|
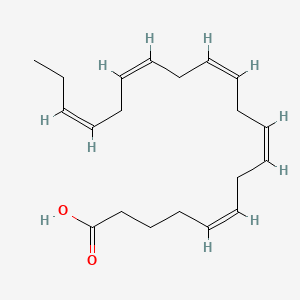
EPA |
Epa is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
5952 |
|
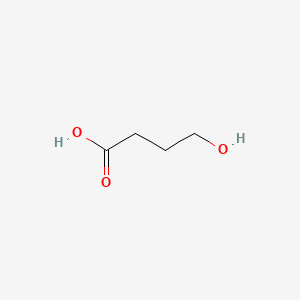
4-hydroxy-butyric acid |
4-hydroxy-butyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
3927 |
|
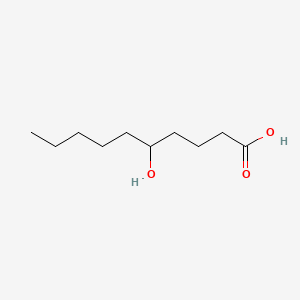
5-hydroxy capric acid |
5-hydroxy capric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
1410 |
|
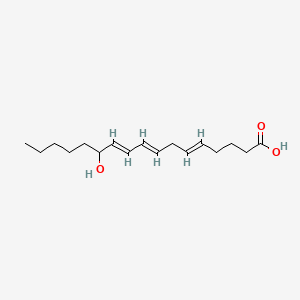
12-hydroxy-5,8,10-heptadecatrienoic acid |
12-hydroxy-5,8,10-heptadecatrienoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
196 |
|
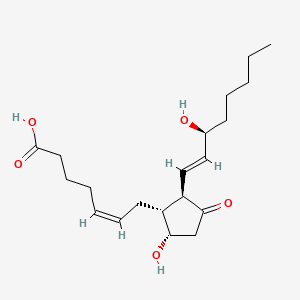
PGD2 |
Pgd2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Pgd2 is associated with abnormalities such as Inflammatory disorder, Pleurisy, Rhinitis, Dehydration and Pneumonia. The involved functions are known as antagonists, fat cell differentiation, Phosphorylation, Process and Gene Expression. Pgd2 often locates in Cell surface, Body tissue, Extracellular, Bone Marrow and Membrane. The associated genes with PGD2 are oxytocin, 1-desamino-(O-Et-Tyr)(2)-, P4HTM gene, PTGS2 gene, PTGDS gene and IL3 gene. The related lipids are 15-deoxyprostaglandin J2, Nonesterified Fatty Acids, Lipopolysaccharides, Steroids and Liposomes. The related experimental models are Knock-out and Rodent Model. |
6464 |
|
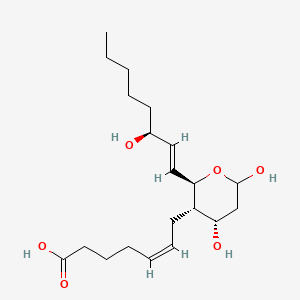
Thromboxane b2 |
Thromboxane b2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Thromboxane b2 is associated with abnormalities such as endothelial dysfunction, Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent, Diabetes Mellitus, Ischemia and Thrombocytosis. The involved functions are known as Platelet Activation, Excretory function, Anabolism, Inflammation and mRNA Expression. Thromboxane b2 often locates in Endothelium, Hepatic and Microsomes, Liver. The associated genes with Thromboxane b2 are PTGS2 gene, prothrombin fragment 2 and CCL14 wt Allele. |
10175 |
|
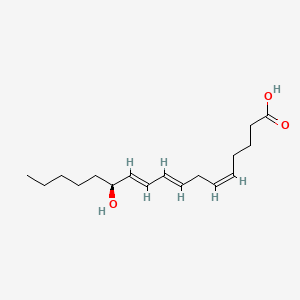
12s-hhtre |
12s-hhtre is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
113 |

|
(r)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid |
(r)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
2710 |
|
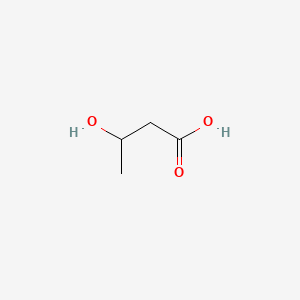
3-hydroxybutyric acid |
3-hydroxybutyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 3-hydroxybutyric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Ketosis. The involved functions are known as fatty acid oxidation, Oxidation, Synthesis, inhibitors and glucose metabolism. 3-hydroxybutyric acid often locates in Blood, Adipose tissue, Protoplasm, Hepatic and Extracellular. The associated genes with 3-hydroxybutyric acid are Genes, Developmental and Oncogene, RET. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Nonesterified, 6-hydroxyhexanoate, tributyrin, 3-Hydroxyvalerate and Valerates. |
4735 |
|
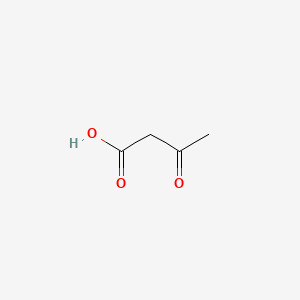
Acetoacetic acid |
Acetoacetic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class.Acetoacetic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Dehydration. The involved functions are known as Biochemical Reaction, intracellular signal transduction, fatty acid elongation, Cytokinesis and Mass-to-Charge Ratio. The associated genes with Acetoacetic acid are CFB gene and mersacidin. Acetoacetic acidis associated with Carbon, Acids, Potassium, Acetoacetic acid and Oximes. The related lipids are Nonesterified Fatty Acids and Stearates. |
2523 |
|
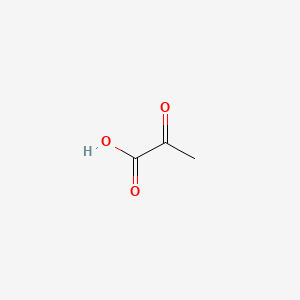
Pyruvic acid |
Pyruvic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
27047 |
|
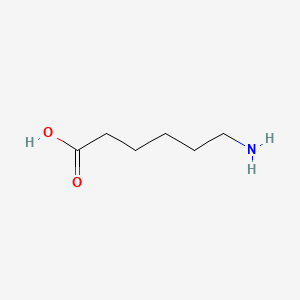
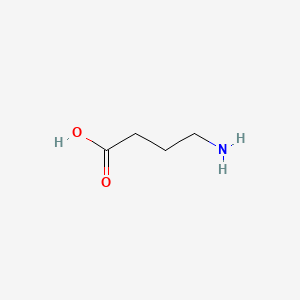
6-aminohexanoic acid |
6-aminohexanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 6-aminohexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular accident, Renal impairment and Scoliosis, unspecified. The involved functions are known as Fibrinolysis, Agent, Hemorrhage, plasminogen activation and inhibitors. 6-aminohexanoic acid often locates in Chest, Blood, Body tissue, peritoneal and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 6-aminohexanoic acid are P4HTM gene, BSND gene, MTPN gene, NDUFS4 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidylserines and Butyric Acid. |
3685 |
|
4-aminobutyric acid |
4-aminobutyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 4-aminobutyric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Epilepsy and Premenstrual syndrome. The involved functions are known as Binding (Molecular Function), neuron survival, Process, Uptake and physiological aspects. 4-aminobutyric acid often locates in Microglial, Neurofilament, Neuraxis, Brain region and Neurites. The associated genes with 4-aminobutyric acid are arginine methyl ester, SLC33A1 gene, NKS1 gene, P4HTM gene and ITSN2 gene. The related lipids are pregnenolone sulfate, pregnane-20-one, Pregnanes, Steroids and endogenous steroids. |
19702 |
|
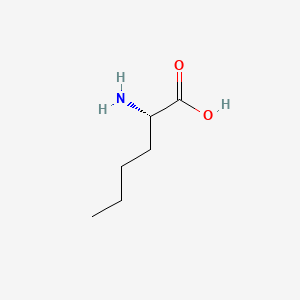
L-norleucine |
L-norleucine is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. L-norleucine is associated with abnormalities such as Neonatal maladjustment syndrome, Virus Diseases, Kidney Failure, Chronic, Infection and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. The involved functions are known as Proteolysis, Metabolic Inhibition, Oxidation, immunoreactivity and Sterility. L-norleucine often locates in Blood, Body tissue, Membrane, Protoplasm and Adipose tissue. The associated genes with L-norleucine are N(6)-carboxymethyllysine, P4HTM gene, Polypeptides, EIF3K gene and aminoacid analog. The related lipids are Liposomes and Membrane Lipids. |
2389 |
|
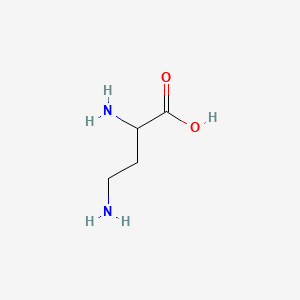
2,4-diamino-butyric acid |
2,4-diamino-butyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
278 |
|
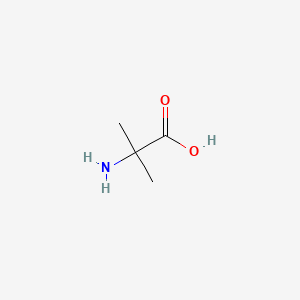
2-amino-isobutyric acid |
2-amino-isobutyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
1792 |

|
2,5-diaminopentanoic acid |
2,5-diaminopentanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Vasodilation, Intestinal Absorption and Pinocytosis. 2,5-diaminopentanoic acid often locates in Mitochondria, Microfilaments, NADH dehydrogenase complex and respiratory chain complex III location sensu Eukarya. The associated genes with 2,5-diaminopentanoic acid are GAPDH gene and iberiotoxin. |
8868 |
|
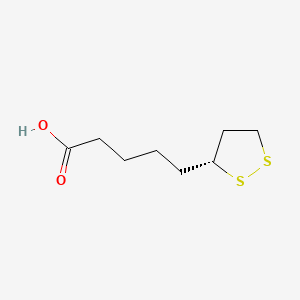
Lipoic acid |
Lipoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
7940 |
|
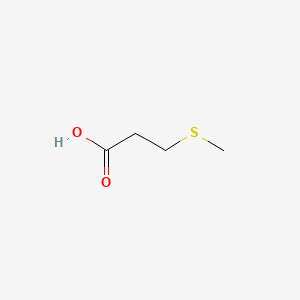
3-methyl-thiopropionic acid |
3-methyl-thiopropionic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
70 |
|
Palmitoyl-EA |
Palmitoyl-ea is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Cytokinesis of the fertilized ovum and phosphatase activity. The related lipids are stearic acid. |
1001 |
|
Aminoadipic acid |
Aminoadipic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Aminoadipic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Diabetes and Proliferative retinopathy NOS. The involved functions are known as Uptake, Process, lysine catabolism, Pressure- physical agent and Proteolysis. Aminoadipic acid often locates in Protoplasm, Chromosomes, Astrocytic, Basal lamina and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Aminoadipic acid are Homologous Gene, Excitatory Amino Acids, allysine, Diaminopimelic Acid and Gene Clusters. |
1114 |
|
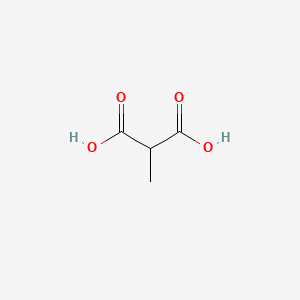
Methylmalonic acid |
Methylmalonic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Methylmalonic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Vitamin B 12 Deficiency, Osteoporosis, Anemia, Anemia, Megaloblastic and Renal impairment. The involved functions are known as Abnormal renal function, Lactation, physiological aspects, phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase activity and Excretory function. Methylmalonic acid often locates in Entire bony skeleton, Blood, Protoplasm, Muscle and Body tissue. The associated genes with Methylmalonic acid are IMPACT gene, ACSF3 gene, CBLC gene, MMADHC gene and LMBRD1 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids and Butanols. |
3174 |
|
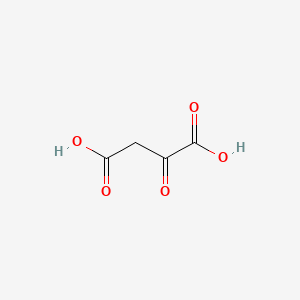
Oxalacetic acid |
Oxalacetic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
3226 |
|
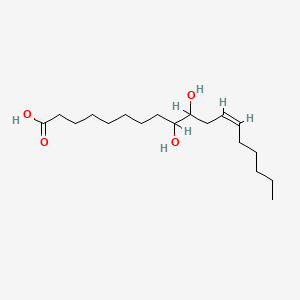
9,10-DiHOME |
9,10-dihome is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
1159 |
|
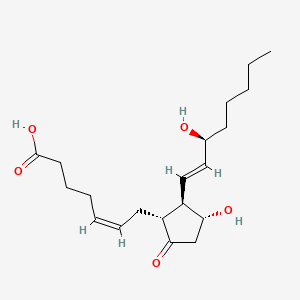
Prostaglandin E2 |
Prostaglandin E2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Prostaglandin e2 is associated with abnormalities such as Renal glomerular disease, Arthritis, Degenerative polyarthritis, Pancreatitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. The involved functions are known as enzyme pathway, Atherogenesis, Anabolism, inhibitors and Oxidants. Prostaglandin e2 often locates in Tissue membrane, Blood, Extracellular, Membrane and Protoplasm. The associated genes with Prostaglandin E2 are PTGS2 gene, TP53 gene, TNFRSF5 gene, FASTK Gene and TNF gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Steroids, monooxyethylene trimethylolpropane tristearate, Fatty Acids, Unsaturated and Promega. The related experimental models are Arthritis, Adjuvant-Induced, Xenograft Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis, Cancer Model and Knock-out. |
49278 |
|
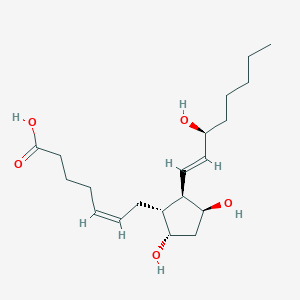
11beta-PGF2 |
11beta-pgf2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
15009 |
|
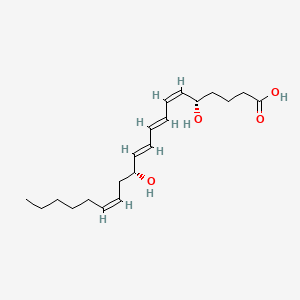
Leukotriene b4 |
Leukotriene b4 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Chemotaxis, release of sequestered calcium ion into cytoplasm and Polymerization. Leukotriene b4 often locates in Protoplasm. The associated genes with Leukotriene b4 are phallacidin. |
9311 |
|
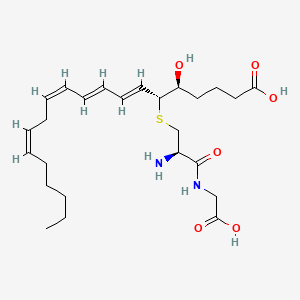
LTD4 |
Ltd4 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Ltd4 is associated with abnormalities such as Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Inflammatory disorder, Asthma, Pneumonia and Allergic asthma. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Signal Transduction, Cell Survival, antagonists and Phosphorylation. Ltd4 often locates in Membrane, Tissue membrane, Protoplasm, Cytoplasmic matrix and membrane fraction. The associated genes with LTD4 are ALOX5 gene, UMOD gene, P4HTM gene, RAF1 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides. |
1167 |
|
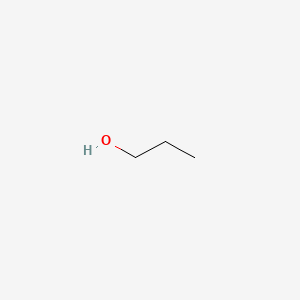
1-propanol |
1-propanol is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
6697 |
|
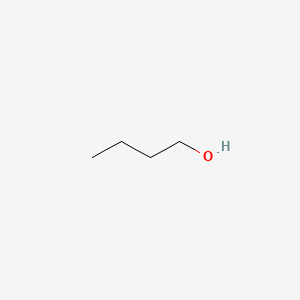
1-butanol |
1-butanol is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
5925 |
|
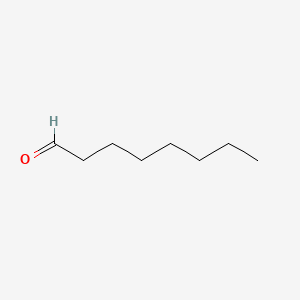
Caprylaldehyde |
Caprylaldehyde is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
677 |
|
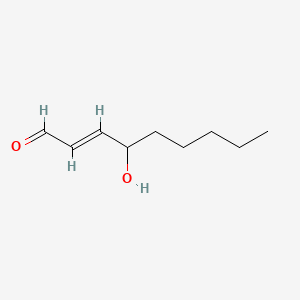
4-hydroxynonenal |
4-hydroxynonenal is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 4-hydroxynonenal is associated with abnormalities such as Chronic disease, Obesity, Diabetes, Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome and Lung diseases. The involved functions are known as protein expression, Glycolysis, mRNA Expression, Regulation and Mitochondrion in division. 4-hydroxynonenal often locates in Muscle, Mitochondria, Adipose tissue, Head and Mouse Muscle. The associated genes with 4-hydroxynonenal are STAT3 gene, SIRT1 gene, PGC gene, IL6 gene and cytochrome c''. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Lipid Peroxides, Promega, Membrane Lipids and oxidized lipid. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out, Transgenic Model, Disease model and Rodent Model. |
5685 |
|
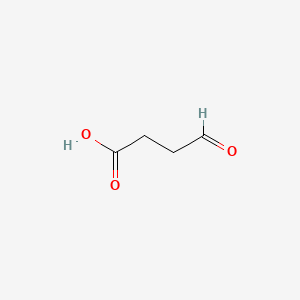
Succinic acid semialdehyde |
Succinic acid semialdehyde is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
546 |
|
Amyl acetate |
Amyl acetate is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
399 |
|
HMG-CoA |
Hmg-coa is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Hmg-coa is associated with abnormalities such as Cardiovascular Diseases, Hypercholesterolemia, Metabolic Diseases, Hyperhomocysteinemia and Morphologically altered structure. The involved functions are known as ketone body biosynthetic process, Regulation, Mutation, enzyme activity and HMG-CoA synthase activity. Hmg-coa often locates in Mitochondria, Cytoplasmic matrix, Hepatic, Membrane and Flank (surface region). The associated genes with HMG-CoA are Human gene, HMGCS2 gene, PPARA gene, ACSL1 Gene and Candidate Disease Gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Sterols, Dehydrocholesterols, Lipopolysaccharides and 7-dehydrocholesterol. |
355 |
|
Oleamide |
Oleamide is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Oleamide is associated with abnormalities such as Blepharoptosis, BOSLEY-SALIH-ALORAINY SYNDROME, abnormal fragmented structure, Syndrome and Hashimoto Disease. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Regulation, receptor ligand, Process and Binding (Molecular Function). Oleamide often locates in receptor complex, Tissue membrane, Membrane, annulus and Connexon. The associated genes with Oleamide are Homologous Gene, FAAH gene, FAAH2 gene, P4HTM gene and Integral Membrane Proteins. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Membrane Lipids, N-acylethanolamines, erucyl amide and linoleamide. |
349 |
|
Palmitamide |
Palmitamide is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Palmitamide often locates in Membrane. The related lipids are Sterols and Sphingolipids. |
34 |
|
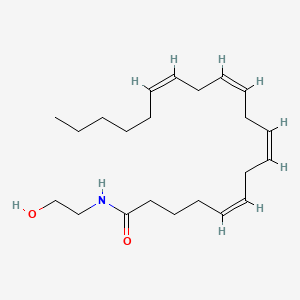
Anandamide |
Anandamide is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Anandamide is associated with abnormalities such as Dehydration. The involved functions are known as Process, Phenomenon, Phosphorylation, Catabolic Process and Gene Expression. Anandamide often locates in Nuchal region, Microglial and Hepatic. The associated genes with Anandamide are SGPL1 gene, SPTLC1 gene, RPSA gene, KDSR gene and SMPD1 gene. The related lipids are Sphingolipids, Lipopolysaccharides, Lysophospholipids, LYSO-PC and lysophosphatidylethanolamine. |
4747 |
|
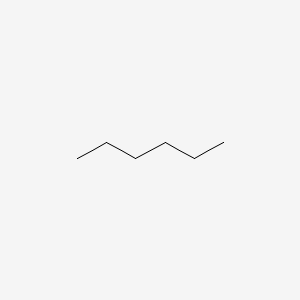
Hexane |
Hexane is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
9183 |
|
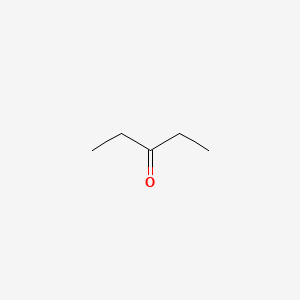
pentan-3-one |
Pentan-3-one is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
127 |
|
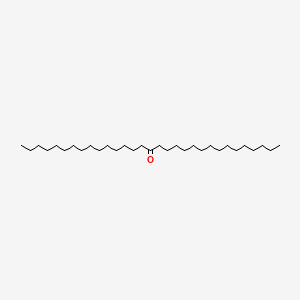
16-hentriacontanone |
16-hentriacontanone is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
17 |
|
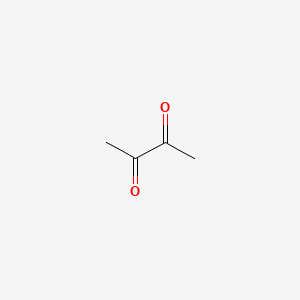
2,3-butanedione |
2,3-butanedione is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The involved functions are known as Physiologic Organization, Biochemical Pathway, physiological aspects, establishment and maintenance of localization and Phosphorylation. 2,3-butanedione often locates in Membrane, Microfilaments, Microtubules, Cell body of neuron and filamentous actin location. The associated genes with 2,3-butanedione are SLC33A1 gene and WASF1 gene. |
2715 |
|
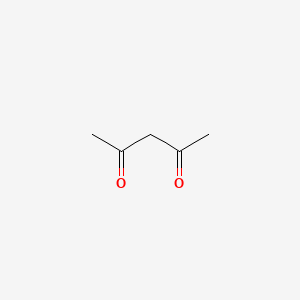
2,4-pentanedione |
2,4-pentanedione is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. The related lipids are Butyrates. |
1440 |
|
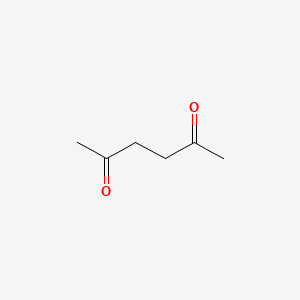
2,5-hexanedione |
2,5-hexanedione is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. |
646 |
|
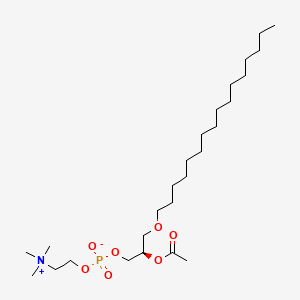
Platelet activating factor |
Platelet activating factor is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Platelet activating factor is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Acute cholecystitis without calculus, Cholecystitis, Colitis and Cholecystitis, Acute. The involved functions are known as Cell Survival, Metabolic Inhibition, lipid oxidation, Apoptosis and Oxidation. Platelet activating factor often locates in soluble, Cellular Membrane, Smooth muscle (tissue), Intima and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with Platelet activating factor are apolipoprotein A-I Milano, Homologous Gene, TSPO gene, HBEGF gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are Hydroxycholesterols, Liposomes, 25-hydroxycholesterol, Lysophosphatidylcholines and Lipopolysaccharides. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model and Transgenic Model. |
7383 |
|
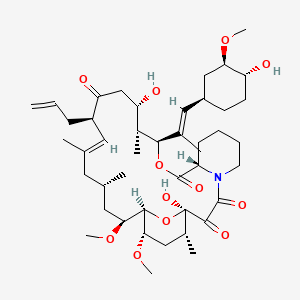
tacrolimus |
Tacrolimus is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Tacrolimus is associated with abnormalities such as Renal glomerular disease. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Fungicidal activity, Metabolic Inhibition, Excretory function and Dephosphorylation. Tacrolimus often locates in Hepatic, Mitochondrial matrix and Inner mitochondrial membrane. The associated genes with Tacrolimus are RHOA gene and BGN gene. |
12730 |
|
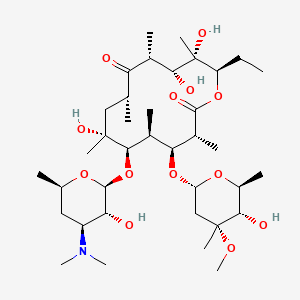
erythromycin |
erythromycin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Erythromycin is associated with abnormalities such as Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, Pneumonia, Infection, Pneumococcal Infections and Exanthema. The involved functions are known as Pharmacodynamics, Sterility, Agent, Drug Kinetics and Adjudication. Erythromycin often locates in Blood, peritoneal, Extracellular, Ribosomes and apicoplast. The associated genes with erythromycin are P4HTM gene, SLC33A1 gene, FAM3B gene, Operon and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Hydroxytestosterones, Steroids, Propionate, Mycolic Acids and campesterol. The related experimental models are Mouse Model and Knock-out. |
19871 |
|
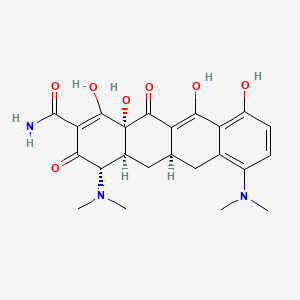
minocycline |
minocycline is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Minocycline is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Soft Tissue Infections, Septicemia, Chronic hyponatremia and Lesion of brain. The involved functions are known as Pharmacodynamics, Gene Expression, Transcriptional Activation, Regulation and Process. Minocycline often locates in Ribosomes, 50S ribosomal subunit, Blood, Skin and Immune system. The associated genes with minocycline are THEMIS gene, KCNK2 gene, RBFOX3 gene, PIWIL2 gene and P4HTM gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Promega, Steroids, Liposomes and Octanols. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis, Genetically Engineered Mouse, Disease model and spinal model. |
9780 |
|
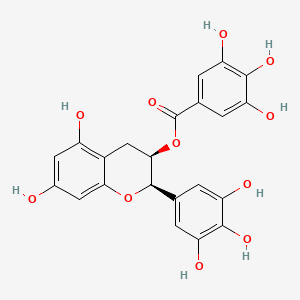
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate |
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. (-)-epigallocatechin gallate is associated with abnormalities such as IMMUNE SUPPRESSION, Infection, Nodule, Lymphopenia and Tumor Immunity. The involved functions are known as Apoptosis, Cellular Immune Response, Specific immune response, Signal and Infiltration. (-)-epigallocatechin gallate often locates in Immune system, Cytoplasmic Granules, Skin, Protoplasm and Body tissue. The associated genes with (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate are C8orf4 gene, Genes, vpr, MAPK8 gene, P4HTM gene and GAG Gene. The related lipids are Promega, Lipopolysaccharides, Palmitates, Fatty Acids and Sphingolipids. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Transgenic Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Arthritis, Collagen-Induced. |
6551 |
|
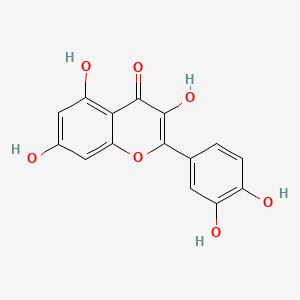
quercetin |
quercetin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Quercetin is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, Myocardial Infarction, Cirrhosis, Coronary Arteriosclerosis and Vascular ring. The involved functions are known as Vasodilation, physiological aspects, Fermentation, Process and Ingredient. Quercetin often locates in Arterial system, Endothelium, Skin, Endothelium, Vascular and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with quercetin are P4HTM gene, SULT gene, UGT1A1 gene, ARHGAP26 gene and PLXNB1 gene. The related lipids are blood lipid, Promega, Steroids, Phosphatidylserines and Fatty Acids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Tissue Model and Cancer Model. |
5377 |
|
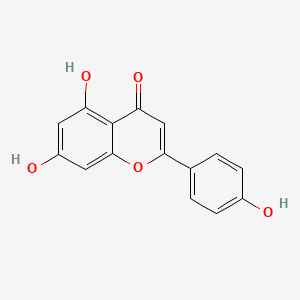
apigenin |
apigenin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Apigenin is associated with abnormalities such as Morphologically altered structure, Chimera disorder, Hypertensive disease, infection induced and Infection. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Gene Expression, Process, Metabolic Inhibition and Cell Death. Apigenin often locates in Vacuole, Cytoplasmic matrix, Cytoplasm, Tissue membrane and Membrane. The associated genes with apigenin are MSMP gene, BCL2 gene, PTGS2 gene, Chromatin and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Steroids, 1-Butanol, agosterol A and Butyrates. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Tissue Model, Knock-out, Xenograft Model and Disease model. |
4250 |
|
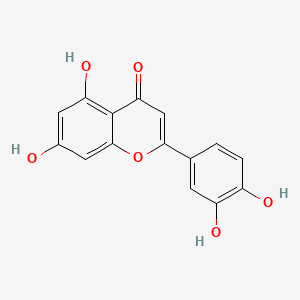
luteolin |
luteolin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Luteolin is associated with abnormalities such as Morphologically altered structure, Nodule, retinal toxicity, CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED and Ischemia. The involved functions are known as Metabolic Inhibition, Cell Death, Caspase Activation, activation of protein kinase C activity by G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway and protein kinase C activity. Luteolin often locates in Mitochondria, Cell-Free System, Protoplasm, Membrane and Body tissue. The associated genes with luteolin are BCL2 gene, TNFSF10 gene, BCL2L1 gene, XIAP gene and MCL1 gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Sterols, blood lipid, Fatty Acids and Steroids. The related experimental models are Xenograft Model, Mouse Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis, Knock-out and Cancer Model. |
3284 |
|
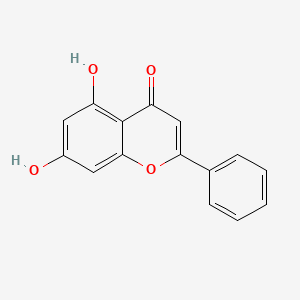
chrysin |
chrysin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Chrysin is associated with abnormalities such as Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, Metabolic Diseases, Hypogonadism, Renal tubular disorder and Colitis. The involved functions are known as Hypoxia, enzyme activity, Oxidation, inhibitors and Cell Survival. Chrysin often locates in Protoplasm, Plasma membrane, Back, Extracellular and Mitochondria. The associated genes with chrysin are CFB gene, P4HTM gene, UGT1A9 gene, CYP1A1 gene and UGT1A1 gene. The related lipids are Promega, estradiol-3-glucuronide, Steroids and Lipopolysaccharides. The related experimental models are Mouse Model. |
1085 |
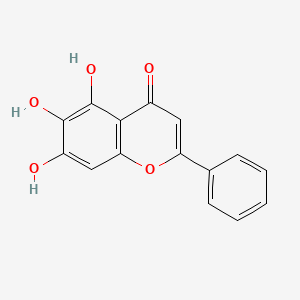
|
baicalein |
baicalein is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Baicalein is associated with abnormalities such as Neurodegenerative Disorders, Fibrillation, Hypertensive disease, Aortic coarctation and Coronary Occlusion. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Polymerization, Process, inhibitors and Pathogenesis. Baicalein often locates in Membrane, Lipid Bilayers, soluble, Cell-Free System and Protoplasm. The associated genes with baicalein are P4HTM gene, BIRC5 gene, TSPO gene, SHOC2 gene and XIAP gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Nonesterified Fatty Acids, iodoresiniferatoxin, Lipopolysaccharides and 17-octadecynoic acid. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model and Parkinsonism, Experimental. |
1997 |
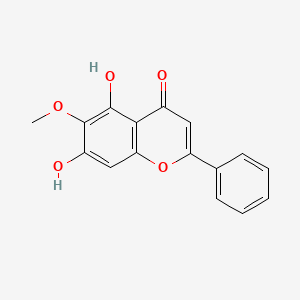
|
Oroxylin A |
Oroxylin A is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. |
180 |
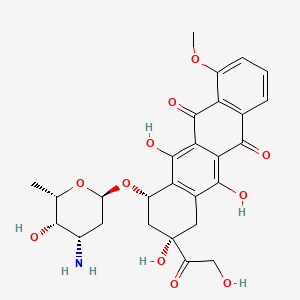
|
doxorubicin |
Adriamycin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Adriamycin is associated with abnormalities such as Cardiomyopathies. The involved functions are known as Transcription, Genetic, Process, Drug effect disorder, Diastasis and Oxidation-Reduction. Adriamycin often locates in Muscle, Myocardium and Entire gastrointestinal tract. |
54913 |
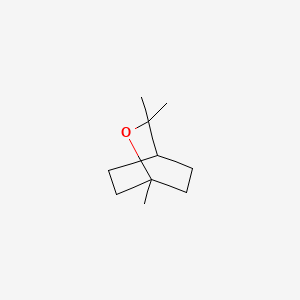
|
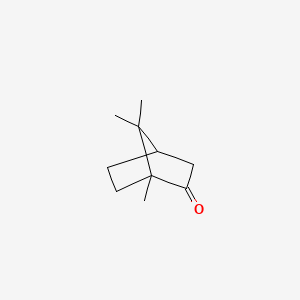
1,8-Cineol |
1,8-cineol is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The involved functions are known as Amplification, enzyme activity and inhibitors. 1,8-cineol often locates in subsynaptic reticulum. The related lipids are palmitoleic acid, pentadecanoic acid, stearic acid and erucic acid. |
1326 |
|
(+)-Camphor |
(+)-camphor is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. (+)-camphor is associated with abnormalities such as Athetoid cerebral palsy. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Synthesis, Feedback and Competitive inhibition. The associated genes with (+)-Camphor are 4S-limonene synthase. The related lipids are palmitoleic acid, pentadecanoic acid, stearic acid and erucic acid. |
3660 |
|
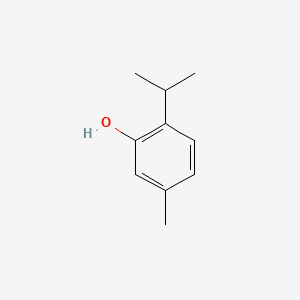
Thymol |
Thymol is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Thymol is associated with abnormalities such as Anemia, end organ damage, Dental caries, CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED and Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. The involved functions are known as synergism, antagonists, Metabolic Inhibition, Pressure- physical agent and Drug Interactions. Thymol often locates in Mucous Membrane, apical membrane, Protoplasm, Extracellular and Serosal. The associated genes with Thymol are HIST1H1C gene, TRPA1 gene, MERTK wt Allele, SLC12A2 gene and TRPV3 gene. The related lipids are Propionate, Pinene, palmitoleic acid, pentadecanoic acid and stearic acid. |
3008 |
|
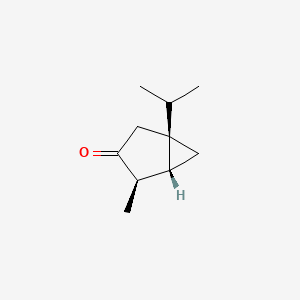
Thujone |
Thujone is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Thujone is associated with abnormalities such as Consumption-archaic term for TB, Malnutrition, Diabetes, abnormal fragmented structure and Dehydration. The involved functions are known as sabinene synthase activity, Anabolism, diterpene biosynthesis, Selection, Genetic and Biochemical Pathway. Thujone often locates in Tissue membrane, Clone, Epithelium, Back and Cell surface. The associated genes with Thujone are monoterpene synthase, Candidate Disease Gene, Recombinant Proteins, HM13 gene and DAND5 gene. The related lipids are Pinene, Palmitates and absinthium. |
241 |

|
D-isothujone |
D-isothujone is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Oxidation, enzyme activity, Adjudication and Stereochemistry. D-isothujone often locates in Clone. The associated genes with D-isothujone are ADRBK1 gene and monoterpene synthase. |
123 |
|
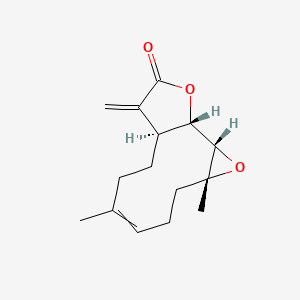
Parthenolide |
Parthenolide is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Parthenolide is associated with abnormalities such as Migraine Disorders, abnormal fragmented structure, Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal, Consumption-archaic term for TB and Infection. The involved functions are known as Apoptosis, Cell Proliferation, Inflammation, pathologic cytolysis and Membrane Potentials. Parthenolide often locates in Mitochondria, Tissue membrane, Cytoplasmic matrix, Cytoplasm and Body tissue. The associated genes with Parthenolide are IGKJ1 gene, BCL2 gene, DDIT3 gene, Procaspase 7 and GAPDH gene. The related lipids are A(2)C. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Xenograft Model, Breast Cancer Model and Cancer Model. |
925 |
|
(-)-Picrotoxinin |
(-)-picrotoxinin is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. |
246 |
|
Phytol |
Phytol is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Phytol is associated with abnormalities such as Simian Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, Hypoglycemia, Refsum Disease, Peripheral Neuropathy and Metabolic Diseases. The involved functions are known as Oxidation, transmethylation, fatty acid oxidation, Lipid Metabolism and chlorophyll catabolic process. Phytol often locates in Mitochondria, Membrane, peroxisome, Cytoplasm and Body tissue. The associated genes with Phytol are ETFDH gene, Homologous Gene, Genome, IMPACT gene and Arabidopsis Proteins. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Nonesterified Fatty Acids, nonadecanoic acid, branched chain fatty acid and pristanic acid. The related experimental models are Mouse Model. |
411 |
|
forskolin |
Forskolin is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. Forskolin is associated with abnormalities such as Cholestasis, Vocal cord dysfunction familial, Hypothyroidism, Renal tubular disorder and Disintegration (morphologic abnormality). The involved functions are known as Cell Proliferation, Anabolism, mRNA Expression, Agent and Signal. Forskolin often locates in Extracellular, Body tissue, Skin, Tissue membrane and Membrane. The associated genes with forskolin are P4HTM gene, SLC33A1 gene, NR1I2 gene, Genes, Reporter and CYP3A gene. The related lipids are Steroids, steroid sulfate, Fatty Acids, LYSO-PC and Lipopolysaccharides. |
24755 |
|
phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate |
Phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate is a lipid of Prenol Lipids (PR) class. The involved functions are known as DNA Fragmentation, Phosphorylation and Irritation. Phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate often locates in low-density lipoprotein particle. The associated genes with phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate are FPR1 gene and ABCB1 gene. |
40921 |
|
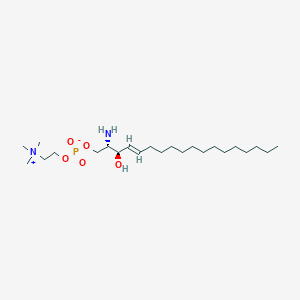
sphingosylphosphorylcholine |
sphingosylphosphorylcholine is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine is associated with abnormalities such as Cerebral Vasospasm, Subarachnoid Hemorrhage, Atherosclerosis, Hypertensive disease and Niemann-Pick Diseases. The involved functions are known as MAP kinase kinase activity, JUN kinase activity, Phosphorylation, biphenyl synthase activity and Cell Death. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine often locates in Adipose tissue, Protoplasm, Body tissue, Membrane and Extracellular. The associated genes with sphingosylphosphorylcholine are UCN3 gene, MAPK9 gene, JUN gene, NAA50 gene and P4HTM gene. The related lipids are Lysophospholipids, lysophosphatidic acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines, Sphingolipids and Saponin. The related experimental models are Mouse Model. |
265 |
|
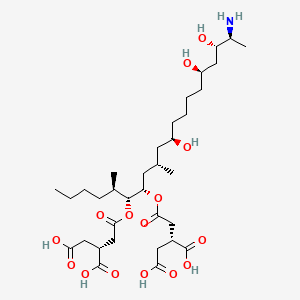
fumonisin b1 |
fumonisin b1 is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. Fumonisin b1 is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Kidney Diseases, Liver diseases, DERMATITIS HERPETIFORMIS, FAMILIAL and Malnutrition. The involved functions are known as Gene Expression, Anabolism, Signal, Biosynthetic Pathways and Regulation. Fumonisin b1 often locates in Body tissue, Microsomes, microsomal membrane, Protoplasm and Mitochondria. The associated genes with fumonisin b1 are Genome, P4HTM gene, FATE1 gene, BCL2 gene and TMEM132D gene. The related lipids are dihydroceramide, ceramide 1-phosphate, Sphingolipids, Fatty Acids and Palmitates. |
902 |
|
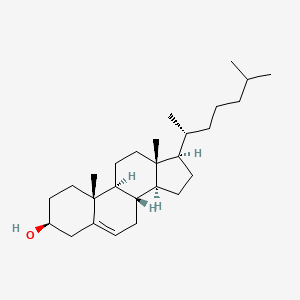
cholesterol |
cholesterol is a lipid of Sterol Lipids (ST) class. Cholesterol is associated with abnormalities such as Trypanosomiasis, Chagas Disease, Cleft Palate, Chondrodysplasia punctata 2, X-linked dominant and Child syndrome. The involved functions are known as Blood Circulation, Sterol Biosynthesis Pathway, Receptor Mediated Endocytosis, Methylation and Signal. Cholesterol often locates in Animal tissue, Blood, Membrane, Plasma membrane and peroxisome. The associated genes with cholesterol are MBD2 gene, SIM, SLC33A1 gene, Genome and NSDHL gene. The related lipids are Sterols, zymosterol, fecosterol, Total cholesterol and 7-dehydrocholesterol. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out, Genetically Engineered Mouse and Disease model. |
98461 |






















































































